标签:
题意,有n个匀速动点,求最小生成树的改变次数。
先求出最开始的最小生成树,当MST中的某条线段v长度被不在MST的线段u取代的时候,最小生成树才会发生变化,
具体来说,已经知道之前的MST,边按照长度排序,在这个时间点之前的瞬间,v一定是MST最长的边,u紧跟在v之后,在这个时间点之后u和v的位置交换了一下,
根据Kruskal算法,对于u和v之前的边没有影响,前面的边连完以后如果u的两个端点不在同一个连通分量里,那么u会被加入形成新的MST,否则MST不变。
根据边长的平方对时间的函数求出所有线段u和v长度相等且之后u更短的时间点,按照时间顺序排序,一旦满足上述条件,就修改MST。
为了维护MST需要维护一个MST到边的映射,为了判断新线段在不在MST中以及忽略旧边需要维护一个边到MST编号的映射。
求时间点时有解的三种情况:
一开始先对线段长度排过序,所以保证Lj>Li,
第一种情况是a=0,一个解,之后j更短。
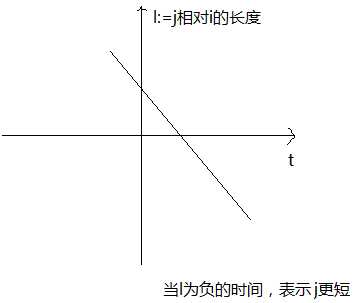
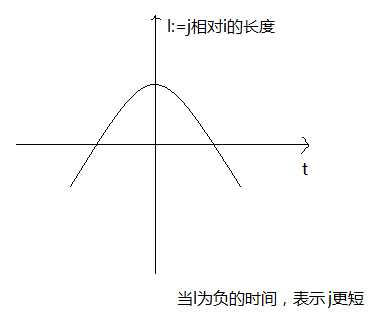
第二种情况是a<0,因为Lj>Li,所以只有大的那个是合法的,之后j更短。
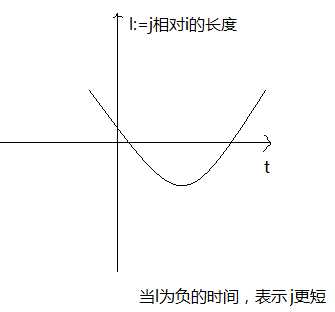
第三种情况,a>0,第一个解是j更短,第二个解是i更短。
7发才过,太难了
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const double eps = 1e-8; struct Event { double t; int u,v; //这个时间点以后u更短 bool operator < (const Event& r) const { return t < r.t; } }; vector<Event> events; #define PB push_back const int maxn = 51; const int maxl = maxn*(maxn-1)>>1; struct Point { double x,y,z,dx,dy,dz; void read(){ scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf",&x,&y,&z,&dx,&dy,&dz); } Point operator - (const Point&r) { return {x-r.x, y-r.y, z-r.z, dx-r.dx, dy-r.dy, dz-r.dz}; } }P[maxn]; #define squ(x) ((x)*(x)) struct Seg { double a,b,c; int u,v; void cal(int i,int j){ u = i; v = j; Point t = P[i]-P[j]; a = squ(t.dx) + squ(t.dy) + squ(t.dz); b = 2*(t.dx*t.x + t.dy*t.y + t.dz*t.z); c = squ(t.x) + squ(t.y) + squ(t.z); } }L[maxl]; bool operator < (const Seg&x, const Seg&y) { return x.c < y.c; } int lcnt; int n; //if equation has two roots, r1 < r2 int solveEqu(double a,double b,double c,double &r1,double &r2) { if(fabs(a)<eps){ if(fabs(b)<eps) return 0; r1 = -c/b; return 1; } double delta = b*b-4.*a*c; if(delta<eps) return 0; delta = sqrt(delta); if(a>0){ r1 = (-b-delta)/(2.*a); r2 = (-b+delta)/(2.*a); }else { r1 = (-b+delta)/(2.*a); r2 = (-b-delta)/(2.*a); } return 2; } int pa[maxl]; int pos[maxl]; //map: Edge to MST int e[maxn]; //map: MST to Edge void initUFS() { for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) pa[i] = i; } int Find(int x) { return x == pa[x]?x:pa[x]=Find(pa[x]); } int main() { //freopen("in.txt","r",stdin); int kas = 0; while(~scanf("%d",&n)){ for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) P[i].read(); events.clear(); lcnt = 0; for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){ for(int j = i+1; j < n; j++){ L[lcnt++].cal(i,j); } } sort(L,L+lcnt);//ascending order for(int i = 0; i < lcnt; i++){ for(int j = i+1; j < lcnt; j++){ double r[2]; double a = L[j].a - L[i].a//j相对i的长度 , b = L[j].b - L[i].b , c = L[j].c - L[i].c; int rcnt = solveEqu(a,b,c,r[0],r[1]); if(rcnt == 1){ if(r[0]>0) events.PB({r[0],j,i}); }else if(rcnt == 2){ if(a<0){ if(r[1]>0) events.PB({r[1],j,i}); }else { if(r[0]>0) events.PB({r[0],j,i}); if(r[1]>0) events.PB({r[1],i,j}); } } } } sort(events.begin(),events.end()); //DeBugEv initUFS(); memset(pos,0,sizeof(int)*lcnt); int idx = 0; for(int i = 0; i < lcnt; i++){ int s1 = Find(L[i].u), s2 = Find(L[i].v); if(s1 != s2){ pa[s1] = s2; e[pos[i] = ++idx] = i; //e[] 下标从1开始。0表不在MST中 if(idx == n-1) break; } } int ans = 1; for(int i = 0; i < events.size(); i++){ Event &ev = events[i]; if(pos[ev.v]&&!pos[ev.u]){ initUFS(); int old = pos[ev.v]; for(int j = 1; j <= idx; j++){ if(j == old) continue; int s1 = Find(L[e[j]].u), s2 = Find(L[e[j]].v); if(s1 != s2){ pa[s1] = s2; } } int s1 = Find(L[ev.u].u), s2 = Find(L[ev.u].v); if(s1 != s2){ ans++; pos[ev.u] = old; pos[ev.v] = 0; e[old] = ev.u; } } } printf("Case %d: %d\n",++kas,ans); } return 0; }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jerryRey/p/4765722.html