标签:

问题大意:农夫约翰为了修理栅栏,要将一块很长的木块切割成N块,准备切成的木板的长度为L1,L2...LN,未切割前的木板的长度恰好为切割后木板的长度的总和,每次切断木板的时候,需要的开销为这块木板的长度,例如长度为21的木板需要切成长度为5,8,8的三块木板,长为21的木板切成长为13和8的板时,开销为21,。再将长度为13的板切成长度为5和8的板时,开销是13,于是合计开销是34,然后要你求切割完的最小开销是什么。
乍眼看这一道题好像有很多种切割方案,似乎是很难解决的,但是我们这样想,就是当我们切一块木板的时候,我们所用的开销就是切割这一块木板所要用到的长度,我们得到了两块木板,这两块木板可以继续切的话,他们的总开销就是这两块木板的和,也就是一块长的木板。那么我们想到最后,就会发现其实就是我们得到了一个这样的东西,就是最小的板会所要用到的开销会占N次(视通过多少次分割得到这块板来定),如果我们要画一幅图来展示这个过程的话。。。
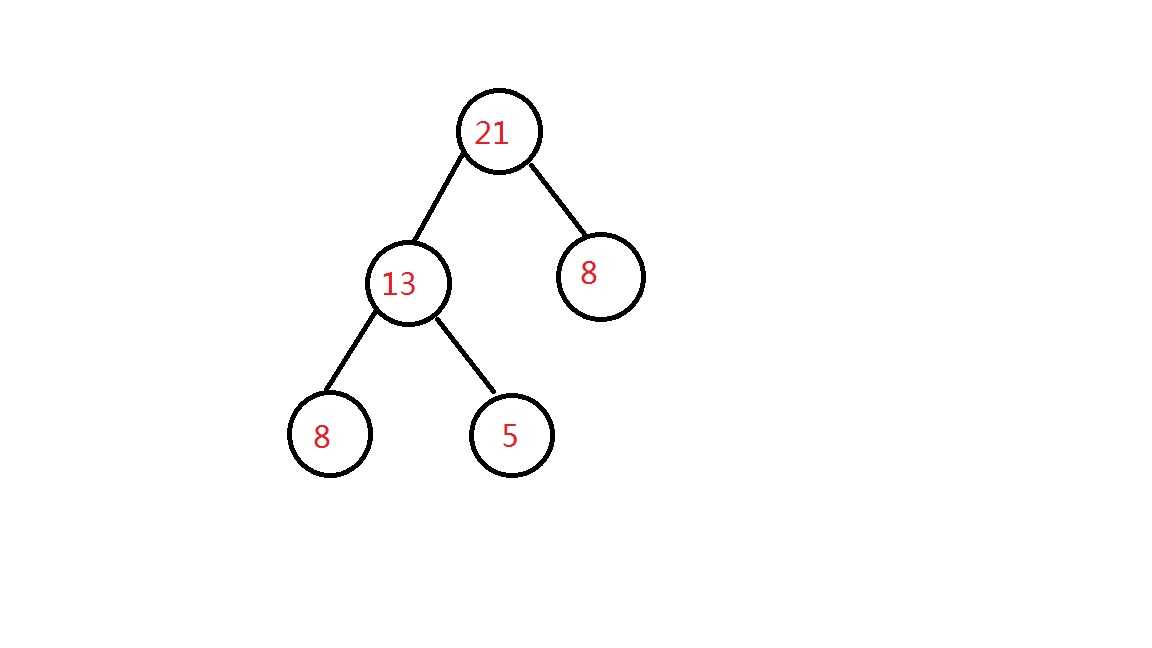
上面最大的开销是34=8*2+5*2+8(也就是二叉树的树叶对应节点大小乘以高度)
那么为了得到最小的开销,我们很容易就发现,我们只要把相对较小的节点放在比较深的地方就可以了,这是一种比较常用的贪婪的思想,证明我就省略了
那么现在我们只用不断地把最小的节点结合起来,最后就会形成最小的开销,那么不断找最小嘛,很容易就想到用堆,堆呢你可以自己写(熟练的话会很快),也可以直接用std(会比较简洁)
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 4 typedef int Position, *Heap; 5 6 int Delete_Min(Heap, int *const); 7 void Push(Heap, int, int *const); 8 9 int main(void) 10 { 11 int N, i, size = 0; 12 int L1, L2, tmp; 13 long long ans = 0; 14 15 while (~scanf("%d",&N)) 16 { 17 Heap pque = (Heap)malloc(sizeof(int)*N); 18 for (i = 0; i < N; i++) 19 { 20 scanf("%d", &tmp); 21 Push(pque, tmp, &size); 22 } 23 while (size > 1) 24 { 25 L1 = Delete_Min(pque, &size); 26 L2 = Delete_Min(pque, &size); 27 28 ans += (long long)L1 + L2; 29 Push(pque, L1 + L2, &size); 30 } 31 free(pque); 32 printf("%lld\n", ans); 33 } 34 } 35 36 int Delete_Min(Heap heap,int *const size) 37 { 38 Position pr = 1, s1, s2, s; 39 int out = heap[1], tmp = heap[(*size)--]; 40 for (; pr <= *size;) 41 { 42 s1 = pr << 1; s2 = s1 + 1; 43 if (s2 <= *size) 44 { 45 if (heap[s1] < heap[s2]){ heap[pr] = heap[s1]; pr = s1; } 46 else{ heap[pr] = heap[s2]; pr = s2; } 47 } 48 else 49 { 50 if (s1 <= *size){ heap[pr] = heap[s1]; pr = s1;break; } 51 else break; 52 } 53 } 54 for (s = pr; s > 1;) 55 { 56 if (s % 2 == 0) 57 { 58 pr = s >> 1; 59 if (heap[pr] > tmp) { heap[s] = heap[pr];s = pr;} 60 else break; 61 } 62 else 63 { 64 pr = (s - 1) >> 1; 65 if (heap[pr] > tmp){ heap[s] = heap[pr];s = pr; } 66 else break; 67 } 68 } 69 heap[s] = tmp; 70 return out; 71 } 72 73 void Push(Heap heap, int item, int *const size) 74 { 75 Position s = ++(*size), pr; 76 for (; s > 1;) 77 { 78 if (s % 2 == 0) 79 { 80 pr = s >> 1; 81 if (heap[pr] > item) { heap[s] = heap[pr]; s = pr; } 82 else break; 83 } 84 else 85 { 86 pr = (s - 1) >> 1; 87 if (heap[pr] > item){ heap[s] = heap[pr]; s = pr; } 88 else break; 89 } 90 } 91 heap[s] = item; 92 }
这是直接写堆的代码
1 #include<iostream> 2 #include<queue> 3 #include<functional> 4 #include<cstdio> 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 int main(void) 9 { 10 int N, i; 11 int L1, L2, tmp; 12 long long ans = 0; 13 14 while (~scanf("%d", &N)) 15 { 16 priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> >pque; 17 for (i = 0; i < N; i++) 18 { 19 scanf("%d", &tmp); 20 pque.push(tmp); 21 } 22 while (pque.size() > 1) 23 { 24 L1 = pque.top(); 25 pque.pop(); 26 L2 = pque.top(); 27 pque.pop(); 28 29 ans += (long long)L1 + L2; 30 pque.push(L1 + L2); 31 }; 32 printf("%lld\n", ans); 33 } 34 }
这是用的std,事实上呢用std是挺方便的,虽然稍微损失了一下性能,我直接用堆是472K,32ms,用std是920k,47ms,相差不大
另外这个思想还可以用来做著名的Huffman编码,其实Huffman以前写了一个,以后会贴出来看看
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/Philip-Tell-Truth/p/4787067.html