标签:style blog http color 使用 os
前言
在实际项目的一些矩阵运算模块中,往往需要对线性方程组进行求解以得到最终结果。
然而,你无法让计算机去使用克莱默法则或者高斯消元法这样的纯数学方法来进行求解。
计算机解决这个问题的方法是迭代法。本文将介绍三种最为经典的迭代法并用经典C++源代码实现之。
迭代法简介
从解的某个近似值出发,通过构造一个无穷序列去逼近精确解的方法。
雅克比迭代法
计算流程:
1. 初始化系数矩阵等计算环境
2. 设置精度控制和迭代次数控制变量
3. 采用如下式子进行迭代计算:
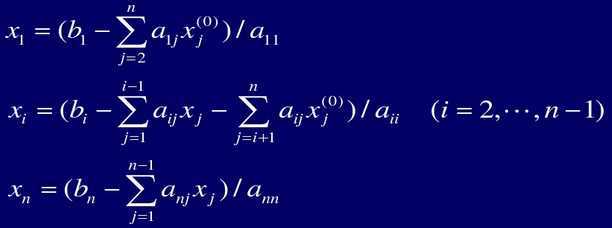
4. 循环执行 3,若(条件a)当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数等于解向量维数或者(b)迭代次数达到最大次数则跳出循环,进入到 5。
5. 若是因为条件a跳出循环则迭代成功,打印解向量;若是因为条件b退出循环则表示在指定的迭代次数内方程组未求解完。
说明:最经典原始的一种解方程组的迭代法。
高斯迭代法
计算流程:
1. 初始化系数矩阵等计算环境
2. 设置精度控制和迭代次数控制变量
3. 采用如下式子进行迭代计算:
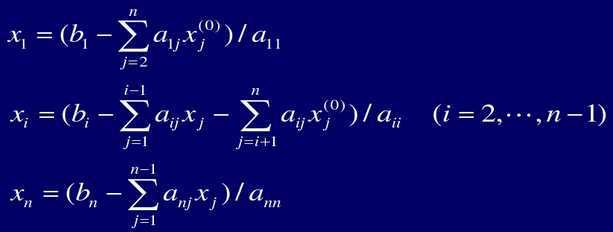
4. 循环执行 3,若(条件a)当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数等于解向量维数或者(b)迭代次数达到最大次数则跳出循环,进入到 5。
5. 若是因为条件a跳出循环则迭代成功,打印解向量;若是因为条件b退出循环则表示在指定的迭代次数内方程组未求解完。
说明:相对于雅克比迭代法,该方法不需要一个额外的辅助向量保存上一次迭代计算的结果,节省了空间。
超松弛迭代法
计算流程:
1. 初始化系数矩阵等计算环境
2. 设置精度控制和迭代次数控制变量以及松弛因子w
3. 采用如下式子进行迭代计算:
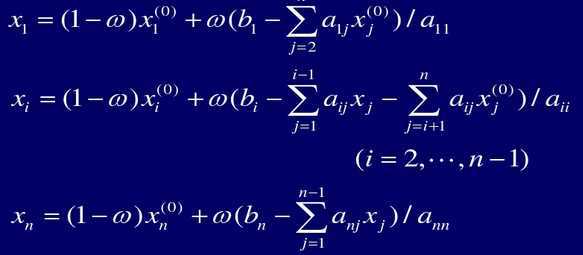
4. 循环执行 3,若(条件a)当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数等于解向量维数或者(b)迭代次数达到最大次数则跳出循环,进入到 5。
5. 若是因为条件a跳出循环则迭代成功,打印解向量;若是因为条件b退出循环则表示在指定的迭代次数内方程组未求解完。
说明:
1. 该方法同样不需要一个额外的辅助向量保存上一次迭代计算的结果。
2. 需要设置一个w因子参数,一般取0-2。当小于1时该方法为低松弛迭代法,高于1时为超松弛迭代法。经验上来看一般取1.4-1.6来实现超松弛迭代。
源代码实现
第一部分:迭代类声明 (Iterator.h)
1 // 头文件保护符 2 #ifndef Iterator_H 3 #define Iterator_H 4 5 // 迭代计算类 6 class CIterator 7 { 8 public: 9 // 构造函数 10 CIterator (); 11 // 析构函数 12 ~CIterator (); 13 // 设置计算环境 (如系数矩阵等) 14 bool SetEnvironment (); 15 // 雅克比迭代法计算方程解 16 bool JacobianCalculate (); 17 // 高斯迭代法计算方程解 18 bool GaussCalculate (); 19 // 超松弛迭代法计算方程解 20 bool RelaxationCalculate (double omiga); 21 // 获取系数矩阵 22 double ** GetMatrixA (); 23 // 获取系数矩阵的阶 24 int GetOrder (); 25 // 获取方程组右值向量 26 double * GetVectorB (); 27 // 获取方程解向量 28 double * GetSolution (); 29 30 private: 31 double **matrixA; // 系数矩阵 32 int order; // 系数矩阵的阶 33 double *vectorB; // 方程组右值向量 34 double *solution; // 解向量 35 }; 36 37 #endif
第二部分:迭代类实现 (Iterator.cpp)
1 #include "Iterator.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <iomanip> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 // 构造函数 8 CIterator :: CIterator () 9 { 10 matrixA = NULL; 11 order = 0; 12 vectorB = NULL; 13 solution = NULL; 14 } 15 16 // 析构函数 17 CIterator :: ~CIterator () 18 { 19 // 释放内存空间 20 if (!vectorB) { 21 delete [] vectorB; 22 vectorB = NULL; 23 } 24 if (!solution) { 25 delete [] solution; 26 solution = NULL; 27 } 28 if (matrixA!=NULL) { 29 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) { 30 delete [] matrixA[i]; 31 matrixA[i] = NULL; 32 } 33 delete [] matrixA; 34 matrixA = NULL; 35 } 36 } 37 38 // 设置计算环境 (如系数矩阵等) 39 bool CIterator :: SetEnvironment () 40 { 41 cout << "系数矩阵阶数: "; 42 cin >> order; 43 cout << endl; 44 45 matrixA = new double *[order]; 46 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) 47 matrixA[i] = new double [order]; 48 49 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) { 50 cout << "第 " << i << " 行系数: "; 51 for (int j=0; j<order; j++) 52 cin >> matrixA[i][j]; 53 } 54 cout << endl; 55 56 vectorB = new double [order]; 57 cout << "b 向量: "; 58 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) 59 cin >> vectorB[i]; 60 cout << endl; 61 62 solution = new double [order]; 63 64 cout << "运算环境搭建完毕" << endl << endl; 65 66 return true; 67 } 68 69 // 雅克比迭代法计算方程解 70 bool CIterator :: JacobianCalculate () 71 { 72 cout << "下面使用雅克比迭代法计算该线性方程组" << endl << endl; 73 74 // 设置迭代精度控制值 75 cout << "迭代精度控制值: "; 76 double bias; 77 cin >> bias; 78 cout << endl; 79 80 // 设置迭代次数控制值 81 cout << "迭代次数控制值: "; 82 int itMax; 83 cin >> itMax; 84 cout << endl; 85 86 // 当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数 87 int meetPrecisionCount = 0; 88 89 // 辅助向量,存放上一次迭代的解向量。 90 double * auxiliary = new double [order]; 91 92 // 初始化解向量 93 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) { 94 auxiliary[i] = 0; 95 solution[i] = 1; 96 } 97 98 // 当前迭代次数 99 int itCur = 0; 100 101 // 若当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数等于解向量维数或者迭代次数达到最大次数则跳出循环 102 while (meetPrecisionCount<order && itCur<itMax) { 103 104 // 当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数清零 105 meetPrecisionCount = 0; 106 107 // 将当前解向量存入辅助向量 108 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) 109 auxiliary[i] = solution[i]; 110 111 // 计算新的解向量 112 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) { 113 114 // 暂存当前解分量 115 double temp = solution[i]; 116 117 // 清零当前解分量 118 solution[i] = 0; 119 120 // 雅克比迭代计算 121 for (int j=0; j<i; j++) { 122 solution[i] += matrixA[i][j]*auxiliary[j]; 123 } 124 for (int j=i+1; j<order; j++) { 125 solution[i] += matrixA[i][j]*auxiliary[j]; 126 } 127 solution[i] = (vectorB[i]-solution[i])/matrixA[i][i]; 128 129 // 更新当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数 130 if (fabs(temp-solution[i])<bias) 131 meetPrecisionCount++; 132 } 133 134 // 当前迭代次数递增 135 itCur++; 136 } 137 138 // 若在规定的迭代次数内未完成计算任务,则返回错误。 139 if (itCur == itMax) return false; 140 141 return true; 142 } 143 144 // 高斯迭代法计算方程解 145 bool CIterator :: GaussCalculate () 146 { 147 cout << "下面使用高斯迭代法计算该线性方程组" << endl << endl; 148 149 // 设置迭代精度控制值 150 cout << "迭代精度控制值: "; 151 double bias; 152 cin >> bias; 153 cout << endl; 154 155 // 设置迭代次数控制值 156 cout << "迭代次数控制值: "; 157 int itMax; 158 cin >> itMax; 159 cout << endl; 160 161 // 当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数 162 int meetPrecisionCount = 0; 163 164 // 初始化解向量 165 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) { 166 solution[i] = 0; 167 } 168 169 // 当前迭代次数 170 int itCur = 0; 171 172 // 若当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数等于解向量维数或者迭代次数达到最大次数则跳出循环 173 while (meetPrecisionCount<order && itCur<itMax) { 174 175 // 当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数清零 176 meetPrecisionCount = 0; 177 178 // 计算新的解向量 179 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) { 180 181 // 暂存当前解分量 182 double temp = solution[i]; 183 184 // 清零当前解分量 185 solution[i] = 0; 186 187 // 高斯迭代计算 188 for (int j=0; j<i; j++) { 189 solution[i] += matrixA[i][j]*solution[j]; 190 } 191 for (int j=i+1; j<order; j++) { 192 solution[i] += matrixA[i][j]*solution[j]; 193 } 194 solution[i] = (vectorB[i]-solution[i])/matrixA[i][i]; 195 196 // 更新当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数 197 if (fabs(temp-solution[i])<bias) 198 meetPrecisionCount++; 199 } 200 201 // 当前迭代次数递增 202 itCur++; 203 } 204 205 // 若在规定的迭代次数内未完成计算任务,则返回错误。 206 if (itCur == itMax) return false; 207 208 return true; 209 } 210 211 // 超松弛迭代法计算方程解 212 bool CIterator :: RelaxationCalculate (double omiga) 213 { 214 cout << "下面使用超松弛迭代法计算该线性方程组" << endl << endl; 215 216 // 设置迭代精度控制值 217 cout << "迭代精度控制值: "; 218 double bias; 219 cin >> bias; 220 cout << endl; 221 222 // 设置迭代次数控制值 223 cout << "迭代次数控制值: "; 224 int itMax; 225 cin >> itMax; 226 cout << endl; 227 228 // 当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数 229 int meetPrecisionCount = 0; 230 231 // 当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数 232 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) { 233 solution[i] = 0; 234 } 235 236 // 当前迭代次数 237 int itCur = 0; 238 239 // 若当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数等于解向量维数或者迭代次数达到最大次数则跳出循环 240 while (meetPrecisionCount<order && itCur<itMax) { 241 242 // 当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数清零 243 meetPrecisionCount = 0; 244 245 // 计算新的解向量 246 for (int i=0; i<order; i++) { 247 248 // 暂存当前解分量 249 double temp = solution[i]; 250 251 // 清零当前解分量 252 solution[i] = 0; 253 254 // 超松弛迭代计算 255 for (int j=0; j<i; j++) { 256 solution[i] += matrixA[i][j]*solution[j]; 257 } 258 for (int j=i+1; j<order; j++) { 259 solution[i] += matrixA[i][j]*solution[j]; 260 } 261 solution[i] = omiga*(vectorB[i]-solution[i])/matrixA[i][i] + (1-omiga)*temp; 262 263 // 更新当前满足迭代精度控制的解分量数 264 if (fabs(temp-solution[i])<bias) 265 meetPrecisionCount++; 266 } 267 268 // 当前迭代次数递增 269 itCur++; 270 } 271 272 // 若在规定的迭代次数内未完成计算任务,则返回错误。 273 if (itCur == itMax) return false; 274 275 return true; 276 } 277 278 // 获取系数矩阵 279 double ** CIterator :: GetMatrixA () 280 { 281 return this->matrixA; 282 } 283 284 // 获取系数矩阵的阶 285 int CIterator :: GetOrder () 286 { 287 return this->order; 288 } 289 290 // 获取方程组右值向量 291 double * CIterator :: GetVectorB () 292 { 293 return this->vectorB; 294 } 295 296 // 获取方程解向量 297 double * CIterator :: GetSolution () 298 { 299 return this->solution; 300 }
第三部分:主函数 (main.cpp)
1 // 迭代计算类 2 #include "Iterator.h" 3 #include <iostream> 4 5 using namespace std; 6 7 // 打印方程解 8 void printResults (CIterator iterator); 9 10 int main() 11 { 12 // 定义迭代类对象 13 CIterator iterator; 14 15 // 设置计算环境 (如系数矩阵等) 16 iterator.SetEnvironment(); 17 18 // 雅克比迭代法计算方程解 19 if (!iterator.JacobianCalculate()) { 20 cout << "规定次数内未完成迭代计算" << endl; 21 return EXIT_FAILURE; 22 } 23 24 // 高斯迭代法计算方程解 25 /* 26 if (!iterator.GaussCalculate()) { 27 cout << "规定次数内未完成迭代计算" << endl; 28 return EXIT_FAILURE; 29 } 30 */ 31 32 // 超松弛迭代法计算方程解 33 /* 34 double omiga = 1.5; // 松弛迭代系数 35 if (!iterator.RelaxationCalculate(omiga)) { 36 cout << "规定次数内未完成迭代计算" << endl; 37 return EXIT_FAILURE; 38 } 39 */ 40 41 // 打印方程解 42 printResults (iterator); 43 44 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 45 } 46 47 // 打印方程解 48 void printResults (CIterator iterator) 49 { 50 cout << "计算成功,打印方程解: " << endl; 51 for (int i=0; i<iterator.GetOrder(); i++) 52 cout << "x" << i << " = " << iterator.GetSolution()[i] << endl; 53 54 cout << endl; 55 }
程序演示
使用超松弛迭代法解如下方程组:
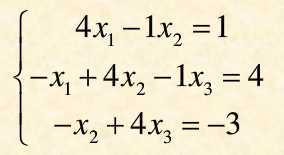
将主函数中雅克比和高斯迭代计算的部分注释掉,运行:
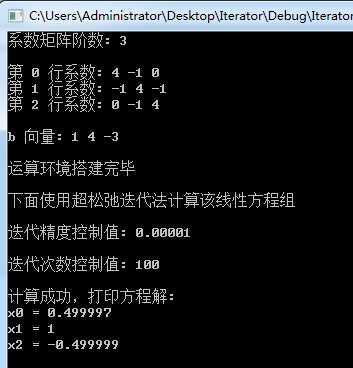
说明
不是每个方程组都能迭代得到解,我们通常将系数矩阵转换为对角占优矩阵(右向量部分也要跟着转)。满足这种条件的方程组的解向量大都能用这几种迭代法算出来。
求解线性方程组的三种基本迭代法,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:style blog http color 使用 os
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/scut-fm/p/3855294.html