标签:
数组的特点是:寻址容易,插入和删除困难;而链表的特点是:寻址困难,插入和删除容易。那么我们能不能综合两者的特性,做出一种寻址容易,插入删除也容易的数据结构?答案是肯定的,这就是我们要提起的哈希表,哈希表有多种不同的实现方法,我接下来解释的是最常用的一种方法—— 拉链法,我们可以理解为“链表的数组” ,如图:
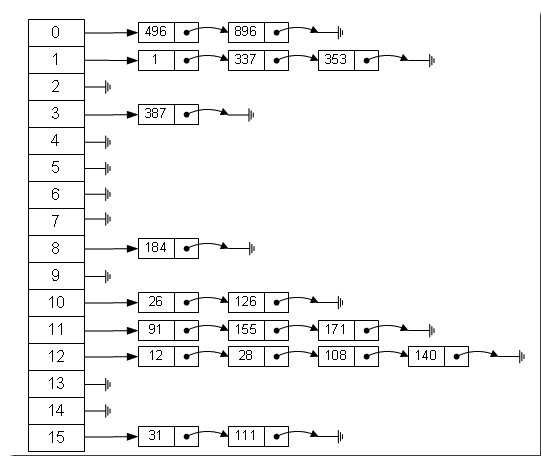
从上图我们可以发现哈希表是由数组+链表组成的,一个长度为16的数组中,每个元素存储的是一个链表的头结点。那么这些元素是按照什么样的规则存储到数组中呢。一般情况是通过hash(key)%len获得,也就是元素的key的哈希值对数组长度取模得到。比如上述哈希表中,12%16=12,28%16=12,108%16=12,140%16=12。所以12、28、108以及140都存储在数组下标为12的位置。
HashMap其实也是一个线性的数组实现的,所以可以理解为其存储数据的容器就是一个线性数组。这可能让我们很不解,一个线性的数组怎么实现按键值对来存取数据呢?这里HashMap有做一些处理。
1.首先HashMap里面实现一个静态内部类Entry,其重要的属性有 key , value, next,从属性key,value我们就能很明显的看出来Entry就是HashMap键值对实现的一个基础bean,我们上面说到HashMap的基础就是一个线性数组,这个数组就是Entry[],Map里面的内容都保存在Entry[]里面。
既然是线性数组,为什么能随机存取?这里HashMap用了一个小算法,大致是这样实现:

//存储时: int hash = key.hashCode();// 这个hashCode方法这里不详述,只要理解每个key的hash是一个固定的int值 int index = hash % Entry[].length; Entry[index] = value; //取值时: int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = hash % Entry[].length; return Entry[index];
到这里我们轻松的理解了HashMap通过键值对实现存取的基本原理
3.疑问:如果两个key通过hash%Entry[].length得到的index相同,会不会有覆盖的危险?
这里HashMap里面用到链式数据结构的一个概念。上面我们提到过Entry类里面有一个next属性,作用是指向下一个Entry。打个比方, 第一个键值对A进来,通过计算其key的hash得到的index=0,记做:Entry[0] = A。一会后又进来一个键值对B,通过计算其index也等于0,现在怎么办?HashMap会这样做:B.next = A,Entry[0] = B,如果又进来C,index也等于0,那么C.next = B,Entry[0] = C;这样我们发现index=0的地方其实存取了A,B,C三个键值对,他们通过next这个属性链接在一起。所以疑问不用担心。也就是说数组中存储的是最后插入的元素。到这里为止,HashMap的大致实现,我们应该已经清楚了。
当然HashMap里面也包含一些优化方面的实现,这里也说一下。比如:Entry[]的长度一定后,随着map里面数据的越来越长,这样同一个index的链就会很长,会不会影响性能?HashMap里面设置一个因素(也称为因子),随着map的size越来越大,Entry[]会以一定的规则加长长度。
Java中hashmap的解决办法就是采用的链地址法。

package com.tfdd.www; /** * @desc * @author chenqm * @date 2016年1月29日 */ public class Entry<K,V> { private final K key; private V value; private Entry<K,V> next; public Entry(K k,V v,Entry<K,V> entry){ key = k ; value = v; next = entry; } public V getValue() { return value; } public void setValue(V value) { this.value = value; } public Entry<K, V> getNext() { return next; } public void setNext(Entry<K, V> next) { this.next = next; } public K getKey() { return key; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + ((key == null) ? 0 : key.hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((next == null) ? 0 : next.hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((value == null) ? 0 : value.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if (this == obj) return true; if (obj == null) return false; if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) return false; Entry other = (Entry) obj; if (key == null) { if (other.key != null) return false; } else if (!key.equals(other.key)) return false; if (next == null) { if (other.next != null) return false; } else if (!next.equals(other.next)) return false; if (value == null) { if (other.value != null) return false; } else if (!value.equals(other.value)) return false; return true; } }

package com.tfdd.www; /** * @desc * @author chenqm * @date 2016年1月29日 */ public class MyHashMap<K,V> { private Entry[] table;//Entry数组表 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY =16; private int size; public MyHashMap() { table = new Entry[DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY]; size = DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY; } //获取数组长度 public int getSize() { return size; } static int indexFor(int h, int length) { return h % length ; } public V get(K key){ if(key==null) return null; int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = indexFor(hash,table.length); for(Entry<K,V> e = table[index];e!=null;e = e.getNext()){ K k = e.getKey(); if(e.getKey().hashCode() == hash &&(key ==k ||k.equals(key))){ return e.getValue(); } } return null; } public V put(K key, V value){ if(key == null) return null; int hash = key.hashCode(); int index = indexFor(hash,table.length); for(Entry<K,V> e = table[index];e!=null;e = e.getNext()){ K k = e.getKey(); if(e.getKey().hashCode() == hash &&(key ==k ||k.equals(key))){ //已经存在 V oldValue = e.getValue(); e.setValue(value); return oldValue; } } //不存在 Entry<K,V> e = table[index]; table[index] = new Entry<K,V>(key,value,e); return null; } }

package com.tfdd.www; /** * @desc * @author chenqm * @date 2016年1月29日 */ public class MyHashMapTest { public static void main(String[] args) { MyHashMap<String,String> map = new MyHashMap<String,String>(); map.put("1", "1"); map.put("2", "2"); map.put("3", "3"); System.out.println(map.get("2")); System.out.println(map.get("3")); } }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/think-in-java/p/5169660.html