标签:
一、策略模式介绍
策略模式:它定义了算法家族,分别封装起来,让它们之间可以互相替换,此模式让算法的变化不会影响到使用算法的客户。
例如:
商场中的收银软件,内部是怎么针对不同的商品打不同的折扣呢?又或者,是怎么根据不同会员等级打不同的折扣呢?
其实内部就是定义了一个算法家族,给每个会员或者商品都指定一个特定的算法,根据不同的算法,打不同的折扣。
策略模式UML图:
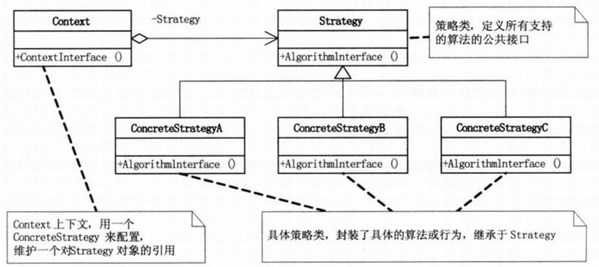
Strategy(抽象算法接口):定义了所有支持算法的公共接口
ConcreteStrategyA、ConcreteStrategyB和ConcreteStrategyC:继承于Strategy,封装了具体的算法
Context(上下文):用来维护不同对象的不同算法实现
二、策略模式代码实现
这里以不同的用户买商品打折为例
首先定义一个抽象算法接口:
1 2 3 4 5 | //抽象算法接口:定义了所有支持算法的公共接口public interface Strategy { //算法方法:打印商品的价格(不同的实现打不同的折扣) public double getPrice(double price);} |
然后定义具体的各个算法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 | //具体的算法:普通用户,不打折public class GeneralUser implements Strategy { @Override public double getPrice(double price) { System.out.println("普通用户,不打折"); return price; }}//具体的算法:注册用户:打9折public class RegisterUser implements Strategy{ @Override public double getPrice(double price) { System.out.println("注册用户:打9折"); return price*0.9; }}//具体的算法:普通会员:打8折public class RegisterVip implements Strategy{ @Override public double getPrice(double price) { System.out.println("普通会员:打8折"); return price*0.8; }}//具体的算法:老会员:打5折public class OldVip implements Strategy{ @Override public double getPrice(double price) { System.out.println("老会员:打5折"); return price*0.5; }} |
接下来开始定义一个上下文,用来维护不同用户不同的折扣。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 | //上下文:用来维护不同对象的不同折扣public class Context { private Strategy strategy;//持有算法族的引用 public Context(Strategy strategy) { super(); this.strategy = strategy; } //打印价钱 public void printPrice(double price){ System.out.println("应付金额:"+Math.round(strategy.getPrice(price))); }} |
客户端测试代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 | public static void main(String[] args) { double price = 998;//商品价格 Strategy generalUser = new GeneralUser();//普通用户 Strategy registerUser = new RegisterUser();//注册用户 Strategy registerVip = new RegisterVip();//普通会员 Strategy oldVip = new OldVip();//老会员 //根据不同的用户打不同的折扣 Context c1 = new Context(generalUser); c1.printPrice(price); Context c2 = new Context(registerUser); c2.printPrice(price); Context c3 = new Context(registerVip); c3.printPrice(price); Context c4 = new Context(oldVip); c4.printPrice(price);} |
打印结果如下:
普通用户,不打折
应付金额:998
注册用户:打9折
应付金额:898
普通会员:打8折
应付金额:798
老会员:打5折
应付金额:499
三、应用场景
策略模式本质:分离算法,选择不同的实现。
应用场景:
JAVASE的布局管理
Spring框架中,Resource接口,资源访问策略
javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet#service();
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/meet/p/5116419.html