TSP问题最简单的求解方法是枚举法。它的解是多维的、多局部极值的、趋于无穷大的复杂解的空间,搜索空间是n个点的所有排列的集合,大小为(n-1)!。可以形象地把解空间看成是一个无穷大的丘陵地带,各山峰或山谷的高度即是问题的极值。求解TSP,则是在此不能穷尽的丘陵地带中攀登以达到山顶或谷底的过程。
这一篇将用遗传算法解决TSP问题。
1)评价。这个评价算法应该比较简单了,就是找计算总距离,小的为优。目标函数转化为适应度函数可以取倒数。
2)突变。为了防止重复访问,不能随机的进行突变。因为每个城市只能访问一次,我们只需要任意的交换两个城市即可。
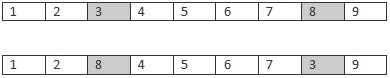
上一行是突变之前,下面一行是突变之后的。
3)交叉。这个操作是个比较关键的步骤,怎样交叉才能才能父母的优秀基因呢?对于TSP问题,我们要找的是一个最优的排列,其中排列的顺序应该是最重要的。
因此在交叉的时候,分别随机的取 父母的部分序列,要保持原有的顺序。
Parents
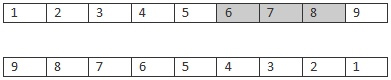
先随机的选取 Parent1 的 一部分,例如 678 部分,。然后把剩下的城市 安装 Parent2 中的顺序,遗传下去。
Chlid
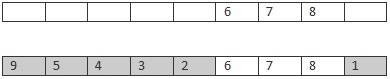
其它基本按照遗传算法的框架来就行了
// TSP.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。
//
#include "stdafx.h"
#include<iostream>
//#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
//#include <stdlib.h>
using namespace std;
#define POPSIZE 200 //种群总数
#define rdint(i)(rand()%(int)(i))
#define rdft()((float)rdint(16384)/(16383.0))
typedef unsigned char BYTE;
//31个城市的坐标
int city[31][2] = { { 1304, 2312 }, 3639, 1315, 4177, 2244, 3712, 1399, 3488, 1535, 3326, 1556, 3238, 1229,
4196, 1004, 4312, 790, 4386, 570, 3007, 1970, 2562, 1756, 2788, 1491, 2381, 1676, 1332, 695, 3715, 1678,
3918, 2179, 4061, 2370, 3780, 2212, 3676, 2578, 4029, 2838, 4263, 2931, 3429, 1908, 3507, 2367, 3394, 2643,
3439, 3201, 2935, 3240, 3140, 3550, 2545, 2357, 2778, 2826, 2370, 2975 };
int* my_unrepeat_rand(int L, int H)
{
const int LEN = H - L + 1;
//int n[LEN];
int *n = new int[LEN];
for (int i = 0; i < LEN; ++i)
{
n[i] = L + i;
}
for (int j = LEN; j > 0; --j)
{
int m = j*rand() /(RAND_MAX + 1.0);
int temp = n[m];
n[m] = n[j - 1];
n[j - 1] = temp;
}
return n;
}
class Chromosome
{
friend class Population;
public:
static const int length = 31;
private:
BYTE gene[length];
double fitness;
double distance;
public:
void initial_chromosome()//初始化染色体
{
distance = 0;
fitness = 0;
int*b = my_unrepeat_rand(0, length - 1);
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
gene[i] = b[i];
delete[]b;
}
BYTE*get_gene()
{
return this->gene;
}
double get_distance()
{
return distance;
}
void calculate_distance()//计算适应度,这里直接取总距离,越小越好
{
distance = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length - 1; i++)
{
distance += sqrt(pow(double(city[gene[i]][0] - city[gene[i + 1]][0]), double(2)) +
pow(double(city[gene[i]][1] - city[gene[i + 1]][1]), double(2)));
}
distance += sqrt(pow(double(city[gene[0]][0] - city[gene[length - 1]][0]), double(2)) + pow(double(city[gene[0]][1] - city[gene[length - 1]][1]), double(2)));
}
pair<Chromosome, Chromosome> cross(Chromosome p1)//交叉操作,选中区间的基因不改变,孩子基因的其他位置的基因从配偶处获得,要保持顺序
{
pair<Chromosome, Chromosome>child;
//srand(time(0));
int m = rand() % length ;
int n = rand() % length;
if (m > n)
{
int temp = m;
m = n;
n = temp;
}
int j = 0,p=0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
if (i >= m&&n >= i)
{
child.first.gene[i] = gene[i];
child.second.gene[i] = p1.gene[i];
continue;
}
bool flag = true;
while (flag)
{
flag = false;
for (int k = m; k <= n; k++)
if (p1.gene[j] == gene[k])
{
flag = true;
break;
}
if (flag)
j++;
}
child.first.gene[i] = p1.gene[j];
j++;
flag = true;
while (flag)
{
flag = false;
for (int k = m; k <= n; k++)
if (gene[p] == p1.gene[k])
{
flag = true;
break;
}
if (flag)
p++;
}
child.second.gene[i] = gene[p];
p++;
}
return child;
}
Chromosome mutation()//变异,选择两个位置交换基因
{
int m = rand() % (length - 1);
int n = rand() % (length - 1);
while (n == m)
{
n = rand() % (length - 1);
}
int temp = gene[m];
gene[m] = gene[n];
gene[n] = temp;
return *this;
}
};
class Population
{
private:
Chromosome pop[POPSIZE];
Chromosome best;
Chromosome worst;
unsigned int Generation;
unsigned int maxgeneration;
double m_dCrossoverRate;//交叉率0.6
double m_dMutationRate;//变异率0.01
bool elitism;//是否在新一代中保存前一代的最优个体
double m_dTotalFitnessScore;
void initial_pop()
{
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
pop[i].initial_chromosome();
};
public:
Population(double pc, double pM, bool ISelitism, unsigned int maxgen) :m_dCrossoverRate(pc), m_dMutationRate(pM), elitism(ISelitism), maxgeneration(maxgen)//构造函数
{
Generation = 1;
initial_pop();
}
void Calcu_fit()//计算适应值
{
m_dTotalFitnessScore = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
{
pop[i].calculate_distance();
}
find_best_worst();
//sort_by_distance(POPSIZE);
double mindis = best.distance;
double maxdis = worst.distance;
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
{
pop[i].fitness = 1 - (pop[i].distance - mindis) / (maxdis - mindis + 0.0001);//double(1000) / pop[i].distance;//
m_dTotalFitnessScore += pop[i].fitness;
}
}
//fitness(i,1)=(1-((len(i,1)-minlen)/(maxlen-minlen+0.0001)))
void sort_by_distance(int k)
{
if (k == 1)
return;
for (int i = 0; i < k-1; i++)
{
if (pop[i].distance < pop[i + 1].distance)
{
double temp = pop[i].distance;
pop[i].distance = pop[i + 1].distance;
pop[i + 1].distance = temp;
}
}
sort_by_distance(k - 1);
}
void find_best_worst()
{
double mindis = 100000000;
double maxdis = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
{
if (pop[i].distance > maxdis)
{
maxdis = pop[i].distance;
worst = pop[i];
}
if (pop[i].distance < mindis)
{
mindis = pop[i].distance;
best = pop[i];
}
}
}
int RouletteWheelSelection()
{
double fSlice = rdft() * m_dTotalFitnessScore;
double cfTotal = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i<POPSIZE; ++i)
{
cfTotal += pop[i].fitness;
if (cfTotal > fSlice)
{
return i;
}
}
}
void Epoch()
{
Calcu_fit();
Chromosome new_pop[POPSIZE+1];
int NewBabies = 0;
if (elitism)
{
NewBabies = 1;
new_pop[0] = best;
}
while (NewBabies < POPSIZE)
{
//select 2 parents
int mum = RouletteWheelSelection();
int dad = RouletteWheelSelection();
while (dad == mum)
{
dad = RouletteWheelSelection();
}pair<Chromosome, Chromosome>child;
if (rdft() < m_dCrossoverRate)
{
child = pop[mum].cross(pop[dad]);
}
else
{
child.first = pop[mum];
child.second = pop[dad];
}
if (rdft() < m_dMutationRate)
{
child.first.mutation();
}
if (rdft() < m_dMutationRate)
{
child.second.mutation();
}
new_pop[NewBabies]=child.first;
new_pop[NewBabies+1] = child.second;
NewBabies += 2;
}
for (int i = 0; i < POPSIZE; i++)
pop[i] = new_pop[i];
++Generation;
}
Chromosome get_best()
{
return best;
}
void run()
{
while (Generation < maxgeneration)
{
Epoch();
}
}
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
time_t t;
srand((unsigned)time(&t));
Population tsp(0.6,0.1,true,1000);
tsp.run();
cout << tsp.get_best().get_distance()<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,未经博主允许不得转载。
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u014568921/article/details/47786275