标签:
一句话:illumina的建库方法,建库时间段,质量还好。。。
the adapters are different in the PCR-free kit compared to the standard TruSeq kit.
The standard TruSeq kit uses Y-shaped adapters that require PCR to create a library that will anneal to the flow cell--or something like that. Otherwise, the buffers should be identical, though it is possible that concentrations will differ. For your purposes, they are not interchangeable because the adapters will not work between kits. At least, I know they will not work from TruSeq without running PCR.
I have learned this the hard way.
###########################################################
I myself have used the old kit & adapters PCR Free (without one cycle of PCR at the end) with no problems with clustering.
Looking at the kits, I would say the only difference between them is that one contains additional PCR reagents and one does not.
###########################################################
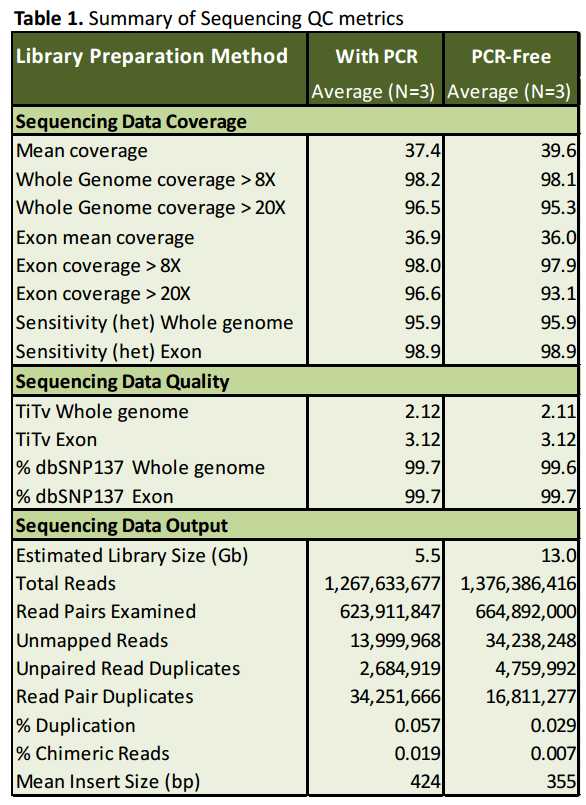
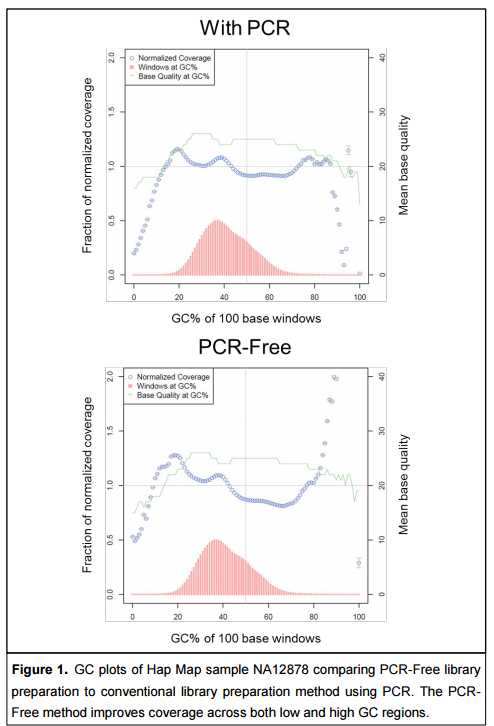
Standard library preparation methods include a PCR enrichment step prior to cluster generation. Biases inherent in PCR amplification result in uneven read coverage and increase the numbers of duplicate fragments present in the library. For the HiSeq instruments in particular, coverage of sequence reads is known to be notably lower in GC rich regions, which can affect mapping quality and variant calling
To compare library preparation methods that employ PCR directly to methods that do not, we constructed libraries for NGS with DNA from a well characterized Hap Map Trio (NA12878, NA12891 & NA12892) using a conventional DNA library preparation kit (hereafter called “With PCR”) and the TruSeq DNA PCR-Free Sample Preparation Kit available from Illumina (hereafter called “PCR-Free”).
PCR-Free Library Preparation & Sequencing Libraries were generated from 1 ug of genomic DNA using the Illumina TruSeq DNA PCR-Free Sample Preparation Kit. Indexed libraries were size selected to ~350 bp using bead-based capture. Normalized libraries were clustered on-board, and 100 bp paired-end sequencing was performed on the HiSeq2500 across 4 lanes of 2 flow cells using rapid run mode
With PCR Library Preparation & Sequencing Libraries were generated from 1 ug of genomic DNA using the Kapa Biosystems library prep kit with Illuminacompatible indexed adapters from BioO Scientific. Indexed libraries were size selected to ~500 bp using a Pippin Prep instrument, followed by 8 cycles of PCR. Normalized libraries were clustered on the cBOT, and 100 bp paired-end sequencing was performed on the HiSeq2000 across 4 lanes of flow cell run in high output mode.
We used familial relationships in the Hap Map trio to calculate the Mendelian error rate (Table 2). Fewer errors were detected in the PCR-Free data compared to With PCR data. However, the improvement was marginal for variants passing filter.
The variant calls for the PCR-Free and With PCR data were highly concordant (Table 3). 1303 variant sites were different, whereas the calls missed in either dataset was comparable. For sample NA12878 we also compared our data to the highly confident integrated call set from the Genome in a Bottle group (GIAB). The data were highly concordant for both WGS datasets.
结论:
Omission of PCR shortens the work flow for WGS library preparation and improves coverage in regions of low and high GC content. Sequencing data quality is comparable to conventional library preparation methods that employ PCR.
freemao
FAFU
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/freemao/p/4851272.html