标签:
def first(): T
first返回RDD中的第一个元素,不排序。
例子:

def count(): Long
count返回RDD中的元素数量
例子:

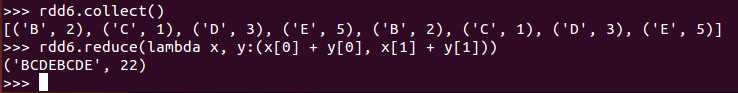
def reduce(f: (T, T) ⇒ T): T
根据映射函数f,对RDD中的元素进行二元计算,返回计算结果(可用于求和,字符串叠加等等)
例子:
def take(num: Int): Array[T]
take用于获取RDD中从0到num-1下标的元素,不排序
例子:

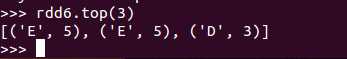
def top(num: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T]): Array[T]
top函数用于从RDD中,按照默认(降序)或者指定的排序规则,返回前num个元素
例子:(注意与take区别)
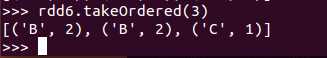
def takeOrdered(num: Int)(implicit ord: Ordering[T]): Array[T]
takeOrdered和top类似,只不过以和top相反的顺序返回元素
例子:(注意与take、top比较)
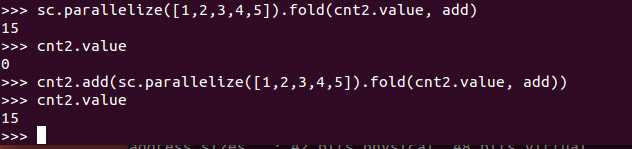
fold(zeroValue, op)
Aggregate the elements of each partition, and then the results for all the partitions, using a given associative and commutative function and a neutral “zero value.”
类似于给一个初值和一个函数,将rdd中每一个值累加到zeroValue中
例子:
lookup(key)
Return the list of values in the RDD for key key. This operation is done efficiently if the RDD has a known partitioner by only searching the partition that the key maps to.
lookup用于(K,V)类型的RDD,指定K值,返回RDD中该K对应的所有V值
例子:(查询)
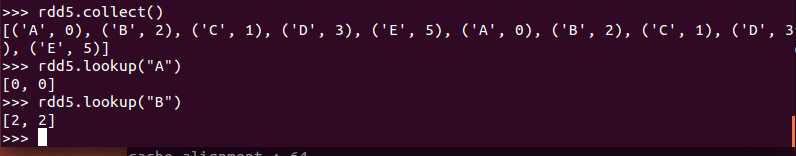
Count the number of elements for each key, and return the result to the master as a dictionary.
countByKey用于统计RDD[K,V]中每个K的数量
例子:
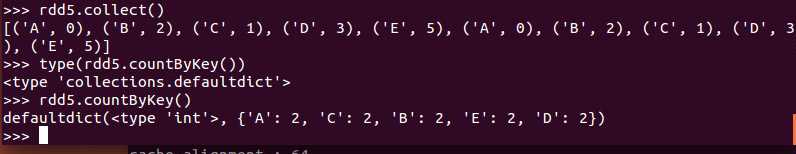
foreach(f)
foreach用于遍历RDD,将函数f应用于每一个元素。
但要注意,如果对RDD执行foreach,只会在Executor端有效,而并不是Driver端。
比如:rdd.foreach(println),只会在Executor的stdout中打印出来,Driver端是看不到的。
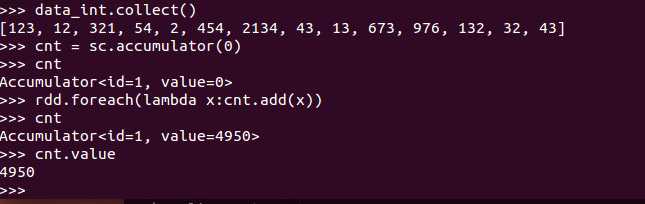
跟accumulator结合很有效
例子:
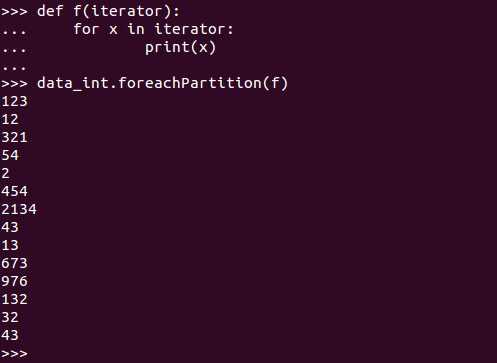
Applies a function to each partition of this RDD.
例子:
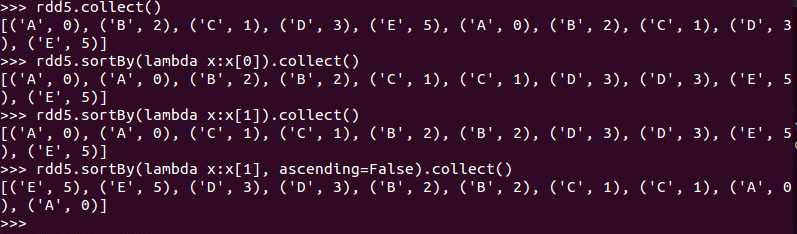
sortBy(keyfunc, ascending=True, numPartitions=None)
Sorts this RDD by the given keyfunc
例子:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/loadofleaf/p/5093746.html