标签:
线性表是数据结构中最简单、最常用的一种线性结构,也是学习数据结构全部内容的基础,其掌握的好坏直接影响着后续知识的学习。下面将通过四个模拟项目来学习线性表的顺序和链式存储结构。
一、学生成绩管理
1、项目简介
学生成绩管理师学校教务部门日常工作的重要组成部分,处理信息量很大。本项目是对学生成绩管理的简单模拟,用菜单选择方式完成下列功能:输出学生数据、学生数据查询、添加学生数据、修改学生数据、删除学生数据。
2、设计思路
本项目的实质是完成对学生成绩信息的建立、查找、插入、修改、删除等功能,可以首先定义项目中的数据结构,然后将每个功能写成一个函数来完成对数据的操作,最后完成主函数以验证各个函数功能并得出运行结果。
3、数据结构
本项目的数据是一组学生的成绩信息,每条学生的成绩信息由学号、姓名、成绩组成,这组学生的成绩信息具有相同特性,数以同一数据对象,相邻数据元素之间存在序偶关系。由此可以看出,这些数据具有线性表中数据元素的性质, 所以该系统的数据采用线性表来存储。
顺序表示线性表的顺序存储结构,是指用一组连续的内存单元依次存放线性表的数据元素。在顺序存储结构下,逻辑关系相邻的两个元素在物理位置上也相邻,这是顺序表的特点。本项目可以采用顺序表的线性表顺序存储结构。
顺序表便于进行随机访问,故线性表的顺序存储结构是一种随机存储结构。
顺序表适宜用于查找这样的静态操作,其优点在于存储密度大。存储空间利用率高,缺点是插入或删除时不方便。
用结构体类型定义每个学生数据,该数组中的每个数据的结构可描述为:
1 typedef struct STU{ 2 char stuno[10]; //学号 3 char name[10]; //姓名 4 float score; //成绩 5 }ElemType;
4、程序清单

1 /*线性表1*/ 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <iomanip> 4 #include <malloc.h> 5 #include <string.h> 6 using namespace std; 7 8 #define MaxListSize 20 9 #define EQUAL 1 10 typedef struct STU{ 11 char stuno[10]; 12 char name[10]; 13 float score; 14 int age; 15 }ElemType; 16 class List{ 17 private: 18 //线性表的数组表示 19 ElemType elem[MaxListSize]; 20 int length; 21 int MaxSize; 22 public: 23 void init(List **L,int ms); //输入学生数据 24 void DestoryList(List &L){ //删除所有学生数据 25 free(&L); 26 } 27 void ClearList(){ //将顺序表置为空表 28 length = 0; 29 } 30 bool ListEnpty(){ //判断顺序表是否为空表 31 return length == 0; 32 } 33 bool ListFull(){ //判断顺序表是否为满 34 return length == MaxSize; 35 } 36 bool ListDelete(int , ElemType &e); //删除某个学生数据 37 void ListTraverse(); //遍历顺序表 38 int ListLength(); //返回顺序表的长度 39 void GetElem(int , ElemType *); //学生数据查询 40 bool UpdateList(ElemType &e, ElemType); //修改学生数据 41 bool ListInsert(int, ElemType &); //添加学生数据 42 void printlist(int); 43 bool Less_EqualList(ElemType *e1,ElemType *e2); 44 bool LocateElem(ElemType e, int type); 45 bool EqualList(ElemType *e1,ElemType *e2); 46 }; 47 48 //接口实现 49 void List::init(List **L, int ms){ 50 *L = (List *)malloc(sizeof(List)); 51 (*L)->length = 0; 52 (*L)->MaxSize = ms; 53 } 54 55 int List::ListLength(){ 56 return length; 57 } 58 59 bool List::ListDelete(int mark, ElemType &e){ 60 int i,j; 61 if(ListEnpty()) 62 return false; 63 if(mark>0){//删除表头元素 64 e = elem[0]; 65 for(i = 1; i < length;i++ ) 66 elem[i-1] = elem[i]; 67 }else if(mark < 0){ 68 e = elem[length-1]; 69 }else{ 70 for(i =0;i<length;i++) 71 if(strcmp(elem[i].name,e.name) == 0) 72 break; 73 if(i>=length)return false; 74 else e=elem[i]; 75 for(j = i+1;j<length;j++) 76 elem[j-1] = elem[j]; 77 } 78 length--; 79 return true; 80 } 81 82 void List::ListTraverse(){ 83 for(int i=0;i<length;i++){ 84 cout<<setw(8)<<elem[i].name; 85 cout<<setw(10)<<elem[i].stuno; 86 cout<<setw(9)<<elem[i].age; 87 cout<<setw(8)<<elem[i].score<<endl; 88 } 89 } 90 91 void List::GetElem(int i, ElemType *e){ 92 *e = elem[i]; 93 } 94 95 bool List::EqualList(ElemType *e1,ElemType *e2){ 96 if(strcmp(e1->name,e2->name)) 97 return false; 98 if(strcmp(e1->stuno,e2->stuno)) 99 return false; 100 if(e1->age != e2->age) 101 return false; 102 if(e1->score != e2->score) 103 return false; 104 return true; 105 } 106 107 bool List::Less_EqualList(ElemType *e1,ElemType *e2){ 108 if(strcmp(e1->name,e2->name) <= 0) 109 return true; 110 else 111 return false; 112 } 113 114 bool List::LocateElem(ElemType e, int type){ 115 int i; 116 switch(type){ 117 case EQUAL: 118 for(i=0;i<length;i++) 119 if(EqualList(&elem[i],&e)) 120 return true; 121 break; 122 default: 123 break; 124 } 125 return false; 126 } 127 128 bool List::UpdateList(ElemType &e, ElemType e1){ 129 for(int i=0;i<length;i++) 130 if(strcmp(elem[i].name,e.name) == 0){ 131 elem[i] = e1; 132 return true; 133 } 134 return false; 135 } 136 137 bool List::ListInsert(int i, ElemType &e){ 138 ElemType *p,*q; 139 if(i <1 || i>length+1)return false; 140 q = &elem[i-1]; 141 for(p = &elem[length-1];p >= q;--p) 142 *(p+1) = *p; 143 *q = e; 144 ++length; 145 return true; 146 } 147 148 void List::printlist(int mark){ 149 int *b = new int[length]; 150 int i,k; 151 cout<<" 姓名 学号 年龄 成绩\n"; 152 if(mark != 0){ 153 for(i=0;i<length;i++)b[i] = i; 154 for(i = 0;i<length;i++){ 155 k = i; 156 for(int j=i+1;j<length;j++){ 157 if(mark == 1 &&elem[b[j]].score < elem[b[k]].score) 158 k = j; 159 if(mark == -1 && elem[b[k]].score < elem[b[j]].score) 160 k = j; 161 } 162 if(k != i){ 163 int x= b[i]; 164 b[i] = b[k]; 165 b[k] = x; 166 } 167 } 168 for(int i = 0;i<length;i++){ 169 cout<<setw(8)<<elem[b[i]].name; 170 cout<<setw(10)<<elem[b[i]].stuno; 171 cout<<setw(9)<<elem[b[i]].age; 172 cout<<setw(8)<<elem[b[i]].score<<endl; 173 } 174 }else{ 175 for(i = 0;i<length;i++){ 176 cout<<setw(8)<<elem[i].name; 177 cout<<setw(10)<<elem[i].stuno; 178 cout<<setw(9)<<elem[i].age; 179 cout<<setw(8)<<elem[i].score<<endl; 180 } 181 } 182 } 183 184 //main函数 185 void main(){ 186 cout<<"linelise1m.cpp 运行结果:\n"; 187 ElemType e1,e2,e3,e4,e5,e6; 188 List *La,*Lb; 189 int k; 190 cout<<"首先调用插入函数.\n"; 191 La->init(&La,4); 192 strcpy(e1.name,"stu1"); 193 strcpy(e1.stuno,"100001"); 194 e1.age = 22; 195 e1.score = 88; 196 La->ListInsert(1,e1); 197 strcpy(e2.name,"stu2"); 198 strcpy(e2.stuno,"100002"); 199 e2.age=21; 200 e2.score=79; 201 La->ListInsert(2,e2); 202 strcpy(e3.name,"stu3"); 203 strcpy(e3.stuno,"100003"); 204 e3.age=19; 205 e3.score=87; 206 La->ListInsert(3,e3); 207 La->printlist(0); 208 cout<<"表La长:"<<La->ListLength()<<endl; 209 cin.get(); 210 211 Lb->init(&Lb,4); 212 strcpy(e4.name,"zmofun"); 213 strcpy(e4.stuno,"100001"); 214 e4.age=20; 215 e4.score=94; 216 Lb->ListInsert(1,e4); 217 strcpy(e5.name,"bobjin"); 218 strcpy(e5.stuno,"100002"); 219 e5.age=23; 220 e5.score=69; 221 Lb->ListInsert(2,e5); 222 strcpy(e6.name,"stu1"); 223 strcpy(e6.stuno,"100001"); 224 e6.age=22; 225 e6.score=88; 226 Lb->ListInsert(3,e6); 227 Lb->printlist(0); 228 cout<<"表Lb长:"<<Lb->ListLength()<<endl; 229 cin.get(); 230 231 k=Lb->ListDelete(-1,e6); 232 if(k==0) cout<<"删除失败!\n"; 233 else cout<<"删除成功!\n"; 234 cout<<"输出表Lb:\n"; 235 Lb->printlist(0); 236 cin.get(); 237 cout<<"按成绩升序输出表Lc\n"; 238 Lb->printlist(1);cin.get(); 239 cout<<"按成绩降序输出表Lc\n"; 240 Lb->printlist(-1);cin.get(); 241 242 }
结果如图:
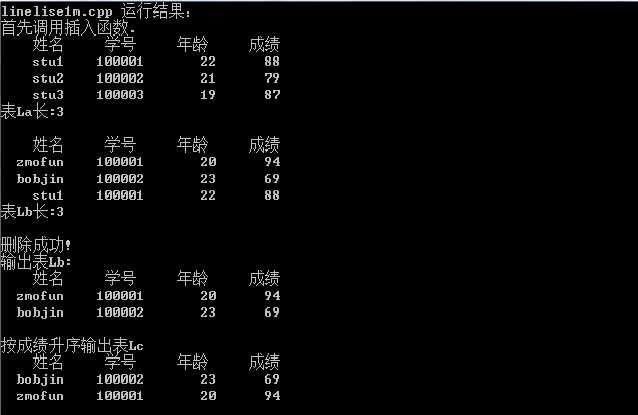
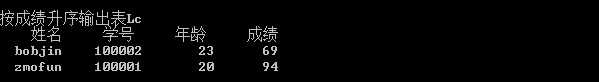
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/baodaren/p/5165922.html