标签:
基本概念:
根节点:没有入边,但有0条或多条出边
内部节点:恰有一条入边和两条或多条出边
页节点:恰有一条入边,没有出边,每一个叶节点都赋予一个类标号(class label)
如何建立决策树
Hunt算法 :通过将训练记录相继划分成较纯的子集,以递归的方式建立决策树。
设Dt是与节点t相关联的训练记录集,而y={y1,y2,---,yc}是类标号,Hunt的递归定义:
决策树归纳设计问题
如何分裂训练记录?
每个递归步都必须选择一个属性测试条件,将记录划分成较小的子集。算法必须提供为不同类型的属性指定测试条件的方法,并提供评估每种测试条件的客观度量
如何停止分裂过程?
分裂节点,直到所用的记录都属于同一类,或所有的记录都具有相同的属性。更多情况下使用其他标准提前终止树的生长过程
选择最佳划分的度量
最佳划分的度量通常是根据划分后子女节点不纯性的程度。不纯的程度越低,类分布就越倾斜。e.g 分布为(0,1)的节点具有零不纯性,而(0.5,0.5)的节点具有最高的不纯性。
不纯性度量公式:Entropy, Gini。
P(i)=第i类的数目/总数目
熵(Entropy)

Gini不纯度公式:
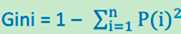
比较父节点(划分前)和子女节点(划分后)的不纯程度,可验证划分的效果,差越大,效果越好。父节点不纯度与子女节点不纯度支之差,叫做增益。
决策树归纳算法
1.计算给定数据集的熵:
def calcShannonEnt(dataSet): numEntries=len(dataSet) labelCounts={} for featVec in dataSet: currentLabel=featVec[-1] if currentLabel not in labelCounts.keys(): labelCounts[currentLabel]=0 labelCounts[currentLabel]+=1 shannonEnt=0.0 for key in labelCounts: prob =float(labelCounts[key])/numEntries shannonEnt-=prob*math.log(prob,2) return shannonEnt
2.选择最好的数据集划分:
def splitDataSet(dataSet, axis, value): retDataSet = [] for featVec in dataSet: if featVec[axis] == value: reducedFeatVec = featVec[:axis] #chop out axis used for splitting reducedFeatVec.extend(featVec[axis+1:]) retDataSet.append(reducedFeatVec) return retDataSet def chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet): numFeatures = len(dataSet[0]) - 1 #the last column is used for the labels baseEntropy = calcShannonEnt(dataSet) bestInfoGain = 0.0; bestFeature = -1 for i in range(numFeatures): #iterate over all the features featList = [example[i] for example in dataSet]#create a list of all the examples of this feature uniqueVals = set(featList) #get a set of unique values newEntropy = 0.0 for value in uniqueVals: subDataSet = splitDataSet(dataSet, i, value) prob = len(subDataSet)/float(len(dataSet)) newEntropy += prob * calcShannonEnt(subDataSet) infoGain = baseEntropy - newEntropy #calculate the info gain; ie reduction in entropy if (infoGain > bestInfoGain): #compare this to the best gain so far bestInfoGain = infoGain #if better than current best, set to best bestFeature = i return bestFeature #returns an integer
3.构建决策树
def createTree(dataSet,labels): classList = [example[-1] for example in dataSet] if classList.count(classList[0]) == len(classList): return classList[0]#stop splitting when all of the classes are equal if len(dataSet[0]) == 1: #stop splitting when there are no more features in dataSet return majorityCnt(classList) bestFeat = chooseBestFeatureToSplit(dataSet) bestFeatLabel = labels[bestFeat] myTree = {bestFeatLabel:{}} del(labels[bestFeat]) featValues = [example[bestFeat] for example in dataSet] uniqueVals = set(featValues) for value in uniqueVals: subLabels = labels[:] #copy all of labels, so trees don‘t mess up existing labels myTree[bestFeatLabel][value] = createTree(splitDataSet(dataSet, bestFeat, value),subLabels) return myTree
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zhq1007/p/4385720.html