标签:
排行界面
public class TopProtocol extends BaseProtocol<List<String>> {@Overridepublic List<String> paserJson(String json) {List<String> datas=new ArrayList<String>();try {JSONArray array=new JSONArray(json);for(int i=0;i<array.length();i++){String str=array.getString(i);datas.add(str);}return datas;} catch (JSONException e) {e.printStackTrace();return null;}}@Overridepublic String getKey() {return "hot";}}
public class DrawableUtils {public static GradientDrawable createShape(int color){GradientDrawable drawable=new GradientDrawable();//相当于shapedrawable.setCornerRadius(UiUtils.dip2px(5));//设置4个角的弧度drawable.setColor(color);// 设置颜色return drawable;}public static StateListDrawable createSelectorDrawable(Drawable pressedDrawable,Drawable normalDrawable){// <selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:enterFadeDuration="200">// <item android:state_pressed="true" android:drawable="@drawable/detail_btn_pressed"></item>// <item android:drawable="@drawable/detail_btn_normal"></item>// </selector>StateListDrawable stateListDrawable=new StateListDrawable();stateListDrawable.addState(new int[]{android.R.attr.state_pressed}, pressedDrawable);// 按下显示的图片stateListDrawable.addState(new int[]{}, normalDrawable);// 抬起显示的图片return stateListDrawable;}}
public class TopFragment extends BaseFragment {private List<String> datas;@Overridepublic View createSuccessView() {ScrollView scrollView=new ScrollView(UiUtils.getContext());scrollView.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.grid_item_bg_normal);LinearLayout layout=new LinearLayout(UiUtils.getContext());int padding=UiUtils.dip2px(13);layout.setPadding(padding, padding, padding, padding);layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);// 设置线性布局的方向int backColor = 0xffcecece;Drawable pressedDrawable=DrawableUtils.createShape(backColor);// 按下显示的图片for(int i=0;i<datas.size();i++){TextView textView=new TextView(UiUtils.getContext());final String str=datas.get(i);textView.setText(str);Random random=new Random(); //创建随机int red = random.nextInt(200)+22;int green = random.nextInt(200)+22;int blue = random.nextInt(200)+22;//有可能都是0或255成白色或者黑色了int color=Color.rgb(red, green, blue);//范围 0-255GradientDrawable createShape = DrawableUtils.createShape(color); // 默认显示的图片StateListDrawable createSelectorDrawable = DrawableUtils.createSelectorDrawable(pressedDrawable, createShape);// 创建状态选择器textView.setBackgroundDrawable(createSelectorDrawable);textView.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);//textView.setTextSize(UiUtils.dip2px(14));int textPaddingV = UiUtils.dip2px(4);int textPaddingH = UiUtils.dip2px(7);textView.setPadding(textPaddingH, textPaddingV, textPaddingH, textPaddingV); //设置paddingtextView.setClickable(true);//设置textView可以被点击textView.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { // 设置点击事件@Overridepublic void onClick(View v) {Toast.makeText(UiUtils.getContext(), str, 0).show();}});layout.addView(textView,new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, -2));// -2 包裹内容}scrollView.addView(layout);return scrollView;}@Overrideprotected LoadResult load() {TopProtocol protocol=new TopProtocol();datas = protocol.load(0);return checkData(datas);}}

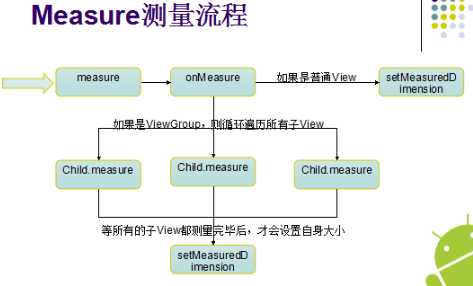
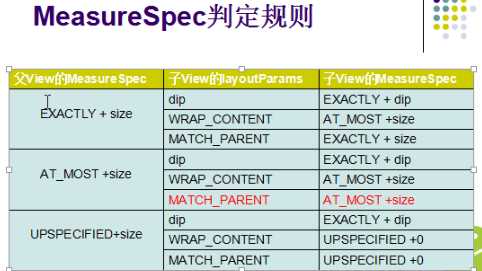
public class Flowlayout extends ViewGroup {private int horizontolSpacing=UiUtils.dip2px(13);private int verticalSpacing=UiUtils.dip2px(13);public Flowlayout(Context context) {super(context);}public Flowlayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {super(context, attrs, defStyle);}private Line currentline;// 当前的行private int useWidth=0;// 当前行使用的宽度private List<Line> mLines=new ArrayList<Flowlayout.Line>();private int width;public Flowlayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);}// 测量 当前控件Flowlayout// 父类是有义务测量每个孩子的@Overrideprotected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {// TODO Auto-generated method stub// MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;// MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;// MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;mLines.clear();currentline=null;useWidth=0;int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); // 获取当前父容器(Flowlayout)的模式width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec)-getPaddingLeft()-getPaddingRight();int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec)-getPaddingBottom()-getPaddingTop(); // 获取到宽和高int childeWidthMode;int childeHeightMode;// 为了测量每个孩子 需要指定每个孩子测量规则childeWidthMode=(widthMode==MeasureSpec.EXACTLY)?MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:widthMode;childeHeightMode=heightMode==MeasureSpec.EXACTLY?MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:heightMode;int childWidthMeasureSpec=MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childeWidthMode, width);int childHeightMeasureSpec=MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(childeHeightMode, height);currentline=new Line();// 创建了第一行for(int i=0;i<getChildCount();i++) {View child=getChildAt(i);System.out.println("孩子的数量:"+getChildCount());// 测量每个孩子child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);int measuredWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();useWidth+=measuredWidth;// 让当前行加上使用的长度if(useWidth<=width){currentline.addChild(child);//这时候证明当前的孩子是可以放进当前的行里,放进去useWidth+=horizontolSpacing;if(useWidth>width){//换行newLine();}}else{//换行if(currentline.getChildCount()<1){currentline.addChild(child); // 保证当前行里面最少有一个孩子}newLine();}}if(!mLines.contains(currentline)){mLines.add(currentline);// 添加最后一行}int totalheight=0;for(Line line:mLines){totalheight+=line.getHeight();}totalheight+=verticalSpacing*(mLines.size()-1)+getPaddingTop()+getPaddingBottom();System.out.println(totalheight);setMeasuredDimension(width+getPaddingLeft()+getPaddingRight(),resolveSize(totalheight, heightMeasureSpec));}private void newLine() {mLines.add(currentline);// 记录之前的行currentline=new Line(); // 创建新的一行useWidth=0;}private class Line{int height=0; //当前行的高度int lineWidth=0;private List<View> children=new ArrayList<View>();/*** 添加一个孩子* @param child*/public void addChild(View child) {children.add(child);if(child.getMeasuredHeight()>height){height=child.getMeasuredHeight();}lineWidth+=child.getMeasuredWidth();}public int getHeight() {return height;}/*** 返回孩子的数量* @return*/public int getChildCount() {return children.size();}public void layout(int l, int t) {lineWidth+=horizontolSpacing*(children.size()-1);int surplusChild=0;int surplus=width-lineWidth;if(surplus>0){surplusChild=surplus/children.size();}for(int i=0;i<children.size();i++){View child=children.get(i);// getMeasuredWidth() 控件实际的大小// getWidth() 控件显示的大小child.layout(l, t, l+child.getMeasuredWidth()+surplusChild, t+child.getMeasuredHeight());l+=child.getMeasuredWidth()+surplusChild;l+=horizontolSpacing;}}}// 分配每个孩子的位置@Overrideprotected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {l+=getPaddingLeft();t+=getPaddingTop();for(int i=0;i<mLines.size();i++){Line line=mLines.get(i);line.layout(l,t); //交给每一行去分配t+=line.getHeight()+verticalSpacing;}}}
public class ProgressView extends View {public ProgressView(Context context) {super(context);}public ProgressView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {super(context, attrs, defStyle);}public ProgressView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {super(context, attrs);}// 绘制控件@Overrideprotected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {super.onDraw(canvas);//canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap, left, top, paint);/*oval 圆的模型 矩形* startAngle 开始的角度* sweepAngle 范围的角度* useCenter 是否填充中间部分* paint 画笔*///canvas.drawArc(oval, startAngle, sweepAngle, useCenter, paint);}}
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/liuyu0529/p/4982185.html