标签:
-----------回顾分割线-----------
此系列旨在开发类似“谁是卧底+杀人游戏”的捉鬼游戏在线版,记录从分析游戏开始的开发全过程,通过此项目让自己熟悉面向对象的SOLID原则,提高对设计模式、重构的理解。
索引目录:
0. 索引(持续更新中)
2. 设计业务对象与对象职责划分(1)(图解旧版本)
3. 设计业务对象与对象职责划分(2)(旧版本代码剖析)
4. 设计业务对象与对象职责划分(3)(新版本业务对象设计)
5. 业务对象核心代码编写与单元测试(游戏开始前:玩家入座与退出)
6. 业务对象核心代码编写与单元测试(游戏开始:抽题、分角色、开启鬼讨论模式)
7. 代码与测试(鬼讨论、鬼投票)
-----------回顾结束分割线-----------
先放上源代码,svn地址:https://115.29.246.25/svn/Catghost/
账号:guest 密码:guest(支持源代码下载,已设只读权限,待我基本做出初始版本后再放到git)
-----------本篇开始分割线----------
一、鬼讨论
二话不说,先上关键篇的“鬼发言”顺序图:

灰常简单,首先对Ghost的父类Player的Speak()方法进行填充:
public void Speak(string statement) { GetSpeakManager().PlayerSpeak(this, statement); }
很明显下一步就要填充SpeakManager类的PlayerSpeak()方法:
public void PlayerSpeak(Player player, string str) { if (IsGhostDiscussing()) { CheckGhostSpeaker(player); } else { CheckCurrentSpeaker(player); } AddToRecord(FormatSpeak(player.NickName, str)); }
依旧遵循显而易见的方法命名,具体如何CheckGhostSpeaker,以及CheckCurrentSpeaker,private方法大家查看代码即可,不贴出来简单的代码浪费时间啦~就是一个if和throw自定义错误类。
测试一下:
[TestMethod] public void GhostDiscussUnitTest() { SetNickNameArray(); foreach (Ghost g in GetPlayerManager().GetPlayerArray(typeof(Ghost))) { g.Speak("hello"); g.Speak("i‘m " + g.NickName); } ShowPlayerListen(); } // 游戏初始化 private void SetNickNameArray() { Table table = Table.GetInstance(); table.Restart(); // clear all except table PlayerManager manager = table.GetPlayerManager(); string[] names = new string[] { "jack", "peter", "lily", "puppy", "coco", "kimi", "angela", "cindy", "vivian" }; for (int order = 0; order < names.Length; order++) { string name = names[order]; manager.SetNickName(order, name); } // game is starting... } // 显示各玩家各自听到的内容 private void ShowPlayerListen() { foreach (Player player in GetPlayerManager().GetAllPlayerArray()) { ShowPlayer(player); Console.WriteLine(Table.GetInstance().GetGame().GetSpeakManager().ShowRecord(player)); } }

测试结果也是完美——只有鬼内部讨论,其他人看不到。
代码度量值也是没问题。只需要看刚才涉及的方法即可。
二、鬼投票(决定首轮发言人)
老规矩,照着顺序图来:
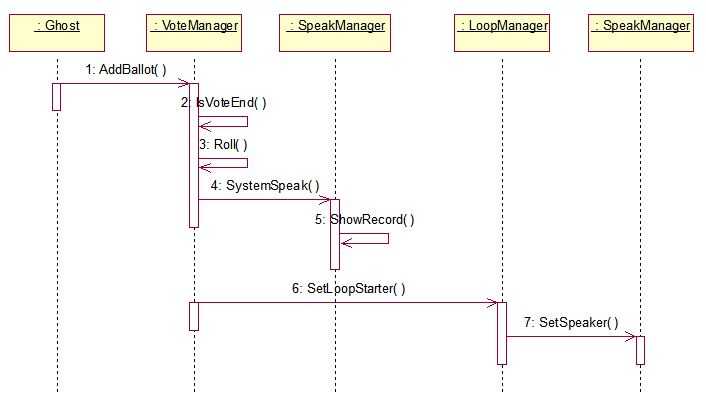
此处是本篇重点与难点。
首先考虑到VoteManager与LoopManager类的创建问题,应该与SpeakManager一样——每个Game只能有一个,故在Game类中增加私有字段保存,并公开GetVoteManager()、GetLoopManager()方法。
public class Game { private bool _isStart; private Table _table; private Subject _subject = new Subject(); private SpeakManager _speakManager = new SpeakManager(); private VoteManager _voteManager = new VoteManager(); private LoopManager _loopManager = new LoopManager(); }
第二步就要处理VoteManager中的内容了,依据之前的分析,需要有一个BallotList字段来记录投票的情况,但此时发现:还需要记录投票人——有哪些人有资格投票,他们都表态了没有,因为鬼讨论时只有鬼能投票,PK时不允许PK者自己投票,被投死的玩家也不能投票——投票人VoterList需要维护;每次的候选人都可能不一样——投死的不能参加候选人,PK时只有PK者才是候选人——候选人CandidateList需要维护。
public class VoteManager {
private List<Player> _voterList; private List<Player> _candidateList; // public method /// <summary> /// 增加选票 /// </summary> /// <param name="voter">投票人</param> /// <param name="candidate">候选人</param> public void AddBallot(Player voter, Player candidate) { } }
那么问题来了:这些投票人、候选人在何时应该变更,变更成什么样的List,这个职责应该谁来负责?Player?玩家自己当裁判肯定不行。VoteManager自身?他根本不知道、也不需要知道游戏进行的情况如何,他只管投票是否结束。应该由放眼整个游戏的Game对象来完成。Game中代码:
public void Start() { CheckGameState(); SetGameStateToStarted(); PublishSubject(); AssignRole(); SetGhostDiscuss(); SetGhostVote(); } /// <summary> /// 设置鬼投票环节的投票人与候选人 /// </summary> private void SetGhostVote() { Player[] voters = GetPlayerManager().GetPlayerArray(typeof(Ghost)); Player[] candidates = GetPlayerManager().GetAllPlayerArray(); GetVoteManager().SetVoterListAndCandidateList(voters, candidates); }
第三步,投票官VoteManager收集选票。注意此时的投票情况BallotList字段改为了字典类型,因为要传递给SpeakManager类谁投了谁的信息。
public class VoteManager { private Dictionary<Player, Player> BallotList; // 投票情况 private List<Player> _voterList; // 投票人 private List<Player> _candidateList; // 候选人 public void AddBallot(Player voter, Player candidate) { CheckVoterIsInList(voter); CheckCandidateIsInList(candidate);
BallotList.Add(voter, candidate); } private void CheckVoterIsInList(Player voter) { if (this._voterList.Contains(voter) && !this.BallotList.ContainsKey(voter)) return;throw new IllegalVoterException(); } private void CheckCandidateIsInList(Player candidate) { if (this._candidateList.Contains(candidate) || candidate == null) return; throw new IllegalCandidateException(); } }
第四步,判断是否投票完毕,此时改IsVoteEnd()为CheckVoteEnd(),这样就能把如果投票完后的动作交给CheckVoteEnd()方法处理,而不用在、也不应该在AddBallot()方法中进行,这是职责分配问题。
private void CheckVoteEnd() { if (BallotList.Count == this._voterList.Count) { Roll(); } }
第五步,唱票。首先展示一下投票情况
private void Roll() { ShowBallotList(); } private void ShowBallotList() { foreach (KeyValuePair<Player, Player> ballot in BallotList) { GetSpeakManager().SystemSpeak(FormatShowBallot(ballot.Key.NickName, ballot.Value.NickName)); } } private string FormatShowBallot(string voterName, string candidateName) { return string.Format("【{0}】投了【{1}】", voterName, candidateName); }
测试:假设鬼都投自己(投票不一致)
public void GhostVoteUnitTest() { SetNickNameArray(); // ghost discussing... // ghost voting foreach (Ghost g in GetPlayerManager().GetPlayerArray(typeof(Ghost))) { g.Vote(g); // not same vote } ShowPlayerListen(); }

结果很好:只有鬼看到谁投了谁。
接下来是,统计票数。需要新增一个统计表(两列,候选人与票数),先初始化候选人表,每个人都是0票,再循环遍历投票情况,给每个得票的候选人+1票。
private void Roll() { ShowBallotList(); Dictionary<Player, int> statistics = new Dictionary<Player, int>(); // initial foreach (Player p in this._candidateList) { statistics.Add(p, 0); } // roll foreach (KeyValuePair<Player, Player> ballot in BallotList) { statistics[ballot.Value] += 1; } HandleRoll(statistics); }
统计完之后,就要处理唱票结果HandleRoll()。首先判断唱票结果是否一致。如果一致则开始轮流发言;如果不一致,则要看是否是鬼讨论阶段,如果是,则提示鬼,且清空投票情况以备鬼再次投票,如果是正常游戏投票阶段,则将进入pk环节,此处先做任务标记。
测试之。没问题。
public void GhostVoteUnitTest() { SetNickNameArray(); // ghost discussing... // ghost voting foreach (Ghost g in GetPlayerManager().GetPlayerArray(typeof(Ghost))) { g.Vote(g); // not same vote } // ghost voting foreach (Ghost g in GetPlayerManager().GetPlayerArray(typeof(Ghost))) { g.Vote(GetPlayerManager().GetAllPlayerArray()[0]); // same vote } ShowPlayerListen(); }

再看代码度量值。
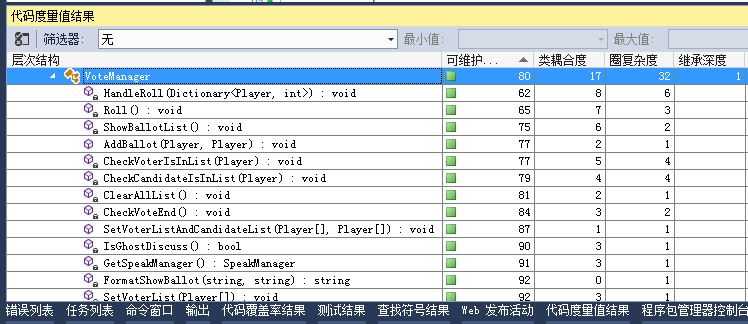
各种不给力。改吧~
先处理可维护性最低的HandleRoll(),先看原样:
private void HandleRoll(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { int max = statistics.Max(s => s.Value); if (statistics.Where(s => s.Value.Equals(max)).Count() == 1) { // Todo: Begin Loop } else { if (IsGhostDiscuss()) { GetSpeakManager().SystemSpeak(GetSetting().GetAppSettingValue("GhostVoteNotSameTip")); ClearBallotList(); } else { // Todo: PK } } }
先做最小的部分:if (IsGhostDiscuss) 里面的内容提取出方法SetGhostVoteAgain(),意味着分离HandleRoll的职责。
if (IsGhostDiscuss()) { SetGhostVoteAgain(); } private void SetGhostVoteAgain() { GetSpeakManager().SystemSpeak(GetSetting().GetAppSettingValue("GhostVoteNotSameTip")); ClearBallotList(); }
在处理最麻烦的lambda表达式部分,我们看到在statistics统计情况中,我们只关心的是Value,而不关心Key,且Value都是int类型,所以可改为:
private void HandleRoll(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { if (CheckRollOnly(statistics.Values.ToArray())) { // Todo: Begin Loop } else { if (IsGhostDiscuss()) { SetGhostVoteAgain(); } else { // Todo: PK } } } private static bool CheckRollOnly(int[] statisticsValues) { int max = statisticsValues.Max(); return statisticsValues.Count(s => s.Equals(max)) == 1; }
如此一来就减少了类的引用次数。看一下代码度量值,果断有效:别忘了测试喔
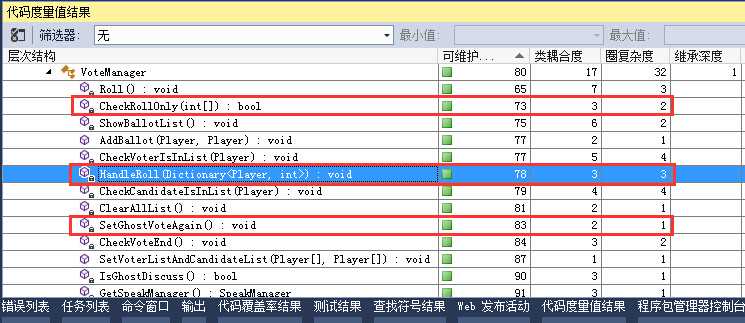
接着改Roll(),先看当前代码:
private void Roll() { ShowBallotList(); Dictionary<Player, int> statistics = new Dictionary<Player, int>(); // initial foreach (Player p in this._candidateList) { statistics.Add(p, 0); } // roll foreach (KeyValuePair<Player, Player> ballot in BallotList) { statistics[ballot.Value] += 1; } HandleRoll(statistics); }
看过《重构》的朋友们也许一眼就看出问题了——注释就是问题。提取出方法为:
private void Roll() { ShowBallotList(); Dictionary<Player, int> statistics = new Dictionary<Player, int>(); InitialStatistics(statistics); RollStatistics(statistics); HandleRoll(statistics); } private void RollStatistics(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { foreach (KeyValuePair<Player, Player> ballot in BallotList) { statistics[ballot.Value] += 1; } } private void InitialStatistics(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { foreach (Player p in this._candidateList) { statistics.Add(p, 0); } }
进一步优化——用数组做传递将减少类引用问题。也减小内存开销。
private void RollStatistics(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { foreach (Player p in BallotList.Values.ToArray()) { statistics[p] += 1; } } private void InitialStatistics(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { foreach (Player p in this._candidateList.ToArray()) { statistics.Add(p, 0); } }
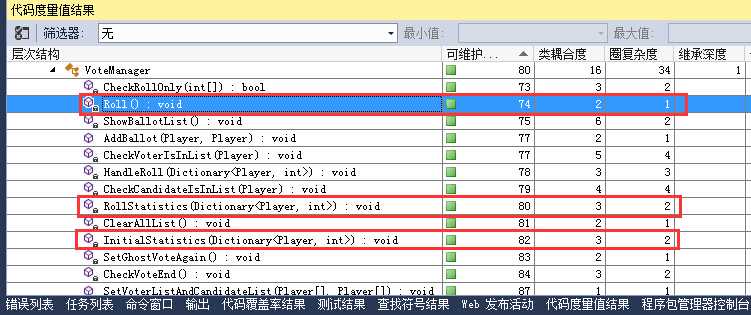
好多了吧,别忘了测试。接下来看ShowBallotList()方法:
private void ShowBallotList() { foreach (KeyValuePair<Player, Player> ballot in BallotList.ToArray()) { ShowBallot(ballot.Key.NickName, ballot.Value.NickName); } } private void ShowBallot(string voterName, string candidateName) { GetSpeakManager().SystemSpeak(FormatShowBallot(voterName, candidateName)); }
用数组Array代替列表List,提取出ShowBallot(string, string)方法以减少类耦合。再看代码度量值(别忘了测试!)
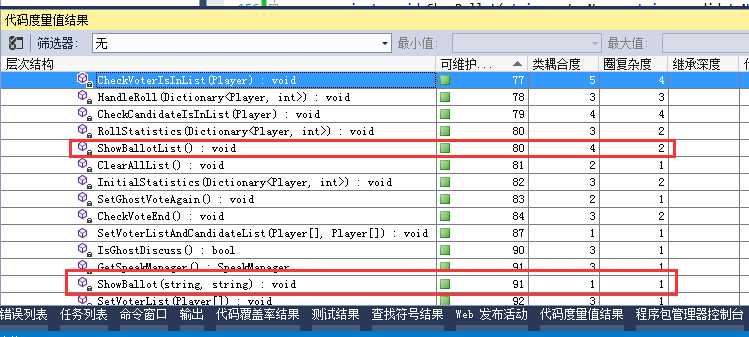
爽多了。接下来改CheckVoterIsInList()、CheckCandidateIsInList()。先看改前版本:
private void CheckVoterIsInList(Player voter) { if (this._voterList == null) throw new IllegalVoteException(); if (this._voterList.Contains(voter) && !this.BallotList.ContainsKey(voter)) return; throw new IllegalVoterException(); } private void CheckCandidateIsInList(Player candidate) { if (this._candidateList == null) throw new IllegalVoteException(); if (this._candidateList.Contains(candidate) || candidate == null) return; throw new IllegalCandidateException(); }
首先发现两个方法的第一句都是判断这次投票是否有效(投票开始了没有,即投票人列表和候选人列表都有了没有)
private void CheckVoterIsInList(Player voter) { CheckIsIllegalVote(); if (this._voterList.Contains(voter) && !this.BallotList.ContainsKey(voter)) return; throw new IllegalVoterException(); } private void CheckCandidateIsInList(Player candidate) { CheckIsIllegalVote(); if (this._candidateList.Contains(candidate) || candidate == null) return; throw new IllegalCandidateException(); } private void CheckIsIllegalVote() { if (this._voterList == null || this._candidateList == null) throw new IllegalVoteException(); }
再详细分解:
private void CheckVoterIsInList(Player voter) { CheckIsIllegalVote(); CheckContainsVoter(voter); CheckHasVoted(voter); } /// <summary> /// 检查是否已投过票 /// </summary> /// <param name="voter">投票人</param> private void CheckHasVoted(Player voter) { if (this.BallotList.ContainsKey(voter)) { throw new IllegalVoterException(); } } /// <summary> /// 检查是否允许投票 /// </summary> /// <param name="voter">投票人</param> private void CheckContainsVoter(Player voter) { if (!this._voterList.Contains(voter)) { throw new IllegalVoterException(); } }
测试,通过。看度量值:
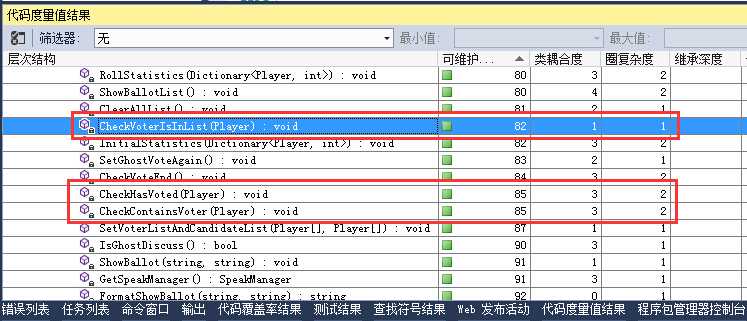
妥妥的没问题,同理修改CheckCandidateIsInList()。此处不赘述。
到此,鬼投票已完成。下面就开始鬼投票一致时,进行的内容。
三、首轮发言开始
回到HandleRoll(),应在Todo: Begin Loop处填写。
private void HandleRoll(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { if (CheckRollOnly(statistics.Values.ToArray())) { // Todo: Begin Loop } else { if (IsGhostDiscuss()) { SetGhostVoteAgain(); } else { // Todo: PK } } }
突然忘了要做什么,没关系,回看一下顺序图:

一目了然:第6步,由VoteManager向LoopManager发送设置首轮发言开始的信号。再由LoopManager向SpeakManager发送首轮发言人,并由LoopManager关闭鬼讨论环节,同时向全场宣告首轮发言人——注意,一定要先关闭鬼讨论环节,不然宣布首轮发言人只有鬼能看到~
经过优化后的代码如下:GetRollOnlyPlayer()的类耦合度为5,略微有些高,但我真不知道怎么再优化了……请各位指教。
private void HandleRoll(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { if (CheckRollOnly(statistics.Values.ToArray())) { SetLoopStart(GetRollOnlyPlayer(statistics)); } else { if (IsGhostDiscuss()) { SetGhostVoteAgain(); } else { // Todo: PK } } } /// <summary> /// 返回投票最高的唯一玩家 /// </summary> /// <param name="statistics">投票情况</param> /// <returns>投票最高的唯一玩家</returns> private Player GetRollOnlyPlayer(Dictionary<Player, int> statistics) { return statistics.OrderByDescending(s => s.Value).FirstOrDefault().Key; } /// <summary> /// 设置循环开始 /// </summary> /// <param name="starter">首发言的玩家</param> private void SetLoopStart(Player starter) { GetLoopManager().SetLoopStarter(starter); }
LoopManager中是这样写的:
public void SetLoopStarter(Player starter) { GetSpeakManager().SetSpeaker(starter); GetSpeakManager().SetOffGhostDiscuss(); GetSpeakManager().ClearRecord(); GetSpeakManager().SystemSpeak(string.Format("鬼选择了【{0}】作为首轮发言人。请【{0}】发言。", starter.NickName)); }
测试,杠杠的。代码度量值也没什么问题,此处就不贴图了。
[TestMethod] public void CurrentSpeakerUnitTest() { SetNickNameArray(); // ghost discussing... // ghost voting Player electPlayer = GetPlayerManager().GetAllPlayerArray()[2]; // elect player foreach (Ghost g in GetPlayerManager().GetPlayerArray(typeof(Ghost))) { g.Vote(electPlayer); // same vote } // current speaker speaking electPlayer.Speak("i‘m first"); // success // player speaking foreach (Player p in GetPlayerManager().GetAllPlayerArray()) { //p.Speak("i‘m " + p.NickName); // exception: 不许场外 } ShowPlayerListen(); }

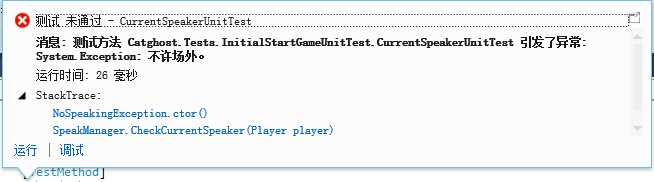
四、检查类职责
别忘了定时回顾各类,检查各类的职责是否有越界、是否职责过多(过多则需要分离职责,可能会新增类)、是否暴露过多(不该public的public了)。
我借助的是vs中查看类图的方法。
到此,本篇结束。代码已上传svn。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lzhlyle/p/Catghost-Models3.html