标签:
class Mammal{}
class Dog extends Mammal {}
class Cat extends Mammal{}
public class TestCast
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Mammal m;
Dog d=new Dog();
Cat c=new Cat();
m=d;//不会报错,子类的对象可以赋值给父类的引用
d=m;//会报错,父类的引用不能直接赋值给子类的对象。想要赋值,必须进行强制类型转换
d=(Dog)m;//不会报错,进行了强制类型转换
d=c;//会报错,虽然这两个类派生自同一个类,但是这两个类之间并没有继承关系,互相属于不同的类,不能直接进行赋值
c=(Cat)m;//不会报错,进行了强制类型转换
d = (Dog)c;//这句是我自己附加的,这句话也会报错。因为不同的类之间也不能进行强制类型转换
}
}
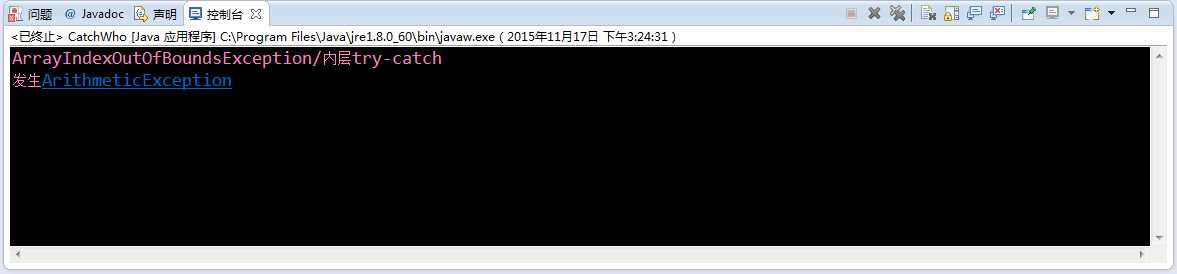
package Seven;
public class CatchWho
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
try
{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException"
+ "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch (ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException"
+ "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
package Seven;
public class CatchWho2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
try
{
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/内层try-catch");
}
throw new ArithmeticException();
}
catch(ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("发生ArithmeticException");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println( "ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException" + "/外层try-catch");
}
}
}
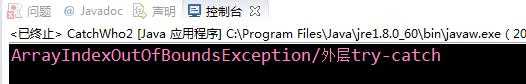
对比CatchWh和CatchWho2这两个例子来看,我们可以得出一个结论:当有try语句的嵌套时,如果内层try语句抛出的异常能够被内层的catch语句处理掉的话,由内层的try语句处理,但这时外层的try语句也是被执行的,因为外层try语句块里面的一个子快执行了。如果内层try语句的catch语句不能成功的处理掉这个异常,这个异常就要向上层try语句抛出了。而且,try语句块里面一旦抛出异常,那么,抛出异常的语句后面的语句都不会被执行。
package Seven;
import javax.swing.*;
public class AboutException {
public static void main(String[] a)
{
int i=1, j=0, k;
k=i/j;
try
{
k = i/j; // Causes division-by-zero exception
//throw new Exception("Hello.Exception!");
}
catch ( ArithmeticException e)
{
System.out.println("被0除. "+ e.getMessage());
}
catch (Exception e)
{
if (e instanceof ArithmeticException)
System.out.println("被0除");
else
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
finally
{
JOptionPane.showConfirmDialog(null,"OK");
}
}
}
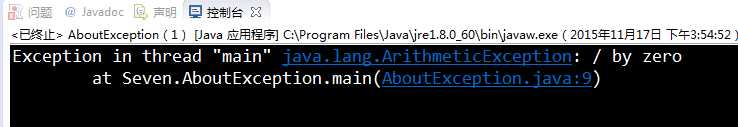
由于k=i/j;语句没有在try语句块里面,因此catch语句块不能处理这个异常。
package Seven;
public class EmbededFinally {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int result;
try {
System.out.println("in Level 1");
try {
System.out.println("in Level 2");
// result=100/0; //Level 2
try {
System.out.println("in Level 3");
result=100/0; //Level 3
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 3:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 3 finally");
}
// result=100/0; //Level 2
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 2:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 2 finally");
}
// result = 100 / 0; //level 1
}
catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("Level 1:" + e.getClass().toString());
}
finally {
System.out.println("In Level 1 finally");
}
}
}
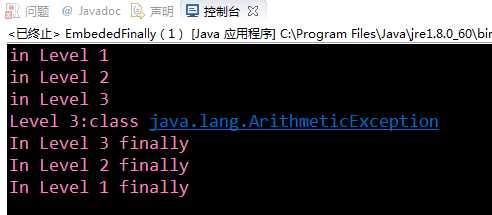
由内层向外层逐层调用。
package Seven;
public class SystemExitAndFinally {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try{
System.out.println("in main");
throw new Exception("Exception is thrown in main");
//System.exit(0);
}
catch(Exception e)
{
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.exit(0);
}
finally
{
System.out.println("in finally");
}
}
}
不一定。一般来说,只有当与fianally语句块对应的try语句块执行的时候,该finallya语句块才能被执行。但是这也不是绝对的,就像在这个例子里面,即使是与finally语句块对应的try语句块被执行了,finally语句块依旧没有被执行。因为catch语句块里面有强行结束程序的语句。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/1102whw/p/4972115.html