标签:
曾几何时,我也敲打过无数次这样的命令:

然而之前的我都只关心过版本号,也就是第一行的内容。今天,我们就来看看第3行输出的内容:JVM的工作模式。
通过百度搜索,只能搜到几篇被重复转载的文章。比如这一篇,这里面基本描述了JVM两种模式的区别:
-Server模式启动时,速度较慢,但是一旦运行起来后,性能将会有很大的提升。
但我认为仅仅知道这些区别还不够。然而,我在百度的搜索结果中很少看见有描述的比较深入的关于JVM两种模式区别的文章。不过我倒是找到了这一篇文章。 这篇文章中提到了如下内容:
当虚拟机运行在-client模式的时候,使用的是一个代号为C1的轻量级编译器, 而-server模式启动的虚拟机采用相对重量级,代号为C2的编译器. C2比C1编译器编译的相对彻底,,服务起来之后,性能更高.
对于这个结果,我觉得还是不够深入。于是FQ通过Google搜索,前几条即为我想要的结果。
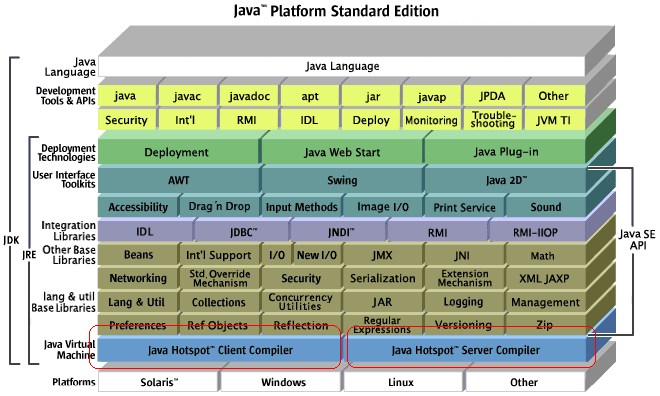
那么,Client和Server模式的JVM到底在哪些方面不同呢?Oracle官方网站的高频问题上这么解释的:
These two systems are different binaries. They are essentially two different compilers (JITs)interfacing to the same runtime system. The client system is optimal for applications which need fast startup times or small footprints, the server system is optimal for applications where the overall performance is most important. In general the client system is better suited for interactive applications such as GUIs. Some of the other differences include the compilation policy,heap defaults, and inlining policy.
大意是说,这两个JVM是使用的不同编译器。Client JVM适合需要快速启动和较小内存空间的应用,它适合交互性的应用,比如GUI;而Server JVM则是看重执行效率的应用的最佳选择。不同之处包括:编译策略、默认堆大小、内嵌策略。
根据《The Java HotSpot Performance Engine Architecture》:
The Client VM compiler does not try to execute many of the more complex optimizations performed by the compiler in the Server VM, but in exchange, it requires less time to analyze and compile a piece of code. This means the Client VM can start up faster and requires a smaller memory footprint.
Note: It seems that the main cause of the difference in performance is the amount of optimizations.
The Server VM contains an advanced adaptive compiler that supports many of the same types of optimizations performed by optimizing C++ compilers, as well as some optimizations that cannot be done by traditional compilers, such as aggressive inlining across virtual method invocations. This is a competitive and performance advantage over static compilers. Adaptive optimization technology is very flexible in its approach, and typically outperforms even advanced static analysis and compilation techniques.
Both solutions deliver extremely reliable, secure, and maintainable environments to meet the demands of today’s enterprise customers.
官方文档是从编译策略和内嵌策略分析了二者的不同,下面的命令则从实际的情况体现了二者在默认堆大小上的差别:
对于Server JVM:
$ java -XX:+PrintFlagsFinal -version 2>&1 | grep -i -E ‘heapsize|permsize|version‘
uintx AdaptivePermSizeWeight = 20 {product}
uintx ErgoHeapSizeLimit = 0 {product}
uintx InitialHeapSize := 66328448 {product}
uintx LargePageHeapSizeThreshold = 134217728 {product}
uintx MaxHeapSize := 1063256064 {product}
uintx MaxPermSize = 67108864 {pd product}
uintx PermSize = 16777216 {pd product}
java version "1.6.0_24"
对于Client JVM:
$ java -client -XX:+PrintFlagsFinal -version 2>&1 | grep -i -E ‘heapsize|permsize|version‘
uintx AdaptivePermSizeWeight = 20 {product}
uintx ErgoHeapSizeLimit = 0 {product}
uintx InitialHeapSize := 16777216 {product}
uintx LargePageHeapSizeThreshold = 134217728 {product}
uintx MaxHeapSize := 268435456 {product}
uintx MaxPermSize = 67108864 {pd product}
uintx PermSize = 12582912 {pd product}
java version "1.6.0_24"
可以很清楚的看到,Server JVM的InitialHeapSize和MaxHeapSize明显比Client JVM大出许多来。
下面是一个例子,它展示了二者执行的效率,该例子来自Onkar Joshi’s blog:
public class LoopTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
spendTime();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(end-start);
}
private static void spendTime() {
for (int i =500000000;i>0;i--) {
}
}
}
注意:这段代码只编译一次,只是运行这段代码的JVM不同而已。不要使用Eclipse中的Run As,因为它会将代码重新编译。这里,我们使用java命令来执行这段代码:
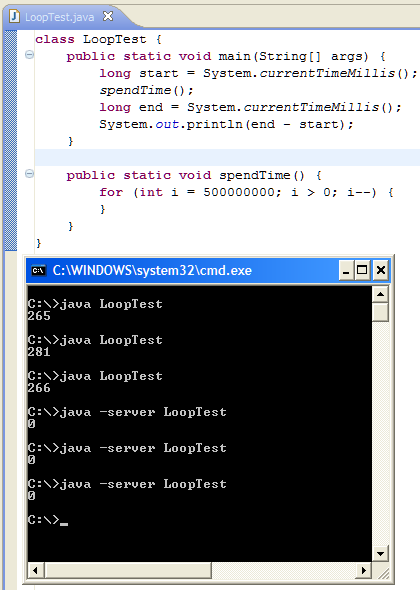
看到区别了吧?
------------------------分 割 线 ---------------------------------
上面的运行结果中还提到了如何切换JVM的工作模式,我们就来看看为什么第一个截图里面输出的是:
Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM
这里需要注意的是,Oracle网站这样说:
Client and server systems are both downloaded with the 32-bit Solaris and Linux downloads. For 32-bit Windows, if you download the JRE, you get only the client, you‘ll need to download the SDK to get both systems.
因此,如果想要在windows平台下切换JVM到Server模式,需要下载JDK而非JRE。打开JDK安装目录(即%JAVA_HOME%):我们可以看到JDK\jre\bin下有一个server和client文件夹,这里面都有一个jvm.dll,但是大小不同,这就是启动JVM必须的文件了:

打开 %JAVA_HOME%\jre\lib\i386\jvm.cfg文件(注意是JDK文件夹下的jre,而非和JDK同级的jre6/7/8),会注意到以下内容(灰色选中部分):

再看看下方的配置,第一行就配置了使用client方式,因此首选使用client模式的JVM,这就是为什么一开始的java -version命令会输出Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM的原因了。现在将第33、34行配置交换一下,再在命令行中输入java -version,则会得到以下结果:

这就将JVM的工作模式切换到Server了,这个修改是全局的,以后使用到的这个JVM都是工作在Server模式的。
当然,如果你不想全局改动,也可以按照下面在java命令后加上-server或者-client来明确指定本次java命令需要JVM使用何种模式来工作,例如:

这个就是语句级的修改了。
注意,不管是全局修改还是语句级的修改,实际上会导致下次执行Java程序时会使用对应目录下的jvm.dll。如何证明?这里我将%JAVA_HOME%\jre\bin下面的server文件夹移动到其他位置,再次运行java -version命令,则会出现下面的错误:

参考页面:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/hotspotfaq-138619.html#compiler_types
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/198577/real-differences-between-java-server-and-java-client
http://www.javacodegeeks.com/2011/07/jvm-options-client-vs-server.html
标签:
原文地址:http://my.oschina.net/itblog/blog/507822