标签:
作为测试,我使用的是二维平面坐标进行的。我们随机选取图片,使用OpenCV的Mat类对象读取图像文件中的数据,然后使用rand函数随机产生k(这里k值取决于输入)个二维坐标值。遍历整个图像像素位置,计算每个坐标相对于任意一个核心点之间的距离L^2(欧氏距离的平方,因为这样计算量会小一些),根据距离值对像素进行分类。当整个图像遍历一遍之后,我们有了一个初步的聚类,然而这个聚类是不好的,主要原因在于聚类的核心点是任意产生的(其原因是由于这个聚类方法是非监督的,我们对数据集和数据点是未知的)。我们需要对每一个数据集进行数据的修整。

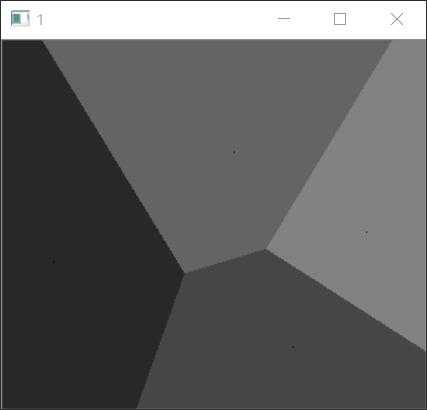
1聚类前图像 2 初步聚类后

3最终聚类后图像 (647*580分辨率)

4 随机点的分布
这3个图,大概能说明K-Means聚类方法的一些原因和问题了。
在看这3个图的时候,请忽略图像的大小变化,关注图像内部的比例变化更好一些(根据距离进行聚类,因此可以忽略不计)。
我在做K-Means 的时候,为了展现效果,将不同的数据集采用不同色彩进行标注,每一个色区中有一个点,标定核心点的位置。
我们可以看出,图2的聚类不规则,3图作为最终聚类的形式,有较大的改观,从4图可以发现,一开始的随机点分布并不如3图当中如此排列有序,但是经过修正后,基本上比较规则,但是仍然不是完全四等分,其中主要原因之一,就是随机点的获取影响的聚类的效果,在我们采取的聚类对象中,可能会好一点,但是在别的距类对象中(数据分布及其不均匀,这样的数据量很大)可能比较糟糕。
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<cv.hpp>
using cv::Mat;
using cv::imread;
using cv::imshow;
using cv::imwrite;
using cv::waitKey;
using cv::cvtColor;
//using cv::Point2i;
using std::vector;
using std::string;
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
//typedef Point2i Point;
struct Point
{
int x;
int y;
unsigned int gray;
unsigned int distance;
double weight;
Point()
{
x = 0;
y = 0;
gray = 0;
distance = 0;
weight = 0;
}
Point(int _x, int _y,unsigned int _gray=0,unsigned int _distance=0,int _weight=0) { x = _x; y = _y; gray =_gray; distance =_distance; weight = _weight; }
Point(const Point&_point) { this->x = _point.x; this->y = _point.y; this->gray = _point.gray; this->distance = _point.distance; this->weight = _point.weight; }
Point& operator=(const Point&_point) { this->x = _point.x; this->y = _point.y; this->gray = _point.gray; this->distance = _point.distance; this->weight = _point.weight; return *this; }
};
void dSort(vector<Point>*vec)
{
vector<Point>::iterator fIt = vec->begin();
for (; fIt != vec->end(); ++fIt)
{
for (vector<Point>::iterator sIt = fIt+1; sIt != vec->end(); ++sIt)
{
if (sIt->distance < fIt->distance)
{
Point tmp(*sIt);
*sIt=*fIt;
*fIt = tmp;
}
}
}
vector<Point>::iterator it = vec->begin();
}
void Weight(vector<Point>*vec,double alpha,double beta,double theta)
{
if (vec->empty())
{
cout << "container is empty" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "start sort" << endl;
dSort(vec);
cout << "end sort" << endl;
double cscore = 0.0;
double dscore = 0.0;
vector<Point>::iterator it = vec->begin();
for (; it != vec->end(); ++it)
{
dscore = (1 / (sqrt(2 * 3.14159)*beta))*(exp((it - vec->begin())*(it - vec->begin()) / (2 * beta*beta)));
//cout << dscore << endl;
dscore *= it->distance;
cscore = (1 / (sqrt(2 * 3.14159)*theta))*(exp((it - vec->begin())*(it - vec->begin()) / (2 * theta*theta)));
cscore *= it->gray;
it->weight = double(alpha*it->distance) + double((1 - alpha)*it->gray);
// cout << "weight=" << it->weight << endl;
}
cout << "after weight" << endl;
}
int squareDistance(const Point& p1, const Point &p2)
{
//cout <<"s"<<p1.x << "," << p1.y <<" "<<p2.x<<","<<p2.y<<endl;
return ((p1.x - p2.x)*(p1.x - p2.x) + (p1.y - p2.y)*(p1.y - p2.y));
}
int colorGap(Mat mat,const Point&p1, const Point&p2)
{
// cout << "c" << p1.x << "," << p1.y << " " << p2.x << "," << p2.y<<endl;
//cout<<"gap="<< abs(mat.at<uchar>(p1.x, p1.y) - mat.at<uchar>(p2.x, p2.y));
return abs(mat.at<uchar>(p1.x, p1.y) - mat.at<uchar>(p2.x, p2.y));
}
const Point & findCentre( vector<Point>&vec)
{
cout << "start centre" << endl;
vector<Point>::iterator it = vec.begin();
int xall = 0;
int yall = 0;
int weight = 0;
for (; it != vec.end(); ++it)
{
xall+= it->x;
yall += it->y;
}
weight=vec.size();
// cout << xall << ‘\t‘ << yall << ‘\t‘ << weight <<‘\t‘<<xall/weight<<endl;
cout << "end centre" << endl;
Point t(xall / weight, yall / weight);
cout << t.x <<‘\t‘<< t.y << endl;
vec.clear();
//cout << "xall=" << xall << "yall=" << yall << "weight=" << weight <<"xall/weight="<<xall/weight<<"yall/weight="<<yall/weight<< endl;
return t;
}
bool stopCondition(int num, Point*pt, vector<Point>*vec)
{
bool flag = 1;
for (int i = 0; i != num; ++i)
{
if (pt[i].x == vec[i].begin()->x&&pt[i].y == vec[i].begin()->y)
flag = flag & 1;
else
flag = flag & 0;
}
return flag;
}
void getPoint(Mat mat, vector<Point> *vec, int num = 5)
{
unsigned int Min = mat.rows*mat.rows + mat.cols*mat.cols;
int pos = 0;
for (int i = 0; i != mat.rows; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j != mat.cols; ++j)
{
Min = mat.rows*mat.rows + mat.cols*mat.cols;
pos = 0;
for (int k = 0; k != num; ++k)
{
Point tmp = *vec[k].begin();
if ((Min > squareDistance(Point(i, j), tmp)))//&&squareDistance(Point(i, j), tmp)<=l_gap)
{
Min = squareDistance(Point(i, j), tmp);
pos = k;
}
}
Point tmp(i, j, colorGap(mat, Point(i, j), vec[pos].front()), Min, 0);
vec[pos].push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
void K_Means(Mat&mat,vector<Point> *vec, int num = 5, double alpha = 0.5,int amp=10,int l_gap=20,int c_gap=30,double threshold=0.5 )
{
int amplitude = 15;
if (mat.empty())
{
cout << "please input the Mat" << endl;
return;
}
Point*start = new Point[num];
for (int i = 0; i != num; ++i)
start[i] = Point(0, 0);
for (int i = 0; i != num; ++i)
{
vec[i].push_back(Point(rand() % mat.rows, rand() % mat.cols));
cout << vec[i].front().x << "," << vec[i].front().y << endl;
}
while (!stopCondition(num, start, vec))
{
cout << "________________________" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i != num; ++i)
{
cout << "start" << start[i].x << ‘\t‘ << start[i].y << endl;
cout << "vec" << vec[i].begin()->x << ‘\t‘ << vec[i].begin()->y << endl;
}
cout << "_____________________________" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i != num; ++i)
{
start[i] = vec[i].front();
}
amplitude = 0;
getPoint(mat, vec, num);
cout << "get the weight and centre" << endl;
for (int x = 0; x != num; ++x)
{
cout << "num=" << x << endl;
// Weight(&vec[x], 0.5, 0.4, 0.4);
Point t(findCentre(vec[x]));
//*vec[x].begin() = t;
vec[x].push_back(t);
cout << vec[x].begin()->x << vec[x].begin()->y << endl;
}
}
getPoint(mat, vec, num);
cout << "paint" << endl;
/*
for (int i = 0; i != num; ++i)
{
double allweight = 0.0;
vector<Point>::iterator it = vec[i].begin();
for (; it != vec[i].end(); ++it)
allweight += it->weight;
it = vec[i].begin();
double aveweight = allweight / (vec[i].size());
*/
/*
for (int i = 0; i != mat.rows; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j != mat.cols; ++j)
mat.at<uchar>(i, j) = 255;
*/
for (int i = 0; i != num;++i)
{
vector<Point>::iterator it = vec[i].begin();
for (; it != vec[i].end(); ++it)
{
mat.at<uchar>(it->x, it->y) = 50 + i * 30;
}
mat.at<uchar>(vec[i].front().x, vec[i].front().y) = 0;
}
}
int main()
{
int number = 0;
vector<Point> *vec;
cin >> number;
vec = new vector<Point>[number];
// for (int i = 0; i != numbe)
Mat mat =imread("2.jpg");
cvtColor(mat, mat, CV_BGR2GRAY);
K_Means(mat, vec,number);
imshow("1", mat);
//imwrite(string("2.jpg"), mat);
waitKey(0);
}
代码格式杂乱无章,作为自己的笔记,先这么凑合吧,等把这个K-Means联合color因子的算法完全写出来,再进行调整也不晚。
这些代码中,其中Weight函数中提出了色彩+距离权重的计算,我们使用两个不同参数的高斯函数进行权重的规约(将数据按照距离进行排序,由小到大。距离越大,相对于高斯函数的中轴越远,将这个距离带入高斯函数中,最终权值较小)。色彩+距离这两个因子使用一个参数进行调节,控制这两个因子在权重中所占比率的大小,这样我感觉效果会好一些。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/dmq5488287/p/5155135.html