标签:
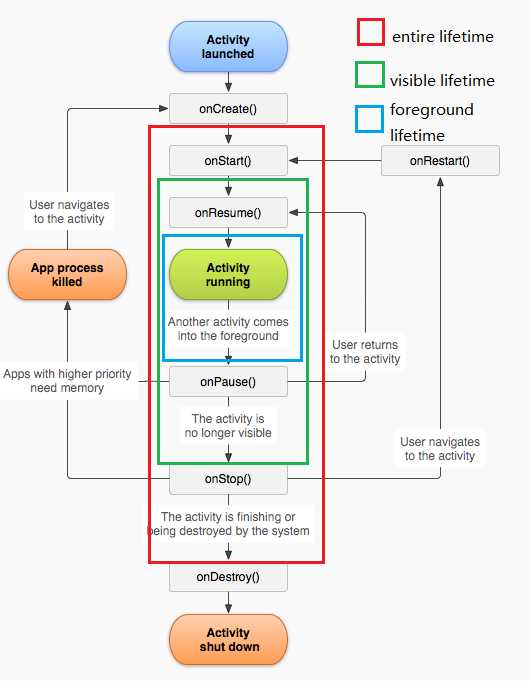
activity启动的时候:onCreate ---> onStart ---> onResume 这个过程不用多说,大家都知道。
1.启动Activity:系统会先调用onCreate方法,然后调用onStart方法,最后调用onResume,Activity进入运行状态。
2.当前Activity被其他Activity覆盖其上或被锁屏:系统会调用onPause方法,暂停当前Activity的执行。
3.当前Activity由被覆盖状态回到前台或解锁屏:系统会调用onResume方法,再次进入运行状态。
4.当前Activity转到新的Activity界面或按Home键回到主屏,自身退居后台:系统会先调用onPause方法,然后调用onStop方法,进入停滞状态。
5.用户后退回到此Activity:系统会先调用onRestart方法,然后调用onStart方法,最后调用onResume方法,再次进入运行状态。
6.当前Activity处于被覆盖状态或者后台不可见状态,即第2步和第4步,系统内存不足,杀死当前Activity,而后用户退回当前Activity:再次调用onCreate方法、onStart方法、onResume方法,进入运行状态。
7.用户退出当前Activity:系统先调用onPause方法,然后调用onStop方法,最后调用onDestory方法,结束当前Activity。
七个方法中除了onRestart()方法,其他都是俩俩对应的,从而又可以将活动分为三种生存期
1.Activity的entire lifetime(全部的生命期)发生在
package com.demo.text; import com.demo.pullrefresh.R; import android.app.Activity; import android.app.AlertDialog; import android.content.Intent; import android.os.Bundle; import android.util.Log; import android.view.Display; import android.view.View; import android.view.View.OnClickListener; import android.view.WindowManager; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.Toast; public class OneActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener { private Button bb_dialog; private Button bb_gotoother; private Button bb_gotootherdialog; /** * 它会在活动的第一次被创建时调用,应该在这个方法完成活动的初始化操作,比如加载布局和绑定事件等 */ @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); Log.d("jiejie", "OneActivity————————onCreate"); init(); } private void init() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub setContentView(R.layout.oneactivity); bb_dialog = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bb_dialog); bb_gotoother = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bb_gotoother); bb_gotootherdialog = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bb_gotootherdialog); bb_dialog.setOnClickListener(this); bb_gotoother.setOnClickListener(this); bb_gotootherdialog.setOnClickListener(this); } @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub switch (arg0.getId()) { case R.id.bb_dialog: AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this); final AlertDialog dialog = builder.create(); View view = View.inflate(OneActivity.this, R.layout.dialog, null); dialog.setView(view, 0, 0, 0, 0);// 设置边距为0,保证在2.x的版本上运行没问题 Button btnCancel = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.btn_cancel); Button btnOK = (Button) view.findViewById(R.id.btn_ok); btnOK.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Toast.makeText(OneActivity.this, ".....", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); dialog.dismiss(); } }); btnCancel.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub dialog.dismiss(); } }); dialog.show(); /* * lp.x与lp.y表示相对于原始位置的偏移. * 当参数值包含Gravity.LEFT时,对话框出现在左边,所以lp.x就表示相对左边的偏移,负值忽略. * 当参数值包含Gravity.RIGHT时,对话框出现在右边,所以lp.x就表示相对右边的偏移,负值忽略. * 当参数值包含Gravity.TOP时,对话框出现在上边,所以lp.y就表示相对上边的偏移,负值忽略. * 当参数值包含Gravity.BOTTOM时,对话框出现在下边,所以lp.y就表示相对下边的偏移,负值忽略. * 当参数值包含Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL时 * ,对话框水平居中,所以lp.x就表示在水平居中的位置移动lp.x像素,正值向右移动,负值向左移动. * 当参数值包含Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL时 * ,对话框垂直居中,所以lp.y就表示在垂直居中的位置移动lp.y像素,正值向右移动,负值向左移动. * gravity的默认值为Gravity.CENTER,即Gravity.CENTER_HORIZONTAL | * Gravity.CENTER_VERTICAL. * * 本来setGravity的参数值为Gravity.LEFT | Gravity.TOP时对话框应出现在程序的左上角,但在 * 我手机上测试时发现距左边与上边都有一小段距离,而且垂直坐标把程序标题栏也计算在内了, Gravity.LEFT, * Gravity.TOP, Gravity.BOTTOM与Gravity.RIGHT都是如此,据边界有一小段距离 */ // Window dialogWindow = dialog.getWindow(); // WindowManager.LayoutParams lp = dialogWindow.getAttributes(); // dialogWindow.setGravity(Gravity.LEFT|Gravity.TOP); // lp.x = 100; // lp.y = 100; // lp.width = 300; // lp.height = 300; // lp.alpha = 0.7f; // dialogWindow.setAttributes(lp); WindowManager m = getWindowManager(); Display d = m.getDefaultDisplay(); android.view.WindowManager.LayoutParams p = dialog.getWindow() .getAttributes(); p.height = (int) (d.getHeight() * 0.4); p.width = (int) (d.getWidth() * 0.75); p.x = 10; p.y = 150; dialog.getWindow().setAttributes(p); break; case R.id.bb_gotoother: startActivity(new Intent(OneActivity.this, OtherClass.class)); break; case R.id.bb_gotootherdialog: startActivity(new Intent(OneActivity.this, OtherDialog.class)); break; default: break; } } /** * 这个方法在活动由不可见变成可见的时候调用 */ @Override protected void onStart() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onStart(); Log.d("jiejie", "OneActivity————————onStart"); } /** * 这个方法在活动准备好和用户进行交互的时候调用。此时的活动一定位于返回栈的栈顶,并且处于运行的状态 */ @Override protected void onResume() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onResume(); Log.d("jiejie", "OneActivity————————onResume"); } /** * 这个方法在系统准备去启动或者恢复另一个活动的时候调用。我们通常会在这个方法中 * 将一些消耗CPU的资源释放掉,以及保存一些关键的数据,但这个方法的执行速度一定要快, 不然会影响到新的栈顶活动的使用。 */ @Override protected void onPause() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onPause(); Log.d("jiejie", "OneActivity————————onPause"); } /** * 这个方法在活动完全不可见的时候调用。它和onPause()方法的主要区别在于, * 如果启动的新活动是一个对话框的活动,那么onPause()方法会得到执行,而onStop() 方法并不会执行 */ @Override protected void onStop() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onStop(); Log.d("jiejie", "OneActivity————————onStop"); } /** * 这个方法在活动被销毁之前调用,之后活动的状态将变成销毁状态 */ @Override protected void onDestroy() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onDestroy(); Log.d("jiejie", "OneActivity————————onDestroy"); } /** * 这个方法在活动由停止变为运行状态之前调用,也是活动被重新启动了。 */ @Override protected void onRestart() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub super.onRestart(); Log.d("jiejie", "OneActivity————————onRestart"); } }
其中子定义对话框的xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft="10dp" android:layout_marginRight="10dp" android:background="#fff" android:orientation="vertical" android:paddingBottom="5dp" > <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center_vertical" android:padding="15dp" android:text="你确定要删除?" android:textSize="20sp" /> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:paddingLeft="4dp" android:paddingRight="4dp" > <Button android:id="@+id/btn_cancel" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="-8dp" android:layout_marginRight="1dp" android:layout_marginTop="-8dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:background="@drawable/selector_btn1" android:text="取 消" android:textColor="@android:color/white" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn_ok" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="-8dp" android:layout_marginLeft="1dp" android:layout_marginTop="-8dp" android:layout_weight="1" android:background="@drawable/selector_btn" android:text="确 定" android:textColor="@android:color/white" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
android:background="@drawable/selector_btn"

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<selector xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<item android:drawable="@drawable/btn_pressed" android:state_pressed="true"></item>
<item android:drawable="@drawable/btn_normal"></item>
</selector>
现在来观察Activity的生命周期
当点击运行时

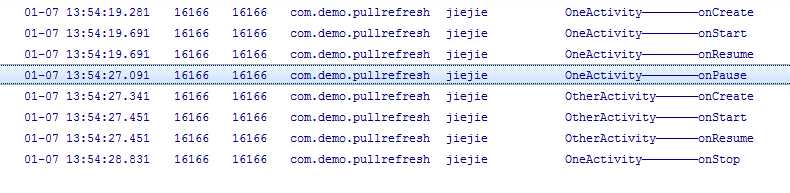
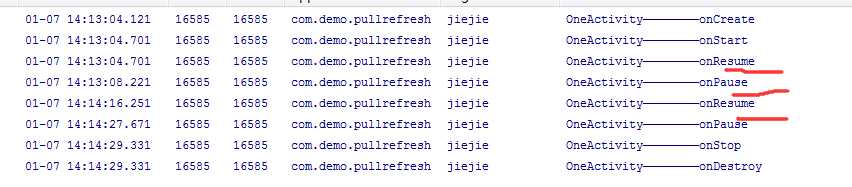
1.随后点击进入另一个Activity 先调用了onPause()系统准备调用另一个活动,过几秒调用了onStop的方法
在另一个Activity 重新返回第一个Activity时(finish下)
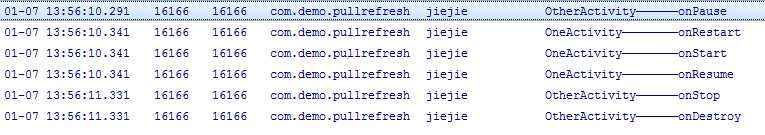
所以我们看下当我在一个Activity(one)来启动另一个Activity(other)随后finish otherActivity 来显示第一个Activity 然后在finish 第一个Activity的生命周期
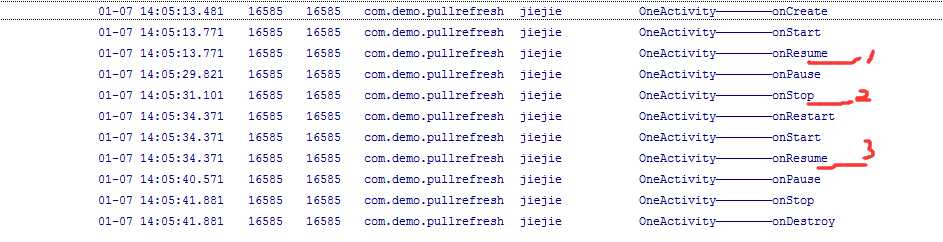
2. 点击跳转按钮,由OneActivity跳转到Otherdialog:
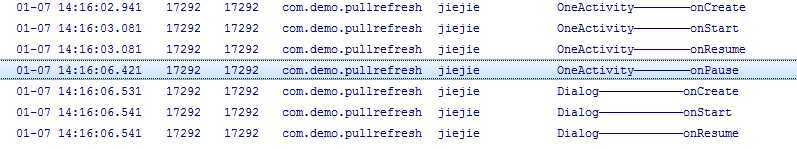
由于SecondActivity是Dialog,所以MainActivity依然可见,所以只调用了它的onPause()方法。
当OneActivity重新获取焦点
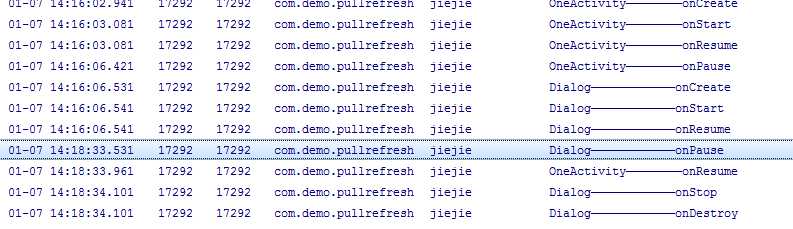
所以它的生命周期为
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/wangfengdange/p/5109794.html