标签:
重写继承方法与非重写继承方法的区别:
c#:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; namespace Test1 { class A { public virtual void Func1() { Console.WriteLine("A - Func1"); } public void Func2() { Console.WriteLine("A - Func2"); } } class B : A { public override void Func1() { Console.WriteLine("B - Func1"); } public void Func2() { Console.WriteLine("B - Func2"); } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { B b = new B(); A a = b; a.Func1(); b.Func1(); Console.WriteLine("-------------------------"); a.Func2(); b.Func2(); } } }
c++:
// Test2.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include <iostream> using namespace std; class A { public: virtual void Func1() { cout<<"A - Func1"<<endl; } void Func2() { cout<<"A - Func2"<<endl; } }; class B : public A { public: void Func1() { cout<<"B - Func1"<<endl; } void Func2() { cout<<"B - Func2"<<endl; } }; int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { B* b = new B(); A* a = b; a->Func1(); b->Func1(); cout<<"---------------------------"<<endl; a->Func2(); b->Func2(); return 0; }
输出结果:
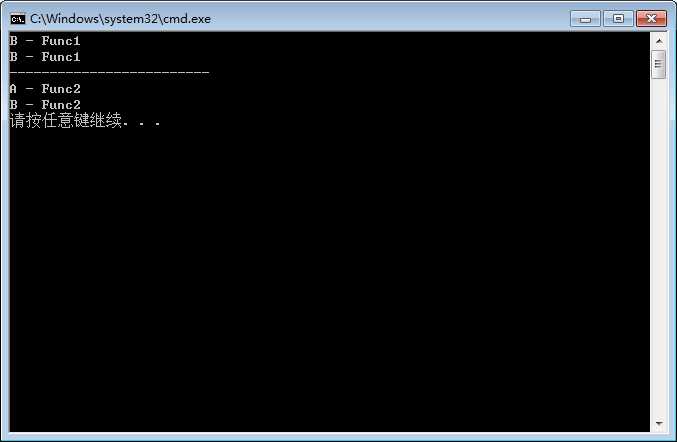
可见:
对重写继承方法,父类和子类的对象均执行子类重写的方法;
对非重写继承方法,父类和子类执行各自的方法。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lgyup/p/4952370.html