标签:
SuBSENSE: A Universal Change Detection Method with Local Adaptive Sensitivity
Abstract:Foreground/background segmentation via change detection in video sequences is often used as a stepping stone in high-level analytics and applications. Despite the wide variety of methods that have been proposed for this problem, none has been able to fully address the complex nature of dynamic scenes in real surveillance tasks. In this paper, we present a universal pixellevel segmentation method that relies on spatiotemporal binary features as well as color information to detect changes. This allows camouflaged foreground objects to be detected more easily while most illumination variations are ignored. Besides, instead of using manually-set, frame-wide constants to dictate model sensitivity and adaptation speed, we use pixel-level feedback loops to dynamically adjust our method’s internal parameters without user intervention. These adjustments are based on the continuous monitoring of model fidelity and local segmentation noise levels. This new approach enables us to outperform all 32 previously tested state-of-the-art methods on the 2012 and 2014 versions of the ChangeDetection.net dataset in terms of overall FMeasure. The use of local binary image descriptors for pixel-level modeling also facilitates high-speed parallel implementations: our own version which used no low-level or architecture-specific instruction reached real-time processing speed on a mid-level desktop CPU. A complete C++ implementation based on OpenCV is available online.
1. Introduction:
以发现视频中感兴趣目标为核心的运动目标检测算法已经成为高层监控应用的基础。 在大部分情况下,“前景目标”物体(交通灯下的车辆)可能断断续续的运动,他们可能不是摄像机视野的焦点;不感兴趣的背景物体可能有有些前景的行为(如:摇摆的树枝,喷泉等等)。简单的背景相减和传统的图像分割方法可能不适合实际视频监控任务,即:标注活跃的区域(active region labeling)。现在的物体检测方法大致分为3个部分:
1. 首先,对场景的背景进行建模,以及分析视频帧进行模型的更新;
2. 其次,根据到来帧与模型的相似性,对所有的像素点都进行前景/背景分割标签的赋予。
3. 最后,用正则化的方法对相邻像素点的信息进行综合处理,并且确保均匀的区域被赋予相通的标签。
背景建模可以用许多不同的方式进行处理: 为了算法的效率,大部分方法依赖于独立的像素级模型,将其融合进较大的背景模型。色彩的亮度在无参模型中被通常用来刻画局部像素表示,或者在参数模型中进行局部分布的预测(local distribution estimation)。由于其简单性,这种方法不能直接解决像素点之间的时空联系,相反将该任务委托给正则化这一步。这通常会产生不太理想的分割结果,因为没有结构化分析(texture analysis),特别当碰到伪装的前景目标时,更是如此。
在所有的情况下,一个典型的较坏的参数是分割噪声:通常看到的“闪烁像素”(blinking pixels, i.e. pixels that often switch between foreground and background classification over time), 这种噪声表明,该模型对特定区域的变化,太过敏感。
In this paper, we present a universal method for change detection, meaning it can be directly applied on most video surveillance scenarios and still result in near-optimal performance. (本文提出了一种普遍的方法)。本文的贡献点大致如下:
1. we first use an improved spatiotemporal binary similarity descriptors along with color intensities to characterize pixel representations in a nonparametric
paradigm. (首先用改进的时空二进制相似性描述算子和色彩亮度,在一个无参模型中来刻画像素表示 (pixel representations))
2. Then, in order to improve out-of-the-box flexibility in complex scenarios, we propose a new feedback scheme to dynamically control our algorithm’s sensitivity and adaptation speed. (为了改善算法在复杂场景下的灵活性,我们提出了一种新的反馈机制来动态的调控我们算法的敏感度和更新速度)
本文的正则化操作主要为:形态学操作和median blurring(中值模糊),可以去掉所有的椒盐分割噪声(salt-and-pepper segmantation noise.)。本文在2012 2014 版本的ChangeDetection.net(CDnet) dataset 上做了实验,结果肯定是比其余的32中方法好咯。。。这不是废话么!囧 。。。
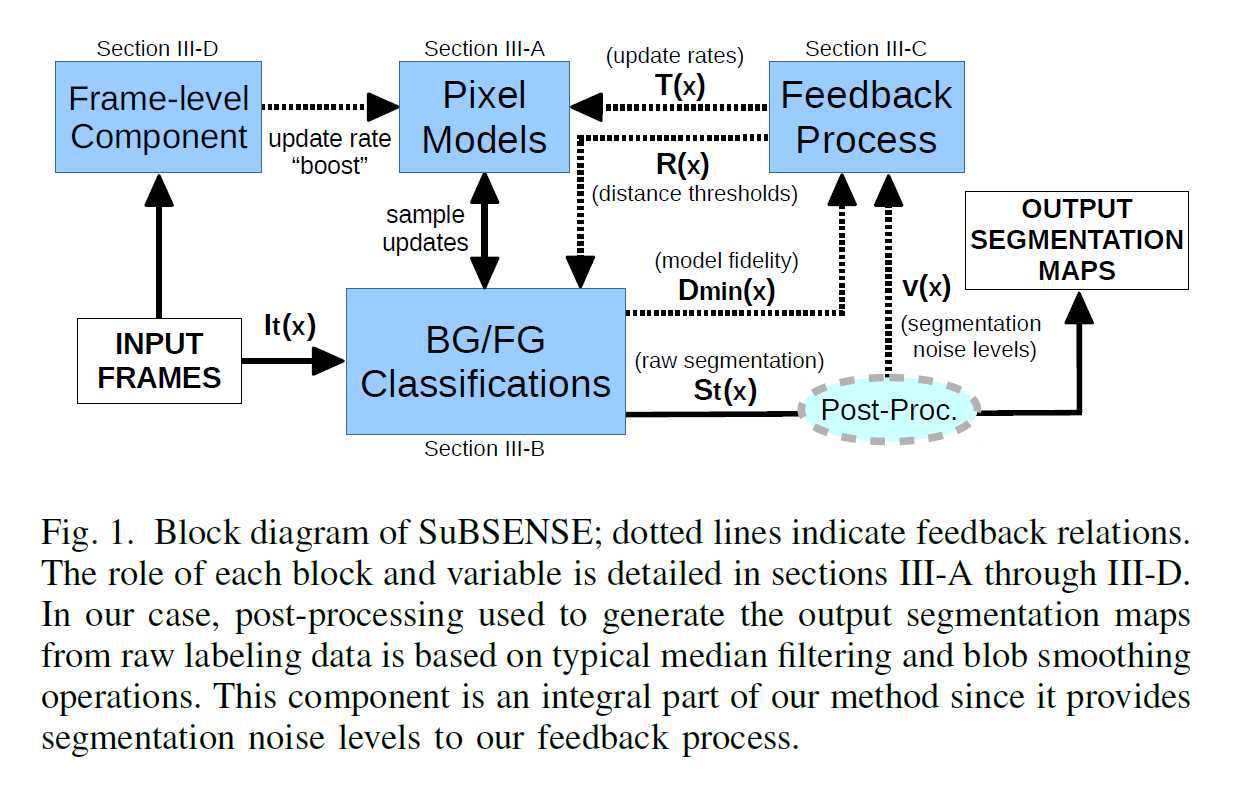
2. Related Work (略)
。。。
3. METHODOLOGY
3.1. Pixel-level modeling (像素级建模)
Pixel-level modeling, as opposed to region-level or objectlevel modeling, usually allows high-speed parallel implementations to be developed with relative ease due to how the workload is already split and kept isolated at a low level. However, the absence of information sharing between such local models puts the entire burden of spatial (or spatiotemporal) labeling coherence on the method’s regularization scheme.
为了解决以上矛盾,本文将像素的RGB值和Local Binary Similarity Pattern (LBSP) features 结合起来,来刻画像素级表示。
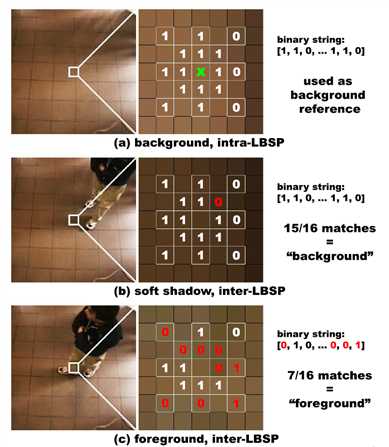
More specifically, the following equation is used to compute an LBSP binary string centered at a given location x:
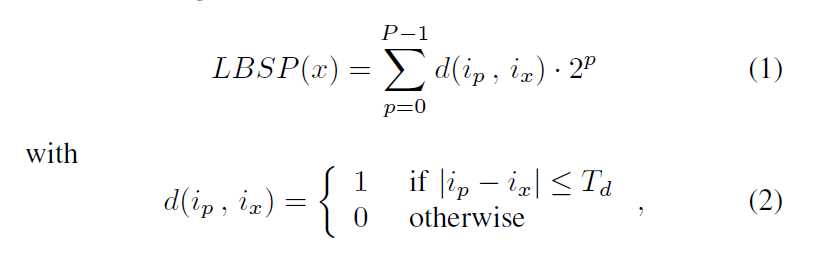
The first major improvement we propose to traditional LBSP features is related to their internal threshold, Td. (间隔阈值)
论文阅读之: 目标检测 TIP 2014 SuBSENSE: A Universal Change Detection Method with Local Adaptive Sensitivity
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangxiaocvpr/p/5001456.html