标签:
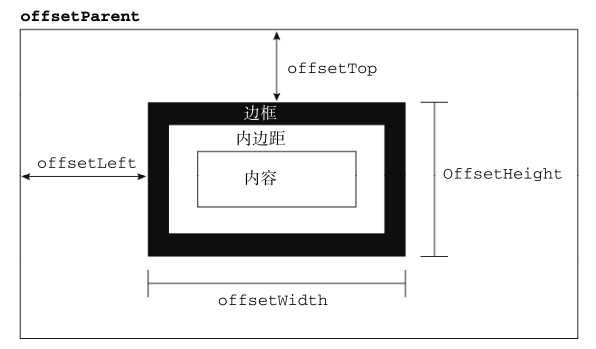
偏移量包括元素在屏幕上占用的所有可见的空间。元素的可见大小由其高度、宽度决定,包括所有内边距、滚动条和边框大小(注意,不包括外边距)。
[注意1]所有偏移量属性都是只读的,而且每次访问他们都需要重新计算
[注意2]若给元素设置了display:none,则它的四个offset属性都为0
【offsetParent】元素的定位父级,(标准浏览器包括IE8下)
【1】若元素自身是fixed定位,则offsetParent是null
【2】若元素有进行过CSS定位(relative\absolute\fixed)的父级,则offsetParent就是在DOM结构中离其最近的进行过CSS定位的父级
【3】若元素没有进行过CSS定位的父级,则offsetParent是<body>元素
【4】<body>的offsetParent是null
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; } ul{ margin: 0; padding: 0; list-style: none; } .box{ width: 500px; height: 500px; background-color: gray; } .list{ height: 300px; width: 300px; background-color: #ccc; border: 10px solid black; } .in{ height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: red; margin: 10px; padding: 10px; border: 1px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="box" id="box"> <ul class="list" id="list"> <li class="in" id="test">test</li> </ul> </div> <body> <script> var oBox = document.getElementById(‘box‘); var oList = document.getElementById(‘list‘); var oTest = document.getElementById(‘test‘); //<body>的定位父级是null console.log(document.body.nodeName); //没有进行CSS定位的父级,所以定位父级是<body> console.log(oList.offsetParent.nodeName); //没有进行CSS定位的父级,所以定位父级是<body> console.log(oTest.offsetParent.nodeName); document.onclick = function(){ oList.style.position = "relative"; //自身有定位,但父级中没有进行CSS定位的,所以定位父级是<body> console.log(oList.offsetParent.nodeName); //oList是oText的进行过CSS定位的父级,所以其定位父级是oList console.log(oTest.offsetParent.nodeName); } </script> </body> </html>
【IE7-浏览器bug】
【1】自身有定位元素(relative\absolute)
【1.1】若无进行过定位的父级元素,则offsetParent是<html>
【1.2】若有进行过定位的父级元素,则offsetParent是进行过定位的父级元素
【2】自身无定位元素(触发haslayout的父元素也具有进行过定位的父级的特征)[与标准相同]
【1.1】若无进行过定位的父级元素,则offsetParent是<body>
【1.2】若有进行过定位的父级元素,则offsetParent是进行过定位的父级元素
【offsetHeight】元素在垂直方向上占用的空间大小,以像素计。包括元素的高度、(可见的)水平滚动条的高度、上边框高度和下边框高度。
【offsetWidth】元素在水平方向上占用的空间大小,以像素计。包括元素的宽度、(可见的)垂直滚动条的宽度、左边框宽度和右边框宽度。
[注意]即使元素加上水平或垂直滚动条,offsetWidth跟offsetHeight的值是不会更改的,因为浏览器渲染时把滚动条的宽度(或高度)算在了元素本身的宽度(或高度)中了
【offsetLeft】元素的左外边框至包含元素的左内边框之间的像素距离
【offsetTop】元素的上外边框至包含元素的上内边框之间的像素距离
其中offsetLeft和offsetTop属性与包含元素有关,包含元素的引用保存在offsetParent属性中。offsetParent属性不一定与parentNode的值相等。例如<td>元素的offsetParent是作为其祖先元素的<table>元素,因为<table>是在DOM层次中距<td>最近的一个具有大小的元素
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; } ul{ margin: 0; padding: 0; list-style: none; } .list{ height: 500px; width: 500px; background-color: #ccc; border: 10px solid black; } .in{ height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: red; margin: 100px; padding: 100px; border: 1px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <ul class="list" id="list"> <li class="in" id="test">test</li> </ul> <script> var oList = document.getElementById(‘list‘); var oTest = document.getElementById(‘test‘); //302px 302px console.log(oTest.offsetWidth,oTest.offsetHeight); //110px 110px,而IE7-浏览器输出100px console.log(oTest.offsetTop,oTest.offsetLeft); document.onclick = function(){ oTest.style.overflow = "scroll"; //加入滚动条后,值依然不发生改变 console.log(oTest.offsetWidth,oTest.offsetHeight); console.log(oTest.offsetTop,oTest.offsetLeft); } </script> </body> </html>
【firefox的bug】
当自身有定位元素,有定位父级,且定位父级设置overflow:hidden时,火狐的offsetLeft会减去定位父级相应方向的边框的宽度。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; } ul{ margin: 0; padding: 0; list-style: none; } .list{ height: 500px; width: 500px; background-color: #ccc; border: 10px solid black; border-left-width: 5px; } .in{ height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: red; margin: 100px; padding: 100px; border: 1px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <ul class="list" id="list"> <li class="in" id="test">test</li> </ul> <script> var oList = document.getElementById(‘list‘); var oTest = document.getElementById(‘test‘); document.onclick = function(){ oList.style.position = "relative"; oList.style.overflow = "hidden"; oTest.style.position = "absolute"; //其他浏览器都输出100 100 而firefox浏览器输出 90 95 console.log(oTest.offsetTop,oTest.offsetLeft); } </script> </body> </html>
要知道某个元素在页面上的偏移量,将这个元素的offsetLeft和offsetTop与其offsetParent的相同属性相加,并加上offsetParent的相应方向的边框,如此循环直到根元素,就可以得到元素到页面的偏移量。
[注意]在默认情况下,IE8-浏览器下<html>和<body>的边框宽度都是medium,而其他浏览器是0px。
兼容写法如下:
html,body{
border: 0;
}
function getElementLeft(element){ var actualLeft = element.offsetLeft; var current = element.offsetParent; while(current != null){ actualLeft += current.offsetLeft + parseFloat(getCSS(current,‘border-left-width‘)); current = current.offsetParent; } return actualLeft + ‘px‘; } function getElementTop(element){ var actualTop = element.offsetTop; var current = element.offsetParent; while(current != null){ actualTop += current.offsetTop + parseFloat(getCSS(current,‘border-top-width‘)); current = current.offsetParent; } return actualTop + ‘px‘; }
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> html,body{ border: 0; } body{ margin: 0; } ul{ margin: 0; padding: 0; list-style: none; } .list{ height: 500px; width: 500px; background-color: #ccc; border: 10px solid black; } .in{ height: 100px; width: 100px; background-color: red; margin: 100px; padding: 100px; border: 1px solid black; } </style> </head> <body> <ul class="list" id="list"> <li class="in" id="test">test</li> </ul> <script> var oList = document.getElementById(‘list‘); var oTest = document.getElementById(‘test‘); function getCSS(obj,attr){ if(window.getComputedStyle){ return getComputedStyle(obj)[attr]; } return obj.currentStyle[attr]; } function getElementLeft(element){ var actualLeft = element.offsetLeft; var current = element.offsetParent; while(current != null){ actualLeft += current.offsetLeft + parseFloat(getCSS(current,‘border-left-width‘)); current = current.offsetParent; } return actualLeft + ‘px‘; } function getElementTop(element){ var actualTop = element.offsetTop; var current = element.offsetParent; while(current != null){ actualTop += current.offsetTop + parseFloat(getCSS(current,‘border-top-width‘)); current = current.offsetParent; } return actualTop + ‘px‘; } oList.style.position = "absolute"; console.log(getElementTop(oTest));//所有浏览器都输出110px console.log(getElementLeft(oTest));//所有浏览器都输出110px </script> </body> </html>
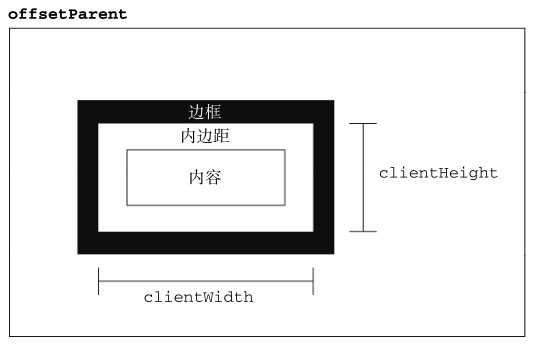
元素的客户区大小(client dimension)指的是元素内容及其内边距所占据的空间大小。
[注意1]若设置为display:none,则值为0
[注意2]客户区大小是只读的,每次访问都要重新计算
【属性】
有关客户区大小的属性有两个:clientWidth和clientHeight。其中,clientWidth属性是元素内容区宽度+左右内边距宽度。clientHeight属性是元素内容区高度+上下内边距高度。
【常用应用】确定浏览器视口大小
[注意]IE6浏览器在标准模式下,视口大小与<html>大小一致;在怪异模式下,视口大小与<body>大小一致。所以兼容写法为:
function getViewport(){ if(document.compatMode == "BackCompat"){ return{ width: document.body.clientWidth, height: document.body.clientHeight }; }else{ return{ width: document.documentElement.clientWidth, height: document.documentElement.clientHeight }; } }
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <body> <script> function getViewport(){ if(document.compatMode == "BackCompat"){ return{ width: document.body.clientWidth, height: document.body.clientHeight }; }else{ return{ width: document.documentElement.clientWidth, height: document.documentElement.clientHeight }; } } //IE7-浏览器返回1895,因为默认有滚动条(可得出滚动条宽度为21px),IE8浏览器返回1916,其他浏览器返回1920 console.log(getViewport().width) </script> </body> </html>
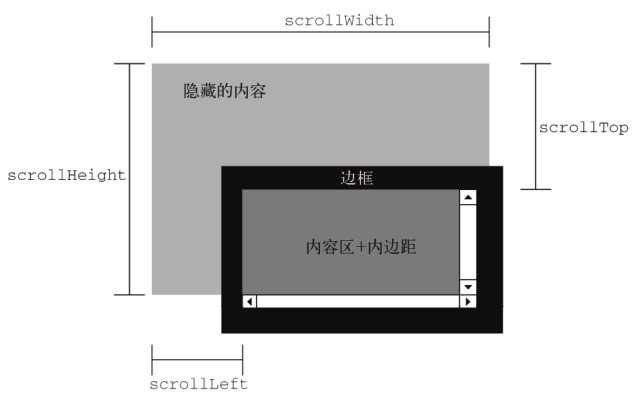
滚动大小是指包含滚动内容的元素的大小。有些元素(如html元素)即使没有执行任何代码也能自动添加滚动条;但另外一些元素,则需要通过CSS的overflow属性进行设置才能滚动。
【scrollHeight和scrollWidth】
【scrollHeight】在没有滚动条的情况下,元素内容的总高度
【scrollWidth】在没有滚动条的情况下,元素内容的总宽度
[注意]scrollWidth和scrollHeight主要用于确定元素内容的实际大小。通常认为<html>元素就是在Web浏览器的视口中滚动的元素。因此,带有垂直滚动条的页面总高度就是document.documentElement.scrollHeight
【scroll和client的区别】
【1】在有滚动条的情况下,scorllHeight表示元素的实际总高度,而clientHeight表示元素的视觉总高度(宽度也类似)
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> .box{ height: 100px; width: 200px; overflow: scroll; } </style> <body> <div class="box" id="box"> 我是测试内容<br> 我是测试内容<br> 我是测试内容<br> 我是测试内容<br> 我是测试内容<br> 我是测试内容<br> 我是测试内容<br> 我是测试内容<br> 我是测试内容<br> </div> <script> var oBox = document.getElementById(‘box‘); //100 162 console.log(oBox.clientHeight,oBox.scrollHeight); //183 183 console.log(oBox.clientWidth,oBox.scrollWidth); </script> </body> </html>
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> html{ height: 2000px; } </style> <body> <script> //500 2000 console.log(document.documentElement.clientHeight,document.documentElement.scrollHeight); //1899 1899(IE9+及其他浏览器,说明滚动条的宽度为1920-1899=21px) //1895(IE8-浏览器) console.log(document.documentElement.clientWidth,document.documentElement.scrollWidth); </script> </body> </html>
【2】在无滚动条的情况下,各浏览器的处理不一致
【2.1】页面有高度时
[a]firefox和IE8+浏览器中<html>的scrollHeight和clientHeight=可视区高度,<body>的scrollHeight和clientHeight=内容实际高度
[b]chrome、opera、safari中<html>scrollHeight=内容实际高度,clientHeight=可视区高度;而<body>中scrollHeight=可视区高度,clientHeight=内容实际高度
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; line-height: 20px; } </style> <body> <br> <script> //(firefox/IE8+)500 500 //(chrome/IE7-/safari/opera)500 20 console.log(document.documentElement.clientHeight,document.documentElement.scrollHeight); //(firefox/IE8+/IE7-)20 20 //(chrome/safari/opera)20 500 console.log(document.body.clientHeight,document.body.scrollHeight); </script> </body> </html>
【2.2】页面无高度时
[a]firefox和IE浏览器中<html>clientHeight=scrollHeight=当前可视区高度,<body>的clientHeight=scrollHeight=0
[b]chrome、opera、safari中,<html>clientHeight=当前可视区高度,scrollHeight=0;<body>clientHeight=0,scrollHeight=当前可视区高度
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; } </style> <body> <script> //(firefox/IE/)500 500 //(chrome/safari/opera)500 0 console.log(document.documentElement.clientHeight,document.documentElement.scrollHeight); //(firefox/IE8)0 0 //(chrome/safari/opera)0 500 console.log(document.body.clientHeight,document.body.scrollHeight) </script> </body> </html>
【2.3】元素无滚动条时
[a]IE7-浏览器的可视高为设置的高度,而滚动高为子元素的实际高度
[b]其他浏览器的可视高等于滚动高都等于设置的高度
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> .box{ height: 100px; } </style> <body> <div class="box" id="box"> 12440<br> 12440<br> 12440<br> </div> <script> var oBox = document.getElementById(‘box‘); //IE7-浏览器的可视高为设置的高度100,而滚动高为子元素的实际高度57 //其他浏览器的可视高等于滚动高都等于100 console.log(oBox.clientHeight,oBox.scrollHeight); </script> </body> </html>
因此要取得文档实际高度时,要取得<html>元素的scrollHeight和clientHeight的最大值
var docHeight = Math.max(document.documentElement.scrollHeight,document.documentElement.clientHeight); var docWidth = Matn.max(document.documentElement.scrollWidth,document.documentElement.clientWidth);
【scrollLeft和scrollTop】
通过scrollLeft和scrollTop属性既可以确定元素当前滚动的状态,也可以设置元素的滚动位置。
【scrollLeft】被隐藏在内容区域左侧的像素数。元素未滚动时,scrollTop的值为0,如果元素被水平滚动了,scrollLeft的值大于0,且表示元素左侧不可见内容的像素宽度。
【scrollTop】被隐藏在内容区域上方的像素数。元素未滚动时,scrollTop的值为0,如果元素被垂直滚动了,scrollTop的值大于0,且表示元素上方不可见内容的像素宽度。
【页面滚动条的兼容】
对于firefox及IE浏览器,使用document.documentElement.scrollTop可获得页面的滚动高度
对于chrome、safari、opera基于webkit的浏览器,使用document.body.scrollTop可获得页面的滚动高度
所以兼容写法是
var docScrollTop = document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; line-height: 2000px; } </style> <body> <br> <script> document.onclick = function(){ document.title = (document.documentElement.scrollTop || document.body.scrollTop); } </script> </body> </html>
getBoundingClineRect()方法返回一个矩形对象,各个浏览器返回的对象包含的属性不相同
(firfox):top/left/right/bottom/width/height/x/y[x=left,y=top]
(chrome\safari\opera\IE9+):top/left/right/bottom/width/height
(IE8-):top/left/right/bottom
[注意1]该方法的所有属性值都没有单位,且给定的是元素在页面中相对于视口的位置
[注意2]IE7-浏览器认为视口的左上角坐标是(2,2),其他浏览器则将(0,0)作为起点坐标。
兼容写法:(利用IE7-浏览器中特性节点的specified属性)
function getBoundingClientRect(obj){ var temp = obj.getBoundingClientRect(); //IE7-浏览器 if(Boolean(obj.attributes[0]) && !obj.attributes[0].specified){ return{ left: temp.left -2, top: temp.top -2, right: temp.right -2, bottom: temp.bottom -2 } }else{ return temp; } }
<!DOCTYPE HTML> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Document</title> <style> body{ margin: 0; line-height: 50px; } .box{ width: 100px; height: 100px; padding: 10px; border: 1px solid black; background-color: lightgreen; } </style> <body> <div> 测试内容<br> 测试内容<br> 测试内容<br> 测试内容<br> 测试内容<br> </div> <div class="box" id="box"></div> <div> 测试内容<br> 测试内容<br> 测试内容<br> 测试内容<br> 测试内容<br> </div> <script> var oBox = document.getElementsByTagName(‘div‘)[1]; function getBoundingClientRect(obj){ var temp = obj.getBoundingClientRect(); //IE7-浏览器 if(Boolean(obj.attributes[0]) && !obj.attributes[0].specified){ return{ left: temp.left -2, top: temp.top -2, right: temp.right -2, bottom: temp.bottom -2 } }else{ return temp; } } document.onclick = function(){ console.log(getBoundingClientRect(oBox).top,document.body.scrollTop); } </script> </body> </html>
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaohuochai/p/4847118.html