标签:
jdk1.8.0_45源码解读——Set接口和AbstractSet抽象类的实现
一、 Set架构
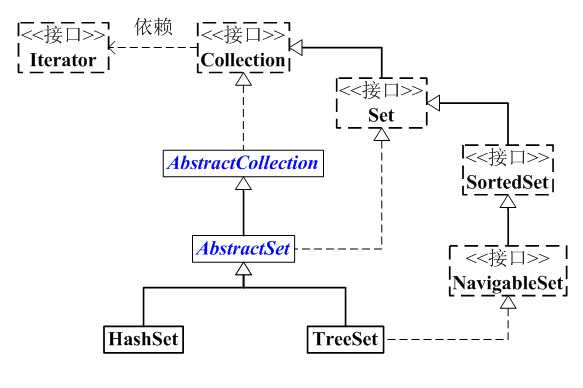
如上图:
(01) Set 是继承于Collection的接口。它是一个不允许有重复元素的集合。
(02) AbstractSet 是一个抽象类,它继承于AbstractCollection。AbstractCollection实现了Set中的绝大部分函数,为Set的实现类提供了便利。
(03) HastSet 和 TreeSet 是Set的两个实现类。
HashSet依赖于HashMap,它实际上是通过HashMap实现的。HashSet中的元素是无序的。
TreeSet依赖于TreeMap,它实际上是通过TreeMap实现的。TreeSet中的元素是有序的。
(04) LinkedHashSet继承于HashSet,是具有可预知迭代顺序的 Set 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现。此实现与 HashSet 的不同之外在于,后者维护着一个运行于所有条目的双重链接列表。此链接列表定义了迭代顺序,即按照将元素插入到 set 中的顺序(插入顺序)进行迭代。
二、 Set接口
一个不包含重复元素的 collection。更确切地讲,set 不包含满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素对 e1 和 e2,并且最多包含一个 null 元素。正如其名称所暗示的,此接口模仿了数学上的 set 抽象。
注:如果将可变对象用作 set 元素,那么必须极其小心。如果对象是 set 中某个元素,以一种影响 equals 比较的方式改变对象的值,那么 set 的行为就是不确定的。此项禁止的一个特殊情况是不允许某个 set 包含其自身作为元素。
public interface Set<E> extends Collection<E> { // Query Operations int size(); boolean isEmpty(); boolean contains(Object o); Iterator<E> iterator(); Object[] toArray(); //返回一个包含set中所有元素的数组 <T> T[] toArray(T[] a); //返回一个包含此set中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型是指定数组的类型 // Modification Operations boolean add(E e); boolean remove(Object o); // Bulk Operations boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c); //如果此set包含指定 collection 的所有元素,则返回 true boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c); boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c); //仅保留set中那些包含在指定 collection中的元素 boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c); //移除set中那些包含在指定 collection中的元素 void clear(); // Comparison and hashing boolean equals(Object o); int hashCode(); //返回set的哈希码 }
三、AbstractCollection抽象类此类提供 Collection 接口的骨干实现,以最大限度地减少了实现此接口所需的工作。继承此抽象类的直接已知子类有:AbstractList,AbstractQueue,AbstractSet,ArrayDeque。
要实现一个不可修改的collection,编程人员只需扩展此类,并提供iterator()和 size()方法的实现,其中iterator()方法返回的迭代器必须实现 hasNext()和 next()。
要实现可修改的collection,编程人员必须另外重写此类的add()方法,否则,会抛出 UnsupportedOperationException),iterator()方法返回的迭代器还必须另外实现其 remove()方法。

public abstract class AbstractCollection<E> implements Collection<E> { protected AbstractCollection() { } public abstract Iterator<E> iterator(); public abstract int size(); public boolean isEmpty() { return size() == 0; } public boolean contains(Object o) { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); //集合中可以含有null值 if (o==null) { while (it.hasNext()) if (it.next()==null) return true; } else { while (it.hasNext()) if (o.equals(it.next())) return true; } return false; } //返回包含此 collection中所有元素的数组。 public Object[] toArray() { // Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements Object[] r = new Object[size()]; Iterator<E> it = iterator(); for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) { if (! it.hasNext()) // fewer elements than expected return Arrays.copyOf(r, i); //返回一个长度为i的数组,元素为r中相应的值 r[i] = it.next(); } //finishToArray(r, it) ensures more elements than expected //r数组已经填满了所有的元素,但如果迭代器中仍有元素,则通过finishToArray(r, it)来重新调整 return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r; } //返回包含此 collection 中所有元素的数组;返回数组的运行时类型与指定数组的运行时类型相同 @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) { // Estimate size of array; be prepared to see more or fewer elements int size = size(); T[] r = a.length >= size ? a : (T[])java.lang.reflect.Array .newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size); Iterator<E> it = iterator(); for (int i = 0; i < r.length; i++) { if (! it.hasNext()) { // fewer elements than expected if (a == r) { r[i] = null; // null-terminate } else if (a.length < i) { return Arrays.copyOf(r, i); } else { System.arraycopy(r, 0, a, 0, i); if (a.length > i) { a[i] = null; } } return a; } r[i] = (T)it.next(); } // more elements than expected return it.hasNext() ? finishToArray(r, it) : r; } //可分配给数组的最大长度 private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8; /** * 在toArray()方法中,如果迭代器中比预料中有更多的元素时,用已经存满的数组和迭代器完成toArray的填充工作 * * @param r 已经存满元素的数组 * @param it collection的正在处理的迭代器 * @return 返回包含给定数组r中的所有元素和迭代器it返回的所有元素的数组 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") private static <T> T[] finishToArray(T[] r, Iterator<?> it) { int i = r.length; while (it.hasNext()) { //迭代器 int cap = r.length; if (i == cap) { int newCap = cap + (cap >> 1) + 1; //新数组扩容1.5倍 // overflow-conscious code if (newCap - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) newCap = hugeCapacity(cap + 1); r = Arrays.copyOf(r, newCap); //返回一个长度为newCap,元素包含r中所有元素的数组 } r[i++] = (T)it.next(); //将迭代器中返回的元素逐个放入数组中 } // trim if overallocated return (i == r.length) ? r : Arrays.copyOf(r, i); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError ("Required array size too large"); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } // Modification Operations public boolean add(E e) { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); } //从此 collection中移除指定的元素 //注意如果iterator()方法返回的迭代器没有实现remove()方法,则在删除指定元素时会报UnsupportedOperationException public boolean remove(Object o) { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); // if (o==null) { while (it.hasNext()) { if (it.next()==null) { it.remove(); //利用迭代器实现的remove()方法进行元素删除 return true; } } } else { while (it.hasNext()) { if (o.equals(it.next())) { it.remove(); return true; } } } return false; } //如果此 collection 包含指定 collection 中的所有元素,则返回 true public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) { for (Object e : c) if (!contains(e)) return false; return true; } //将指定 collection 中的所有元素都添加到此 collection中 public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { boolean modified = false; for (E e : c) if (add(e)) modified = true; return modified; } //移除此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection中的所有元素 public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); //检查给定的对象引用是否为null,若是,抛出NullPointerException boolean modified = false; Iterator<?> it = iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { if (c.contains(it.next())) { //如果给定的集合中包含该元素,则删除 it.remove(); modified = true; } } return modified; } //仅保留此 collection 中那些也包含在指定 collection的元素,和removeAll(Collection<?> c)正好相反 public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); boolean modified = false; Iterator<E> it = iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { if (!c.contains(it.next())) { //如果给定的集合中不包含该元素,则删除 it.remove(); modified = true; } } return modified; } //移除此 collection中的所有元素 public void clear() { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); while (it.hasNext()) { it.next(); it.remove(); } } //返回此 collection 的字符串表示形式:[e1, e2, ...] public String toString() { Iterator<E> it = iterator(); if (! it.hasNext()) return "[]"; StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); sb.append(‘[‘); for (;;) { E e = it.next(); sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e); if (! it.hasNext()) return sb.append(‘]‘).toString(); sb.append(‘,‘).append(‘ ‘); } } }
四、AbstractSet抽象类
此类提供 Set 接口的骨干实现,从而最大限度地减少了实现此接口所需的工作。
注意,此类并没有重写 AbstractCollection 类中的任何实现(包括add()方法)。它仅仅添加了 equals 和 hashCode 的实现。

public abstract class AbstractSet<E> extends AbstractCollection<E> implements Set<E> { protected AbstractSet() { } // 比较指定对象与此 set的相等性,如果指定的对象也是一个set,并且两个set有相同的大小,元素,则返回true。 public boolean equals(Object o) { if (o == this) return true; //1.先检查指定的对象是不是set if (!(o instanceof Set)) return false; Collection<?> c = (Collection<?>) o; //2.再检查指定set的大小与这个set的大小是否相等 if (c.size() != size()) return false; try { //3.最后检查这个set是否包含指定set中的所有元素 return containsAll(c); } catch (ClassCastException unused) { return false; } catch (NullPointerException unused) { return false; } } //返回此set的哈希码值:即该set中所有元素的哈希值之和 public int hashCode() { int h = 0; Iterator<E> i = iterator(); while (i.hasNext()) { E obj = i.next(); if (obj != null) h += obj.hashCode(); } return h; } //从此 set中移除包含在指定 collection中的所有元素 public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) { Objects.requireNonNull(c); boolean modified = false; //如果此set的大小>指定集合c的大小 if (size() > c.size()) { //迭代指定集合c中的元素,并在此set中逐个删除 for (Iterator<?> i = c.iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) modified |= remove(i.next()); } else { for (Iterator<?> i = iterator(); i.hasNext(); ) { if (c.contains(i.next())) { i.remove(); modified = true; } } } return modified; } }
jdk1.8.0_45源码解读——Set接口和AbstractSet抽象类的实现
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/CherishFX/p/4788432.html