标签:
配置VS2013 OpenCL环境
1. 安装CUDA安装包
由于目前的CUDA安装包自带显卡驱动、CUAD工具、OpenCL的SDK;其中OpenCL的相关内容的默认目录有:
-
CL文件夹的目录:C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v7.0\include
-
OpenCL.lib文件目录:C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v7.0\lib
-
OpenCL.dll文件目录:C:\Program Files\NVIDIA Corporation\OpenCL
2. 新建空项目
可以通过VS2013的VC++模板新建一个空项目;
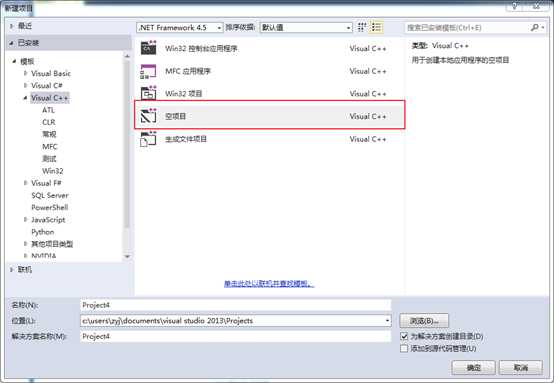
图 1
3. 添加文件
为了验证配置的正确性,所以为项目添加两个文件:cl_kernel.cl和main.cpp。
1) 添加cl_kernel.cl文件
其中在项目所在的目录下新建一个cl_kernel.cl文件,其内容为附录1所示,目录结构如图 1所示。同时在VS2013的项目中将cl_kernel.cl文件添加到项目的"源文件"筛选器中,如图 2所示。
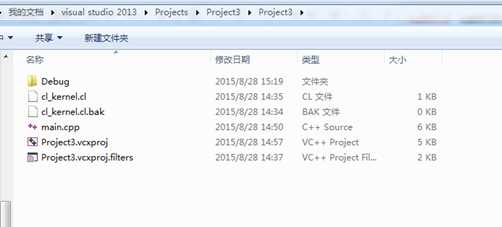
图 2
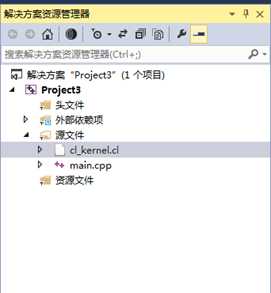
图 3
2) 添加main.cpp文件
类似cl_kernel.cl文件操作,同样将main.cpp文件添加到项目中。
4. 配置CL目录
需要将OpenCL的SDK的头文件包含到项目中,具体操作方法为:
在项目->属性->配置属性->C/C++->常规->附加包含目录->配置,然后添加CL文件夹的目录:C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v7.0\include。如图 3所示。
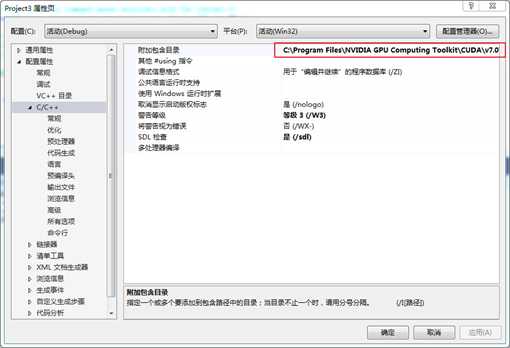
图 4
5. 配置预处理器
项目->属性->配置属性->c/c++->预处理器定义->编辑,然后添加"_CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS",否则会报错。
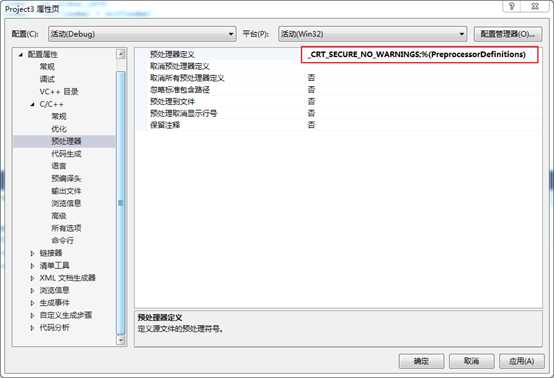
图 5
6. 配置外部依赖OpenCL.lib目录
具体操作:项目->属性->配置属性->链接器->常规->附加库目录。然后将OpenCL.lib文件所在的目录添加进去,其中需要注意的是将程序Debug成32位和64位平台添加的Opencl.lib目录是不同的,如图 4所示,是Debug成Win32平台,所以只加"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v7.0\lib\Win32"路径;若是Debug成X64,则添加的路径为"C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v7.0\lib\x64"。同时需要在"启用增量链接"选项中选否。
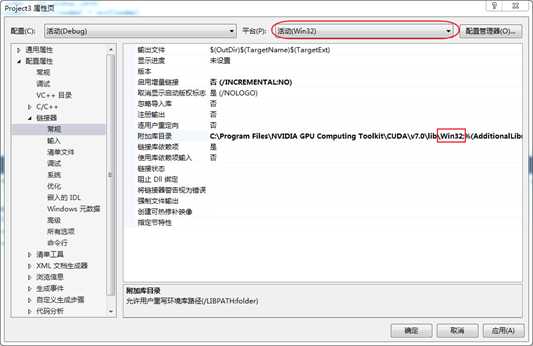
图 6
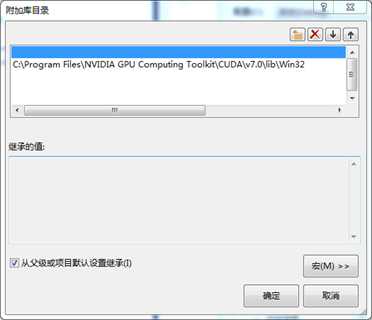
图 7
7. 配置OpenCL.lib文件
项目->属性->配置属性->连接器->输入->附件依赖库->编辑,接着添加OpenCL.lib
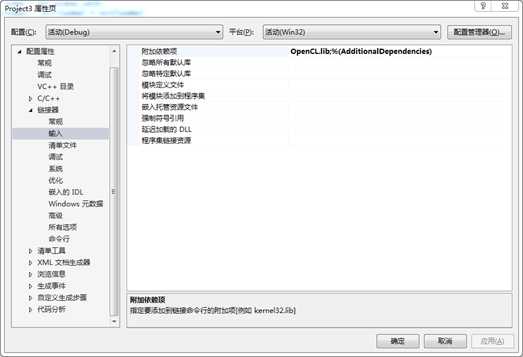
图 8
8. 运行结果图
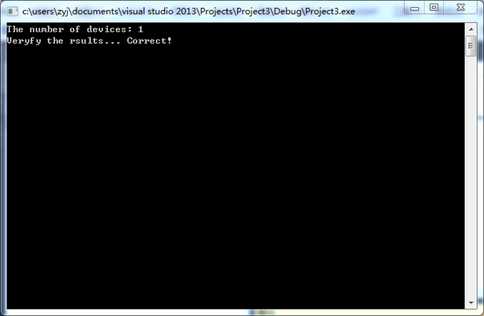
图 9
附录1 cl_kernel.cl文件
1 __kernel void MyCLAdd(__global int *dst, __global int *src1, __global int *src2)
2
3 {
4
5 int index = get_global_id(0);
6
7 dst[index] = src1[index] + src2[index];
8
9 }
1 #include <CL/cl.h>
2
3 #include <stdio.h>
4
5 #include <iostream>
6
7 using namespace std;
8
9
10
11 int main(void){
12
13 cl_uint numPlatforms = 0; //the NO. of platforms
14
15 cl_platform_id platform = nullptr; //the chosen platform
16
17 cl_context context = nullptr; // OpenCL context
18
19 cl_command_queue commandQueue = nullptr;
20
21 cl_program program = nullptr; // OpenCL kernel program object that‘ll be running on the compute device
22
23 cl_mem input1MemObj = nullptr; // input1 memory object for input argument 1
24
25 cl_mem input2MemObj = nullptr; // input2 memory object for input argument 2
26
27 cl_mem outputMemObj = nullptr; // output memory object for output
28
29 cl_kernel kernel = nullptr; // kernel object
30
31
32
33 cl_int status = clGetPlatformIDs(0, NULL, &numPlatforms);
34
35 if (status != CL_SUCCESS)
36
37 {
38
39 cout << "Error: Getting platforms!" << endl;
40
41 return 0;
42
43 }
44
45
46
47 /*For clarity, choose the first available platform. */
48
49 if (numPlatforms > 0)
50
51 {
52
53 cl_platform_id* platforms = (cl_platform_id*)malloc(numPlatforms* sizeof(cl_platform_id));
54
55 status = clGetPlatformIDs(numPlatforms, platforms, NULL);
56
57 platform = platforms[0];
58
59 free(platforms);
60
61 }
62
63 else
64
65 {
66
67 puts("Your system does not have any OpenCL platform!");
68
69 return 0;
70
71 }
72
73
74
75 /*Step 2:Query the platform and choose the first GPU device if has one.Otherwise use the CPU as device.*/
76
77 cl_uint numDevices = 0;
78
79 cl_device_id *devices;
80
81 status = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 0, NULL, &numDevices);
82
83 if (numDevices == 0) //no GPU available.
84
85 {
86
87 cout << "No GPU device available." << endl;
88
89 cout << "Choose CPU as default device." << endl;
90
91 status = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU, 0, NULL, &numDevices);
92
93 devices = (cl_device_id*)malloc(numDevices * sizeof(cl_device_id));
94
95
96
97 status = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_CPU, numDevices, devices, NULL);
98
99 }
100
101 else
102
103 {
104
105 devices = (cl_device_id*)malloc(numDevices * sizeof(cl_device_id));
106
107 status = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, numDevices, devices, NULL);
108
109 cout << "The number of devices: " << numDevices << endl;
110
111 }
112
113
114
115 /*Step 3: Create context.*/
116
117 context = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, devices, NULL, NULL, NULL);
118
119
120
121 /*Step 4: Creating command queue associate with the context.*/
122
123 commandQueue = clCreateCommandQueue(context, devices[0], 0, NULL);
124
125
126
127 /*Step 5: Create program object */
128
129 // Read the kernel code to the buffer
130
131 FILE *fp = fopen("cl_kernel.cl", "rb");
132
133
134
135 //错误 1 error C4996 : ‘fopen‘ : This function or variable may be unsafe.Consider using fopen_s instead.To disable deprecation, use _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS.See online help for details.c : \users\zyj\documents\visual studio 2013\projects\project3\project3\main.cpp 67 1 Project3
136
137
138
139
140
141 if (fp == nullptr)
142
143 {
144
145 puts("The kernel file not found!");
146
147 goto RELEASE_RESOURCES;
148
149 }
150
151 fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
152
153 size_t kernelLength = ftell(fp);
154
155 fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_SET);
156
157 char *kernelCodeBuffer = (char*)malloc(kernelLength + 1);
158
159 fread(kernelCodeBuffer, 1, kernelLength, fp);
160
161 kernelCodeBuffer[kernelLength] = ‘\0‘;
162
163 fclose(fp);
164
165
166
167 const char *aSource = kernelCodeBuffer;
168
169 program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1, &aSource, &kernelLength, NULL);
170
171
172
173 /*Step 6: Build program. */
174
175 status = clBuildProgram(program, 1, devices, NULL, NULL, NULL);
176
177
178
179 /*Step 7: Initial inputs and output for the host and create memory objects for the kernel*/
180
181 int __declspec(align(32)) input1Buffer[128]; // 32 bytes alignment to improve data copy
182
183 int __declspec(align(32)) input2Buffer[128];
184
185 int __declspec(align(32)) outputBuffer[128];
186
187
188
189 // Do initialization
190
191 int i;
192
193 for (i = 0; i < 128; i++)
194
195 input1Buffer[i] = input2Buffer[i] = i + 1;
196
197 memset(outputBuffer, 0, sizeof(outputBuffer));
198
199
200
201 // Create mmory object
202
203 input1MemObj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, 128 * sizeof(int), input1Buffer, nullptr);
204
205 input2MemObj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY | CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, 128 * sizeof(int), input2Buffer, nullptr);
206
207 outputMemObj = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY, 128 * sizeof(int), NULL, NULL);
208
209
210
211 /*Step 8: Create kernel object */
212
213 kernel = clCreateKernel(program, "MyCLAdd", NULL);
214
215
216
217 /*Step 9: Sets Kernel arguments.*/
218
219 status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&outputMemObj);
220
221 status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&input1MemObj);
222
223 status = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), (void *)&input2MemObj);
224
225
226
227 /*Step 10: Running the kernel.*/
228
229 size_t global_work_size[1] = { 128 };
230
231 status = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(commandQueue, kernel, 1, NULL, global_work_size, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);
232
233 clFinish(commandQueue); // Force wait until the OpenCL kernel is completed
234
235
236
237 /*Step 11: Read the cout put back to host memory.*/
238
239 status = clEnqueueReadBuffer(commandQueue, outputMemObj, CL_TRUE, 0, global_work_size[0] * sizeof(int), outputBuffer, 0, NULL, NULL);
240
241
242
243 printf("Veryfy the rsults... ");
244
245 for (i = 0; i < 128; i++)
246
247 {
248
249 if (outputBuffer[i] != (i + 1) * 2)
250
251 {
252
253 puts("Results not correct!");
254
255 break;
256
257 }
258
259 }
260
261 if (i == 128)
262
263 puts("Correct!");
264
265 RELEASE_RESOURCES:
266
267 /*Step 12: Clean the resources.*/
268
269 status = clReleaseKernel(kernel);//*Release kernel.
270
271 status = clReleaseProgram(program); //Release the program object.
272
273 status = clReleaseMemObject(input1MemObj);//Release mem object.
274
275 status = clReleaseMemObject(input2MemObj);
276
277 status = clReleaseMemObject(outputMemObj);
278
279 status = clReleaseCommandQueue(commandQueue);//Release Command queue.
280
281 status = clReleaseContext(context);//Release context.
282
283
284
285 free(devices);
286
287 }








