标签:
Let‘s define logical OR as an operation on two logical values (i. e. values that belong to the set {0, 1}) that is equal to 1 if either or both of the logical values is set to 1, otherwise it is 0. We can define logical OR of three or more logical values in the same manner:
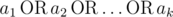 where
where 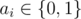 is equal to 1 if some ai = 1, otherwise it is equal to 0.
is equal to 1 if some ai = 1, otherwise it is equal to 0.
Nam has a matrix A consisting of m rows and n columns. The rows are numbered from 1 to m, columns are numbered from 1 to n. Element at row i (1 ≤ i ≤ m) and column j (1 ≤ j ≤ n) is denoted as Aij. All elements of A are either 0 or 1. From matrix A, Nam creates another matrix B of the same size using formula:
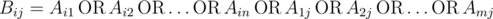 .
.
(Bij is OR of all elements in row i and column j of matrix A)
Nam gives you matrix B and challenges you to guess matrix A. Although Nam is smart, he could probably make a mistake while calculating matrix B, since size of A can be large.
The first line contains two integer m and n (1 ≤ m, n ≤ 100), number of rows and number of columns of matrices respectively.
The next m lines each contain n integers separated by spaces describing rows of matrix B (each element of B is either 0 or 1).
In the first line, print "NO" if Nam has made a mistake when calculating B, otherwise print "YES". If the first line is "YES", then also print mrows consisting of n integers representing matrix A that can produce given matrix B. If there are several solutions print any one.
2 2
1 0
0 0
NO

//1085422276 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std ; typedef long long ll; #define mem(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a)) #define pb push_back #define meminf(a) memset(a,127,sizeof(a)); inline ll read() { ll x=0,f=1;char ch=getchar(); while(ch<‘0‘||ch>‘9‘){ if(ch==‘-‘)f=-1;ch=getchar(); } while(ch>=‘0‘&&ch<=‘9‘){ x=x*10+ch-‘0‘;ch=getchar(); }return x*f; } //**************************************** #define maxn 1000+5 #define mod 1000000007 int c[maxn][maxn],b[maxn][maxn],a[maxn][maxn]; int main(){ int n=read(); int m=read(); memset(b,-1,sizeof(b)); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ scanf("%d",&a[i][j]); } } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ if(a[i][j]==0){ for(int k=1;k<=m;k++){ b[i][k]=0; } for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){ b[k][j]=0; } } } } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ if(b[i][j]==-1)b[i][j]=1; } } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ int aa=0; for(int k=1;k<=m;k++){ aa|=b[i][k]; } for(int k=1;k<=n;k++){ aa|=b[k][j]; } c[i][j]=aa; } }bool flag=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ if(c[i][j]!=a[i][j])flag=1; } } if(!flag){ cout<<"YES"<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){ cout<<b[i][j]<<" "; } cout<<endl; } } else cout<<"NO"<<endl; return 0; }
Codeforces Round #277 (Div. 2) B.OR in Matrix 模拟
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zxhl/p/4948733.html