标签:
Interpreter 解释器模式(行为型模式)
动机(Motivation)
在软件构建过程中,如果某一特定领域的问题比较复杂,类似的模式不断重复出现,如果使用普通的编程方式来实现将面临非常频繁的变化。
在这种情况下,将特定领域的问题表达为某种语法规则下的句子,然后构建一个解释器来解释这样的句子,从而达到解决问题的目的。
意图(Intent)
给定一个语言,定义它的文法的一种表示,并定义一种解释器,这个解释器用来解释语言中的句子。——《设计模式》GoF
中文数字转换为阿拉伯数字
public class Context { private string statement; private int data; public Context(string statement) { this.statement = statement; } public string Statement { get { return statement; } set { statement = value; } } public int Data { get { return data; } set { data = value; } } } public abstract class Expression { protected Dictionary<string, int> table = new Dictionary<string, int>(); public Expression() { table.Add("一", 1); table.Add("二", 2); table.Add("三", 3); table.Add("四", 4); table.Add("五", 5); table.Add("六", 6); table.Add("七", 7); table.Add("八", 8); table.Add("九", 9); } public virtual void Interpret(Context context) { if (context.Statement.Length == 0) { return; } foreach (string key in table.Keys) { int value = table[key]; if (context.Statement.EndsWith(key + GetPostfix())) { context.Data += value * Multiplier(); context.Statement = context.Statement.Substring(0, context.Statement.Length - GetLength() - 1); } if (context.Statement.EndsWith("零")) { context.Statement = context.Statement.Substring(0, context.Statement.Length - 1); } } } public abstract string GetPostfix(); public abstract int Multiplier(); public virtual int GetLength() { return this.GetPostfix().Length; } } public class GeExpression : Expression { public override string GetPostfix() { return string.Empty; } public override int Multiplier() { return 1; } public override int GetLength() { return 0; } } public class ShiExpression : Expression { public override string GetPostfix() { return "十"; } public override int Multiplier() { return 10; } } public class BaiExpression : Expression { public override string GetPostfix() { return "百"; } public override int Multiplier() { return 100; } } public class QianExpression : Expression { public override string GetPostfix() { return "千"; } public override int Multiplier() { return 1000; } } public class WanExpression : Expression { public override string GetPostfix() { return "万"; } public override int Multiplier() { return 10000; } public override void Interpret(Context context) { if (context.Statement.Length == 0) { return; } List<Expression> tree = new List<Expression>(); tree.Add(new GeExpression()); tree.Add(new ShiExpression()); tree.Add(new BaiExpression()); tree.Add(new QianExpression()); foreach (string key in table.Keys) { if (context.Statement.EndsWith(this.GetPostfix())) { int temp = context.Data; context.Data = 0; context.Statement = context.Statement.Substring(0, context.Statement.Length - 1); foreach (Expression exp in tree) { exp.Interpret(context); } context.Data = temp + this.Multiplier() * context.Data; } } } }
客户端调用代码:
static void Main(string[] args) { string roman = "一千零五十万三千六百零二"; Context context = new Context(roman); List<Expression> tree = new List<Expression>(); tree.Add(new GeExpression()); tree.Add(new ShiExpression()); tree.Add(new BaiExpression()); tree.Add(new QianExpression()); tree.Add(new WanExpression()); foreach (Expression exp in tree) { exp.Interpret(context); } Console.WriteLine("{0} = {1}", roman, context.Data); Console.ReadKey(); }
输出:
一千零五十万三千六百零二 = 10503602
这段代码是将中文的数字转换为阿拉伯数字,如果按照面向过程的算法肯定是来截取字符串进行判断然后组合成正确的数字。在这段代码中则利用了Interpreter模式将位数进行表达式的封装。
首先看抽象Expression类,首先它封装了一个字典类,这个字典保存了中文的1-9的字符及其对应的阿拉伯数字。Interpret方法,遍历字典中的每个中文数字,并且判断截取中文数字加其后缀是否是结尾,如果是,则将对应的值乘以对应的位数,对应的位数是一个纯虚函数Multiplier,由派生类自己实现。在取得了对应的Expression的值后需要将中文数字语句中对应的字符串去掉。
在WanExpression中,我们重写了Interpret函数,这是由于万位数可以由千位以下的数字来描述,如三千二百万。重写Interpret函数的算法如下,先将千以下的表达式(包括千)加入一个List保存起来,然后遍历数字表,如果当前的表达式已经截取到万,那么先将已取得的数值用中间临时变量保存起来,将当前表达式的数字值置为0。然后将万以后的文字截取。再依次用List里面的千、百、十、个的Expression进行解释,最后取得的数值乘以万对应的位数加上临时变量。
在Main函数里使用List保存了个十百千万的表达式,依次用这些表达式来解析上下文。注意,解析的顺序是个十百千万的顺序。
结构(Structure)
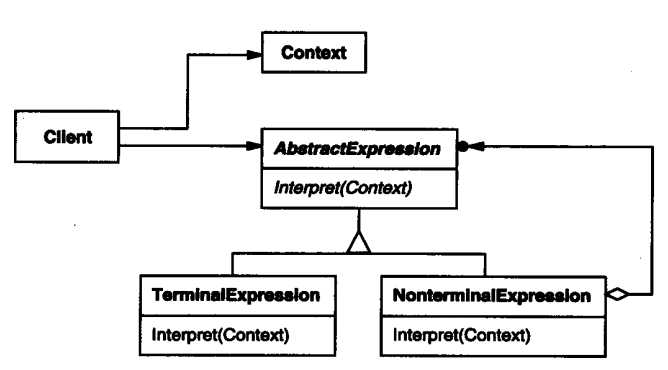
Interpreter模式的几个要点
转载请注明出处:
作者:JesseLZJ
出处:http://jesselzj.cnblogs.com
设计模式15:Interpreter 解释器模式(行为型模式)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/jesselzj/p/4772093.html