标签:
Problem Description
In Geometry, the problem of track is very interesting. Because in some cases, the track of point may be beautiful curve. For example, in polar Coordinate system,ρ=cos3θ is like rose, ρ=1−sinθ is a Cardioid, and so on. Today, there is a simple problem about it which you need to solve.
Give you a triangle ΔABC and
AB = AC. M is the midpoint of BC. Point P is in ΔABC and makes min{∠MPB+∠APC,∠MPC+∠APB} maximum. The track of P is Γ. Would
you mind calculating the length of Γ?
Given the coordinate of A, B, C, please output the length of Γ.
Input
There are T (1≤T≤104) test cases. For each case, one line includes six integers the coordinate of A, B, C in order. It is guaranteed that AB = AC and three points are not collinear. All coordinates do not exceed 104 by absolute value.
Output
For each case, first please output "Case #k: ", k is the number of test case. See sample output for more detail. Then, please output the length of Γ with exactly 4 digits after the decimal point.
Sample Input
1
0 1 -1 0 1 0
Sample Output
Case #1: 3.2214
题目稍微转换一下就变成求∠MPB+∠APC=∠MPC+∠APB=180的点p的轨迹了。
这最后结论是一道平面几何题,高中数竞虽然搞过平面几何,不过基本全部忘光了,定理也只记得一个梅涅劳斯定理了。。。虽然当时就很弱。。
高中数竞时小烈平几就很强@hqwhqwhq,果然赛后题解交代了轨迹寻找的过程。。
http://blog.csdn.net/u014610830/article/details/48753415
虽然找的过程没怎么看懂,不过证明过程基本看懂了。
如果能猜出轨迹的话题目也就解决了,剩下就是怎么证明这个轨迹满足条件了。
首先三角形的高AM是满足条件的,基本是没问题的。
其次B和C点在极限情况下发现也是满足条件的,由于对称性,基本上剩余轨迹就是过B和C的一种图形。。。
运气好的话猜到它是个圆就能解决。。。
盗一张图:
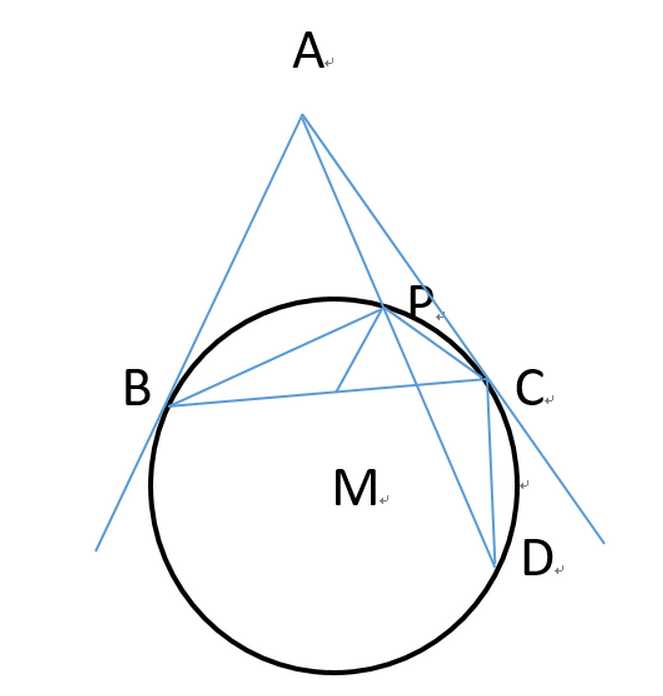
结论是剩余的图是AB过B的垂线与AC过C的垂线交于点M,以M为圆心,BM为半径的圆弧。
接下来证明:
对于圆弧上某一点P,AP延长交圆于点D,
目测的话,∠BPM = ∠CPD。结论就是这个,接下来就是证明这个。
由于B、P、C、D四点共圆,根据托勒密定理:
CP*BD+BP*CD = BC*DP
由根据割线定理:
AB*AB = AP*AD
于是可得,三角形APB相似于三角形ABD
于是BP/BD = AB/AD
同理得:CP/CD = AC/AD
又AB=AC
于是BP/BD = CP/CD
即BP*CD = CP*BD
联合上面的托勒密得2BP*CD = 2CP*BD = BC*DP = 2BM*DP
提取BP*CD = BM*DP
即BP/BM = DP/CD
又∠MBP = ∠CDP(同弧所对圆周角相等)
于是三角形MBP相似于三角形CDP
于是结论得证。
代码:
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> #include <cmath> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <set> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <string> #define LL long long using namespace std; const double PI = acos(-1); inline double dis(double xA, double yA, double xB, double yB) { double ans = (xA-xB)*(xA-xB) + (yA-yB)*(yA-yB); return sqrt(ans); } void work() { double xA, yA, xB, yB, xC, yC; double a, h, d, ans, v, r; scanf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf", &xA, &yA, &xB, &yB, &xC, &yC); d = dis(xB, yB, xC, yC)/2; h = dis(xA, yA, xB, yB); a = asin(d/h); v = PI-2*a; r = h*tan(a); ans = sqrt(h*h-d*d)+v*r; printf("%.4lf\n", ans); } int main() { //freopen("test.in", "r", stdin); int T; scanf("%d", &T); for (int times = 1; times <= T; ++times) { printf("Case #%d: ", times); work(); } return 0; }
ACM学习历程—HDU5476 Explore Track of Point(平面几何)(2015上海网赛09题)
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/andyqsmart/p/4857623.html