标签:
本章讲解C++标准程序库中的通用工具。它们是由短小精干的类和函数构成。
Pairs(对组)
class pair可以将两个值视为一个单元。STL内多处使用了pair。尤其容器map和multimap,就是使用pairs来管理key/value的成对元素。
struct pair定义与<utility>:

namespace std{ template <class T1,class T2> struct pair{ //type names for the values typedef T1 first_type; typedef T2 second_type; //member T1 first; T2 second; //default constructor pair():first(T1()),second(T2()) {} //constructor for two values pair(cosnt T1&a,const T2& b):first(a),second(b) {} //copy constructor with implicit conversions template<class U,class V> pair(const pair<U,V>& p):first(p.first),second(p.second) {} }; //comparisons template<class T1,class T2> bool operator==(const pair<T1,T2>&,const pair<T1,T2>&); template<class T1,class T2> bool operator<(const pair<T1,T2>&,const pair<T1,T2>&); ... //convenience function to create a pair template<class T1,class T2> pair<T1,T2> make_pair(const T1&,const T2&); }
make_pair()
template函数可以让你无需写出型别,就可以生成一个pair对象:

namespace std{ template<class T1,class T2> pair<T1,T2> make_pair(const T1& x,const T2& y){ return pair<T1,T2>(x,y); } }
因此我们可以这样使用make_pair()
std::make_pair(42,‘@‘)
而不必费力地这么写
std::pair<int,char>(42,‘@‘)
Class auto_ptr
auto_ptr是一种智能型指针(smart pointer),帮助程序员防止“被异常抛出时发生资源泄漏”。
auto_ptr是这样的一种指针:它是“它所指向的随想”的拥有者(owner)。所以,当身为对象拥有者的auto_ptr销毁时,该对象也将遭到销毁。auto_ptr要求一个对象只能有一个拥有者。
这个智能型指针应该保证,无论在何种情形下,只要自己被摧毁,就一定连带释放其所指资源。
auto_ptr拥有权的转移
auto_ptr的copy构造函数和assignment操作符负责将拥有权交出去。试看下例copy构造函数的运用:
std::auto_ptr<ClassA> ptr1(new ClassA); std::auto_ptr<ClassA> ptr2(ptr1);
一开始ptr1拥有那个new出来的对象,在第二条语句中,拥有权由ptr1转交给ptr2.ptr2就拥有了那个new出来的对象,而ptr1不再拥有它。这样,对象就只会被delete一次--在ptr2被销毁的时候。
赋值动作也差不多
std::auto_ptr<ClassA> prt1(new ClassA); std::auto_ptr<ClassA> ptr2; ptr2=ptr1;
如果ptr2被赋值之前正拥有另一个对象,赋值动作发生时会调用delete,将该对象删除。
拥有权的转移,使得auto_ptr产生一种特殊用法:某个函数可以利用auto_ptr将拥有权转交给另一个函数。这种事情可以在两种情形下出现:
1.某函数是数据的终点。如果auto_ptr以by value方式呗当做一个参数传递给某函数。此时被调用端的参数获得了这个auto_ptr的拥有权,如果函数不再将它传递出去,它指向的对象就会在函数退出时被删除:
void sink(std::auto_ptr<ClassA>);
2.某函数是数据的起点。当一个auto_ptr被返回,其拥有权便转交给调用端
std::auto_ptr<ClassA> f() { std::auto_ptr<ClassA> ptr(new ClassA); ... return ptr; } void g() { std::auto_ptr<ClassA> p; p=f(); }
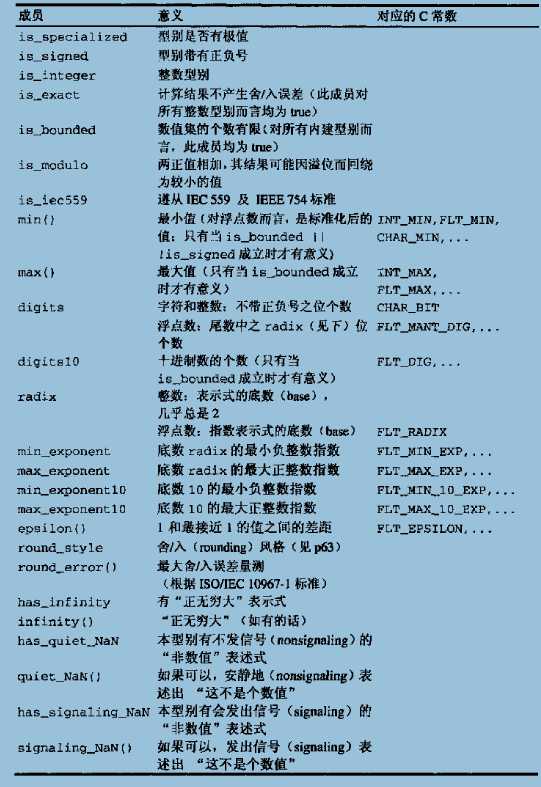
数值极限(numeric Limits)
一般说来,数值型别的极值是一个与平台相关的特性。C++标准程序库通过template numeric_limits提供这些极值。
下面是numeric_limits<>的使用范例
#include <iostream> #include <limits> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { cout<<"max(short):"<<numeric_limits<short>::max()<<endl; cout<<"max(int):"<<numeric_limits<int>::max()<<endl; }
下表给出了class numeric_limits<>的所有成员
辅助函数
1.挑选较小值和较大值
namespace std{ template<class T> inline const T& min(const T& a,const T& b) {return b < a ? b : a;} template<class T> inline const T& max(const T& a,const T& b) {return a < b ? b : a;} }
上述两个函数还有另一个版本,接收一个额外的template参数作为“比较准则”:
namespace std{ template<class T,class Compare> inline const T& min(const T& a,const T& b,Compared comp) { return comp(b,a) ? b : a; } template<class T,class Compare> inline const T& min(const T& a,const T& b,Compared comp) { return comp(a,b) ? b : a; } }
下面这个例子示范了如何传入特定的比较函数作为操作,以此方式来运用max():
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; bool int_ptr_less(int *a,int* b) { return *a < *b; } int main() { int x=17; int y=42; int* px=&x; int* py=&y; pmax=max(px,py,int_ptr_less); }
2.两值互换
函数swap()用来交换两对象的值。
namespace std{ template<class T> inline void swap(T& a,T& b){ T tmp(a); a=b; b=tmp; } }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/runnyu/p/4813418.html