标签:
(referrence: GeeksforGeeks)
Like Merge Sort, Quick Sort is also a divide & conquer problem.
It picks an element as pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot.
1. Always pick first element as pivot.
2. Always pick last element as pivot (implemented below)
3. Pick a random element as pivot.
4. Pick median as pivot.
Target: Given an array and an element x of array as pivot, put x at its correct position in sorted array and put all smaller elements (smaller than x) before x, and put all greater elements (greater than x) after x.
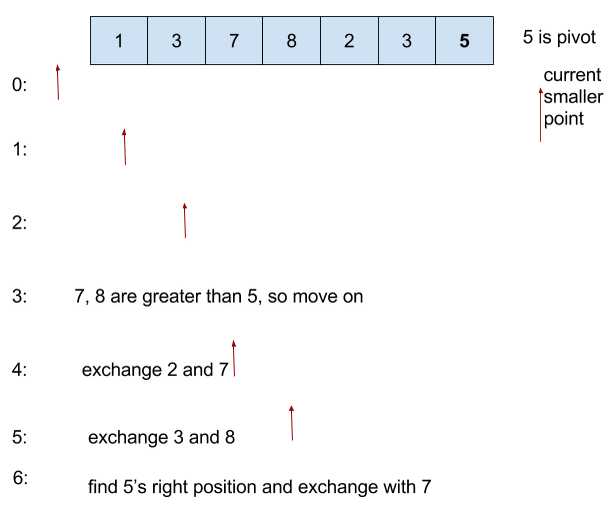
Follow the method given in CLRS book, we pick last element as pivot.
We start from the leftmost element and keep track of index of smaller (or equal to) elements as i. While traversing, if we find a smaller element, we swap current element with arr[i]. Otherwise we ignore current element.
Example
1 public class Solution { 2 private void swap(int[] nums, int index1, int index2) { 3 int tmp = nums[index1]; 4 nums[index1] = nums[index2]; 5 nums[index2] = tmp; 6 } 7 8 // Pick last element as pivot 9 // Place all smaller elements before pivot 10 // Place all bigger elements after pivot 11 private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) { 12 int pivot = nums[end]; 13 int currentSmaller = start - 1; 14 for (int i = start; i < end; i++) { 15 // If current element <= pivot, put it to right position 16 if (nums[i] <= pivot) { 17 currentSmaller++; 18 swap(nums, i, currentSmaller); 19 } 20 } 21 // Put pivot to right position 22 currentSmaller++; 23 swap(nums, end, currentSmaller); 24 return currentSmaller; 25 } 26 27 public void quickSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) { 28 // Stop criterion: start = end 29 if (start < end) { 30 int p = partition(nums, start, end); 31 quickSort(nums, start, p - 1); 32 quickSort(nums, p + 1, end); 33 } 34 } 35 }
For partition step, time complexity is O(n).
Time taken by Quick Sort in general can be written as following:
T(n) = T(k) + T(n - k - 1) + O(n)
1. Worst Case:
The worst case occurs when the partition process always picks greatest or smallest element as pivot. If we consider above partition strategy where last element is always picked as pivot, the worst case would occur when the array is already sorted in increasing or decreasing order.
T(n) = T(n - 1) + O(n) -> T(n) = O(n2)
2. Best Case:
The best case occurs when the partition process always picks the middle element as pivot.
T(n) = 2T(n/2) + O(n) -> T(n) = O(n log n)
3. Average Case:
We can get an idea of average case by considering the case when partition puts O(n/9) elements in one set and O(9n/10) elements in other set.
T(n) = T(n/9) + T(9n/10) + O(n) -> T(n) = O(n log n)
QuickSort is faster in practice, because its inner loop can be efficiently implemented on most architectures, and in most real-world data. QuickSort can be implemented in different ways by changing the choice of pivot, so that the worst case rarely occurs for a given type of data. However, merge sort is generally considered better when data is huge and stored in external storage.
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ireneyanglan/p/4865428.html