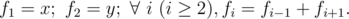然后就是取模运算和负数处理了。负数取模会返回负数。因为我是快速幂的写法,最后返回的数一定是在(-Mod, Mod)之间的,所以直接加上一个Mod,然后再取一次模就好了。
/******************************************************************************
* COPYRIGHT NOTICE
* Copyright (c) 2014 All rights reserved
* ----Stay Hungry Stay Foolish----
*
* @author :Shen
* @name :B
* @file :G:\My Source Code\【ACM】比赛\0719 - CF\B.cpp
* @date :2014/07/19 20:57
* @algorithm :Matrix Fast Power Method
******************************************************************************/
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int64;
const int MAXN = 2;
const int MAXM = 2;
const int Mod = 1000000007;
struct Matrax{
int n, m;
int64 mat[MAXN][MAXM];
Matrax(): n(-1), m(-1){}
Matrax(int _n, int _m): n(_n), m(_m){
memset(mat, 0, sizeof(mat));
}
void Unit(int _s){
n = _s; m = _s;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++){
mat[i][j] = (i == j)? 1: 0;
}
}
}
void print(){
printf("n = %d, m = %d\n", n, m);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++)
printf("%8d", mat[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
};
Matrax add_mod(const Matrax& a,const Matrax& b,const int64 mod){
Matrax ans(a.n, a.m);
for (int i = 0; i < a.n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < a.m; j++){
ans.mat[i][j] = (a.mat[i][j] + b.mat[i][j]) % mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Matrax mul(const Matrax& a,const Matrax& b){
Matrax ans(a.n, b.m);
for (int i = 0; i < a.n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < b.m; j++){
int64 tmp = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < a.m; k++){
tmp += a.mat[i][k] * b.mat[k][j];
}
ans.mat[i][j] = tmp;
}
}
return ans;
}
Matrax mul_mod(const Matrax& a, const Matrax& b, const int mod){
Matrax ans(a.n, b.m);
for (int i = 0; i < a.n; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < b.m; j++){
int64 tmp = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < a.m; k++){
tmp += (a.mat[i][k] * b.mat[k][j]) % mod;
}
ans.mat[i][j] = tmp % mod;
}
}
return ans;
}
Matrax pow_mod(const Matrax& a, int64 k, const int mod){
Matrax p(a.n, a.m), ans(a.n, a.m);
p = a; ans.Unit(a.n);
if (k==0) return ans;
else if (k==1) return a;
else {
while (k){
if (k & 1){
ans = mul_mod(ans, p, mod);
k--;
}
else {
k /= 2;
p = mul_mod(p, p, mod);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
int64 x, y, n, res;
void solve(){
cin >> x >> y >> n;
if (n == 1) res = x;
else if (n == 2) res = y;
else
{
Matrax ans(2, 1);
//tmp = cef ^ (n - 2);
//ans = tmp * beg;
//res = ans.mat[0][0];
Matrax cef(2, 2);
cef.mat[0][0] = 1; cef.mat[0][1] = -1;
cef.mat[1][0] = 1; cef.mat[1][1] = 0;
//cef.print();
Matrax beg(2, 1);
beg.mat[0][0] = y; beg.mat[1][0] = x;
Matrax tmp(2, 2);
tmp = pow_mod(cef, n - 2, Mod);
//tmp.print();
ans = mul_mod(tmp, beg, Mod);
//ans.print();
res = ans.mat[0][0];
}
if (res < 0) res += Mod;
cout << res << endl;
}
int main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}