标签:
ClassLoader类加载器是负责加载类的对象。ClassLoader 类是一个抽象类。如果给定类的二进制名称(即为包名加类名的全称),那么类加载器会试图查找或生成构成类定义的数据。一般策略是将名称转换为某个文件名,然后从文件系统读取该名称的“类文件”。java.lang.ClassLoader类的基本职责就是根据一个指定的类的名称,找到或者生成其对应的字节代码,然后从这些字节代码中定义出一个 Java 类,即 java.lang.Class类的一个实例。除此之外,ClassLoader还负责加载 Java 应用所需的资源,如图像文件和配置文件等。 作为所有类加载器的基类,ClassLoader的内部实现机制还是值得我们细细研究一下的。所以今天我就带领大家一起来看一下Classloader的内部实现源码。
首先我们来看一下Classloader类的两个构造方法。

从上边的帮助文档中我们可以发现,在创建一个classloader的实例时我们可以显示的指出他的父加载器,也可以不指定,不指定的时候他的默认的父加载器是系统加载器。我们来看一下源码的实现:
/**
* Creates a new class loader using the <tt>ClassLoader</tt> returned by
* the method {@link #getSystemClassLoader()
* <tt>getSystemClassLoader()</tt>} as the parent class loader.
*/
protected ClassLoader() {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkCreateClassLoader();
}
this.parent = getSystemClassLoader();
initialized = true;
}
/**
* Creates a new class loader using the specified parent class loader for
*/
protected ClassLoader(ClassLoader parent) {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkCreateClassLoader();
}
this.parent = parent;
initialized = true;
}
从上面源码我们可以发现,classloader中一定有一个parent的属性来指定当前loader的附加器。其源码也证明了我们刚才上面的说法。
看完构造方法的实现,下一步我们来看一下ClassLoader中一个特别重要的方法loadclass方法,这个方法就是用来加载类的。这个方法在jdk中有个重载的方法,但是其实是一个样的。一个带有是否链接类的方法,一个不带。下面我们就看一下这个方法的源码:
public Class<?> loadClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(name, false);
}
/**
* Loads the class with the specified <a href="#name">binary name</a>. The
* default implementation of this method searches for classes in the
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* If the class could not be found
*/
protected synchronized Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
// First, check if the class has already been loaded
Class c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClass0(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// If still not found, then invoke findClass in order
// to find the class.
c = findClass(name);
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
关于这个方法的源码解释,我感觉我没必要解释什么,因为在API中已经有详细的解释了。我在解释肯定也不如他解释的好,所以我们来看一下API是怎么解释的吧:
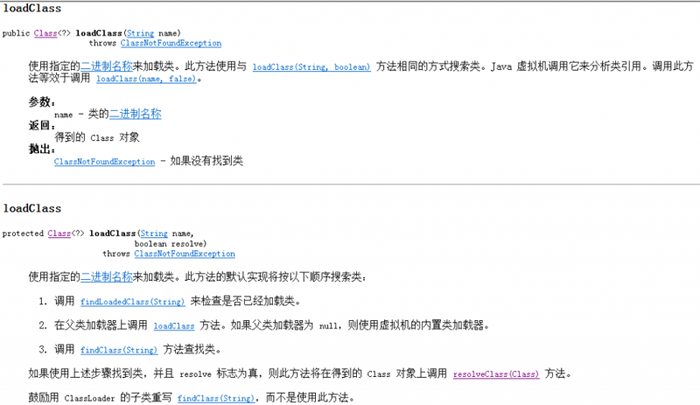
虽然jdk已经解释的很清楚了,但是有一点我还是要在补充一下。从上面的源码我们可以看出loadClass方法是一个递归的方法,一直往上找,一直找到根类加载器为止,然后让类加载器去加载这个类。至于跟加载器是怎么实现的我们就不得而知了。因为跟类加载加载类时一个本地方法,他是用c++写的。我们无法看到他的源码。这样验证了在前面我们所说的类加载器的父类委托机制。
下面我们来看一下findClass方法,我们在上面的代码中发现。在loadClass方法中有调用这个findclass方法,下面我们首先来看一下API对这个方法的介绍:

从上面介绍我们可以看出,这个方法主要是来查找我们的类文件的。我们在自定义我们自己的类加载器的时候应该重写这个方法,因为jdk中对这个方法基本没有实现什么,这就需要我们自己来重写这个方法,用我们自己的所定义的方法去查找类文件。不信。你可以看一下他的源码实现:
protected Class<?> findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(name);
}
暂时先介绍这些吧。其他的方法基本都差不多,最近感觉博客越来越难写,越来越吃力。越来越发现底层理论的缺乏。希望通过自己的努力,可以慢慢改变这个现状。
标签:
原文地址:http://my.oschina.net/u/1175007/blog/492961