标签:
java中String类里的String.equals()方法:
源代码:
public boolean equals(Object anObject)
{
//如果是同一个对象
if (this == anObject)
{
return true;
}
//如果传递进来的参数是String类的实例
if (anObject instanceof String)
{
String anotherString = (String)anObject;
int n = count;//字符串长度
if (n == anotherString.count) //如果长度相等就进行比较
{
char v1[] = value;//取每一个位置的字符
char v2[] = anotherString.value;
int i = offset;
int j = anotherString.offset;
while (n-- != 0) //对于每一位置逐一比较
{
if (v1[i++] != v2[j++])
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
对于object类的equals()方法,判断调用该方法的对象与要比较的对象是不是同一个对象(判断地址),而String类中的equals()方法,则判断当前字符串与传递进来的字符串的内容是否一致。
object类中的equals()方法:
public boolean equals(Object obj)
{
//调用equal的对象的地址和参数对象的地址是否相等
return (this == obj);
}
另外,对于java中的其他类,如果没有重写object类中的equals()方法,我们就可以认为调用该类的equals()方法就是判断这两个类是不是同一个类。只要是使用new 类名(),这种形式生成的类(除单例外),我们都可以认为是不同的类(地址不同)。
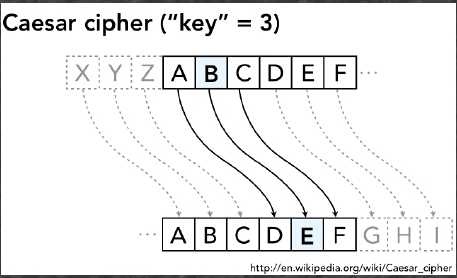
package 字串加密; import javax.swing.JOptionPane;
public class Password { public static void main(String args[]) { String password; password = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("请输入要加密或者要破解的字符串:"); String output; output = "字符串:"+password; char[] c = new char[password.length()]; password.getChars(0, password.length(), c,0); //加密 for(int i=0;i<password.length();i++) { if(c[i]==‘x‘) c[i]=‘a‘; else if(c[i]==‘y‘) c[i]=‘b‘; else if(c[i]==‘z‘) c[i]=‘c‘; else if (c[i] == ‘ ‘) c[i]=c[i]; else c[i]+=3; } output=new String(c); //解密 char[] d = new char[password.length()]; password.getChars(0, password.length(), d,0); for(int i=0;i<password.length();i++) { if(d[i]==‘c‘) d[i]=‘z‘; else if(d[i]==‘b‘) d[i]=‘y‘; else if(d[i]==‘a‘) d[i]=‘x‘; else if(d[i] == ‘ ‘) d[i]=d[i]; else d[i]-=3; } String o=new String(d); output +="\n\n解密后的字符串是:"+o;//定义输出格式 JOptionPane.showMessageDialog( null,"加密后的字符串是:"+output,"字符串"+password, JOptionPane.PLAIN_MESSAGE); System.exit(0); } }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/274761783cyf/p/4907713.html