标签:
为了在手机画面上显示Activity的window,android内部会做一下内容:
1) 创建一个Window在Window里构建View Hierachy。
2) 与WindowManager建立联系。
3) 为了与SystemServer通信,打开Binder设备。
4) 把Window注册上去,确定View Hierachy大小,位置。
5) 确定大小,位置后在Surface中开始Draw。
6) 把Surface输出在LCD中。
就这样我们就能从手机屏幕中看到了。
Activity的启动简单来说就两种:
首先我们看一下Manifast.xml文件(为了体现两种启动方式而自定义的Manifast)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" package="android.com.activitytest" android:versionCode="1" android:versionName="1.0"> <application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<!-- MainActivity是点击应用程序图标来启动Activity--> <activity android:name=".MainActivity" android:label="@string/app_name"> <intent-filter> <action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" /> <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> </intent-filter> </activity> <!-- SubActivity是MainActivity调用startActivity函数来启动Activity-->
<activity android:name=".SubActivity" android:label="@string/sub_activity"> </activity>
</application> </manifest>
1. MainActivity的启动
首先我们先分析MainActivity的启动
分析之前我们先看一下Manifast中的 <category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" /> ,表示要用LAUNCHER启动。
当我们点击相应的应用程序图标时,Launcher就会启动对应的应用程。
下面是Launcher的源代码
public final class Launcher extends Activity implements View.OnClickListener, OnLongClickListener, LauncherModel.Callbacks, AllAppsView.Watcher { ...... /** * Launches the intent referred by the clicked shortcut. * * @param v The view representing the clicked shortcut. */ public void onClick(View v) { Object tag = v.getTag(); if (tag instanceof ShortcutInfo) { // Open shortcut final Intent intent = ((ShortcutInfo) tag).intent; int[] pos = new int[2]; v.getLocationOnScreen(pos); intent.setSourceBounds(new Rect(pos[0], pos[1], pos[0] + v.getWidth(), pos[1] + v.getHeight())); startActivitySafely(intent, tag); } else if (tag instanceof FolderInfo) { ...... } else if (v == mHandleView) { ...... } } void startActivitySafely(Intent intent, Object tag) { intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK); try { startActivity(intent); } catch (ActivityNotFoundException e) { ...... } catch (SecurityException e) { ...... } } ...... }
从代码中可知,当我们点击某个应用程序图标时会触发Launcher的public void onClick(View v)点击事件。
然后调用ShortcutInfo中的startActivitySafely(intent, tag);- > startActivity(intent);。
startActivity函数是启动的Activity的startActivity函数。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java
public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper implements LayoutInflater.Factory, Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback, OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks { ...... @Override public void startActivity(Intent intent) { startActivityForResult(intent, -1); } ...... }
还会调用startActivityForResult来进一步处理,第二个参数传入-1表示不需要这个Actvity结束后的返回结果。
public class Activity extends ContextThemeWrapper implements LayoutInflater.Factory, Window.Callback, KeyEvent.Callback, OnCreateContextMenuListener, ComponentCallbacks { ...... public void startActivityForResult(Intent intent, int requestCode) { if (mParent == null) { Instrumentation.ActivityResult ar = mInstrumentation.execStartActivity( this, mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), mToken, this, intent, requestCode); ...... } else { ...... } ...... }
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Instrumentation.java
public class Instrumentation { ...... public ActivityResult execStartActivity( Context who, IBinder contextThread, IBinder token, Activity target, Intent intent, int requestCode) { IApplicationThread whoThread = (IApplicationThread) contextThread; if (mActivityMonitors != null) { ...... } try { int result = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault() .startActivity(whoThread, intent, intent.resolveTypeIfNeeded(who.getContentResolver()), null, 0, token, target != null ? target.mEmbeddedID : null, requestCode, false, false); ...... } catch (RemoteException e) { } return null; } ...... }
重要角色出来了ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()返回ActivityManagerService。
ActivityManagerService是在另外一个进程中所以需要调用它的代理服务。即ActivityManagerProxy。
frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java(内部类)
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager { ...... public int startActivity(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions, int grantedMode, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded, boolean debug) throws RemoteException { Parcel data = Parcel.obtain(); Parcel reply = Parcel.obtain(); data.writeInterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor); data.writeStrongBinder(caller != null ? caller.asBinder() : null); intent.writeToParcel(data, 0); data.writeString(resolvedType); data.writeTypedArray(grantedUriPermissions, 0); data.writeInt(grantedMode); data.writeStrongBinder(resultTo); data.writeString(resultWho); data.writeInt(requestCode); data.writeInt(onlyIfNeeded ? 1 : 0); data.writeInt(debug ? 1 : 0); mRemote.transact(START_ACTIVITY_TRANSACTION, data, reply, 0); reply.readException(); int result = reply.readInt(); reply.recycle(); data.recycle(); return result; } ...... }
最终还会调用ActivityManagerService(frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java)的startActivity函数
而在此函数中没有其他动作,仅仅做了一个转发,调用了ActivityStack.startActivityMayWait函数
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
public class ActivityStack { ...... final int startActivityMayWait(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions, int grantedMode, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, boolean onlyIfNeeded, boolean debug, WaitResult outResult, Configuration config) { ...... boolean componentSpecified = intent.getComponent() != null;
intent = new Intent(intent); // 解析AndroidManifest.xml,得知activity的报名及activity的类名。
ActivityInfo aInfo; try { ResolveInfo rInfo = AppGlobals.getPackageManager().resolveIntent( intent, resolvedType, PackageManager.MATCH_DEFAULT_ONLY | ActivityManagerService.STOCK_PM_FLAGS); aInfo = rInfo != null ? rInfo.activityInfo : null; } catch (RemoteException e) { ...... } if (aInfo != null) { // 指定具体的组件类,通知应用启动对应的组件。
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName( aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name)); ...... } synchronized (mService) { int callingPid; int callingUid; if (caller == null) { ...... } else { callingPid = callingUid = -1; } mConfigWillChange = config != null && mService.mConfiguration.diff(config) != 0; ...... if (mMainStack && aInfo != null && (aInfo.applicationInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_CANT_SAVE_STATE) != 0) { ...... } int res = startActivityLocked(caller, intent, resolvedType, grantedUriPermissions, grantedMode, aInfo, resultTo, resultWho, requestCode, callingPid, callingUid, onlyIfNeeded, componentSpecified); if (mConfigWillChange && mMainStack) { ...... } ...... if (outResult != null) { ...... } return res; } } ...... }
最后调用startActivityLocked
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
public class ActivityStack { ...... final int startActivityLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent intent, String resolvedType, Uri[] grantedUriPermissions, int grantedMode, ActivityInfo aInfo, IBinder resultTo, String resultWho, int requestCode, int callingPid, int callingUid, boolean onlyIfNeeded, boolean componentSpecified) { int err = START_SUCCESS; ProcessRecord callerApp = null; if (caller != null) { callerApp = mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller); if (callerApp != null) { callingPid = callerApp.pid; callingUid = callerApp.info.uid; } else { ...... } } ...... ActivityRecord sourceRecord = null; ActivityRecord resultRecord = null; if (resultTo != null) { int index = indexOfTokenLocked(resultTo); ...... if (index >= 0) { sourceRecord = (ActivityRecord)mHistory.get(index); if (requestCode >= 0 && !sourceRecord.finishing) { ...... } } } int launchFlags = intent.getFlags(); if ((launchFlags&Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_FORWARD_RESULT) != 0 && sourceRecord != null) { ...... } ...... ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord(mService, this, callerApp, callingUid, intent, resolvedType, aInfo, mService.mConfiguration, resultRecord, resultWho, requestCode, componentSpecified); ...... return startActivityUncheckedLocked(r, sourceRecord, grantedUriPermissions, grantedMode, onlyIfNeeded, true); } ...... }
从caller(ApplicationThread)中获取进程(launcher进程)信息保存在ProcessRecord callerApp=mService.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
创建即将要启动的Activity的相关信息ActivityRecord r = new ActivityRecord函数。
而在startActivityUncheckedLocked函数中把Task保存在r.task域中,同时,添加到mService中去,这里的mService就是ActivityManagerService了。调用startActivityLocked(r, newTask, doResume)
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
public class ActivityStack { ...... private final void startActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean newTask, boolean doResume) { final int NH = mHistory.size(); int addPos = -1; if (!newTask) { ...... } // Place a new activity at top of stack, so it is next to interact // with the user. if (addPos < 0) { addPos = NH; } // If we are not placing the new activity frontmost, we do not want // to deliver the onUserLeaving callback to the actual frontmost // activity if (addPos < NH) { ...... } // Slot the activity into the history stack and proceed mHistory.add(addPos, r); r.inHistory = true; r.frontOfTask = newTask; r.task.numActivities++;
//NH表示当前系统中历史任务的个数 if (NH > 0) { // We want to show the starting preview window if we are // switching to a new task, or the next activity‘s process is // not currently running. ...... } else { // If this is the first activity, don‘t do any fancy animations, // because there is nothing for it to animate on top of. ...... } ...... if (doResume) { resumeTopActivityLocked(null); } } ...... }
resumeTopActivityLocked(null); 函数获得堆栈顶端的Activity,即MainActivity。
MainActivity创建了ActivityRecord后,它的app域一直保持为null。有了这些信息后,上面这段代码就容易理解了,它最终调用startSpecificActivityLocked进行下一步操作。
rameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStack.java
public class ActivityStack { ...... private final void startSpecificActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) { // 由于是第一次启动应用程序的Activity,所以下面语句
ProcessRecord app = mService.getProcessRecordLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo.uid); ...... if (app != null && app.thread != null) { try { realStartActivityLocked(r, app, andResume, checkConfig); return; } catch (RemoteException e) { ...... } } mService.startProcessLocked(r.processName, r.info.applicationInfo, true, 0, "activity", r.intent.getComponent(), false); } ...... }
mService.getProcessRecordLocked此函数是在AMS中,路径如下
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
在此函数中创建一个ProcessRecord,调用startProcessLocked。
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
在startProcessLocked函数中:
int pid = Process.start("android.app.ActivityThread", mSimpleProcessManagement ? app.processName : null, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, null);
在这我们可以看到他会启动一个Process,而这个Process由Zygote创建的。在前几节中我们讲过有关Zygote,在那里我们提过Zygote的客户端也可以是AMS。从这里我们可以看出这一点。
接下来通过ActivityThread会调用Activity的onCread()。
2. SubActivity的启动
其实利用MainActivity中的组件(如:button.onclick)去startActivity是与Launcher中启动时一样的,从上面分析的内容中可以看出Luancher最终也会调用startActivity。
仅仅是调用subActivity时不会建立一个Process,仅仅利用当场线程去创建而已。然后退回到Main函数时时从ActivityStack中Pause的Activity重新显现出来。
可以参考下面的图:
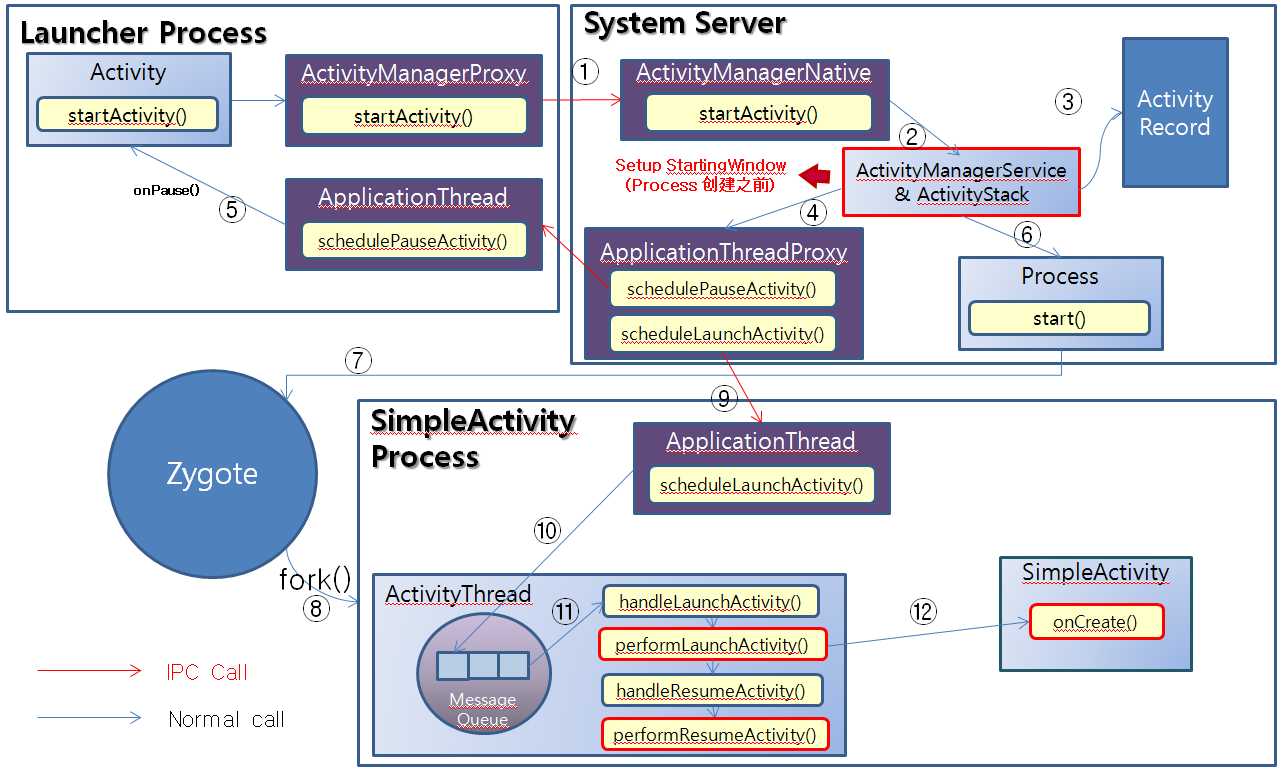
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hongguang-kim/p/4825393.html