标签:
progress_diplay可以在显示台显示程序执行的进度。
(1)类摘要
#include "stdafx.h" #include<stdlib.h> #include <vector> #include<iostream> #include <fstream> #include <boost/progress.hpp> using namespace std; using namespace boost; class progress_display : private noncopyable//noncopyable子类可以继承,但是禁止拷贝(即只能单例化) { public://explicit关键字,表示不能发生隐式转换 explicit progress_display( unsigned long expected_count, std::ostream & os = std::cout, const std::string & s1 = "\n", //leading strings const std::string & s2 = "", const std::string & s3 = "" ) // os is hint; implementation may ignore, particularly in embedded systems : m_os(os), m_s1(s1), m_s2(s2), m_s3(s3) { restart(expected_count); } void restart( unsigned long expected_count ) // Effects: display appropriate scale // Postconditions: count()==0, expected_count()==expected_count { _count = _next_tic_count = _tic = 0; _expected_count = expected_count; m_os << m_s1 << "0% 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100%\n" << m_s2 << "|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|----|" << std::endl // endl implies flush, which ensures display << m_s3; if ( !_expected_count ) _expected_count = 1; // prevent divide by zero } // restart unsigned long operator+=( unsigned long increment ) // Effects: Display appropriate progress tic if needed. // Postconditions: count()== original count() + increment // Returns: count(). { if ( (_count += increment) >= _next_tic_count ) { display_tic(); } return _count; } unsigned long operator++() { return operator+=( 1 ); } unsigned long count() const { return _count; } unsigned long expected_count() const { return _expected_count; } private: std::ostream & m_os; // may not be present in all imps const std::string m_s1; // string is more general, safer than const std::string m_s2; // const char *, and efficiency or size are const std::string m_s3; // not issues unsigned long _count, _expected_count, _next_tic_count; unsigned int _tic; void display_tic() { // use of floating point ensures that both large and small counts // work correctly. static_cast<>() is also used several places // to suppress spurious compiler warnings. unsigned int tics_needed = static_cast<unsigned int>( (static_cast<double>(_count)/_expected_count)*50.0 ); do { m_os << ‘*‘ << std::flush; } while ( ++_tic < tics_needed ); _next_tic_count = static_cast<unsigned long>((_tic/50.0)*_expected_count); if ( _count == _expected_count ) { if ( _tic < 51 ) m_os << ‘*‘; m_os << std::endl; } } // display_tic };
(2)用法
#include "stdafx.h" #include<stdlib.h> #include <vector> #include<iostream> #include <fstream> #include <boost/progress.hpp> using namespace std; using namespace boost; int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { vector<string> v(100); for (vector<string>::iterator& i=v.begin();i!=v.end();i++) { *i="asd"; } ofstream fs("./test.txt");//打开一个文件输出流,记得包含fstrean头文件 progress_display pd(v.size());//实例化一个显示类的基数(即进度条里最多的个数作为分母) for(vector<string>::iterator& x=v.begin();x!=v.end();x++) { fs<<*x<<endl;//想test写入文件 ++pd;//更新进度条 } return 0; }
3.注意事项
当我们想显示进度的同时还可以显示中间的一些空字符行号,当我们下面这样做时
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { vector<string> v(100,"aaa"); v[10]=""; v[23]=""; ofstream fs("./test.txt");//打开一个文件输出流,记得包含fstrean头文件 progress_display pd(v.size());//实例化一个显示类的基数(即进度条里最多的个数作为分母) for(vector<string>::iterator& x=v.begin();x!=v.end();x++) { fs<<*x<<endl;//想test写入文件 ++pd;//更新进度条 if(x->empty()) { cout<<"null string #"<<(x-v.begin()); } } return 0; }
当我们按上面这样做时会发现:
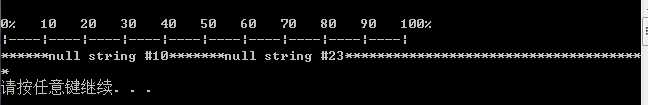
这样会打乱我们们进度条的显示:
所以我们只能下面这样做:
// test1.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点。 // #include "stdafx.h" #include<stdlib.h> #include <vector> #include<iostream> #include <fstream> #include <boost/progress.hpp> using namespace std; using namespace boost; int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[]) { vector<string> v(100,"aaa"); v[10]=""; v[23]=""; ofstream fs("./test.txt");//打开一个文件输出流,记得包含fstrean头文件 progress_display pd(v.size());//实例化一个显示类的基数(即进度条里最多的个数作为分母) for(vector<string>::iterator& x=v.begin();x!=v.end();x++) { fs<<*x<<endl;//想test写入文件 ++pd;//更新进度条 if(x->empty()) { cout<<"null string #"<<(x-v.begin()); pd.restart(v.size());//将pd重新设置到开始 pd+=(x-v.begin()+1);//同时再将进度显示到我们需要显示的那 } } return 0; }
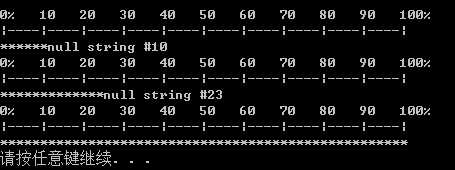
结果:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yanliang12138/p/5136407.html