标签:
我们先来看一个图
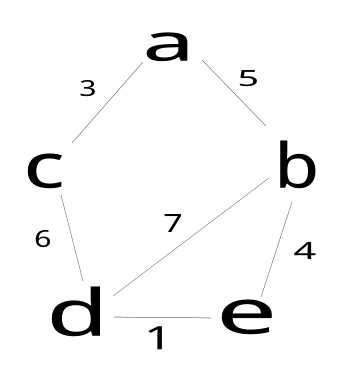
我们想将这个图的信息存储到邻接表中,我们需要一个数组保存节点信息,还要有一个节点用来保存与该节点相邻的节点信息.
1 typedef struct arc_node 2 { 3 int pos; 4 int distance; 5 struct arc_node * next; 6 } Arc_node;//保存Node节点的相邻节点信息 7 8 typedef struct node 9 { 10 node_type info; 11 Arc_node * next; 12 } Node;//保存节点信息 13 14 typedef struct graph 15 { 16 Node vertexs[MAX_NUM]; 17 int vertex, arc; 18 } Graph;//邻接表
如果将上面的图用邻接表存储,我们将回看到这样一幅图
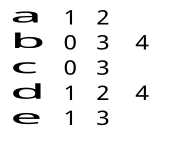
每个字符后面的数字代表与它相邻的节点在数组中的位置(在Arc_node里存有权值,这里没有显示)
构造邻接表:
1)先输入节点个数及节点信息.
2)在输入某节点的相邻节点及权值.(这时,每输入一个相邻节点,就构建一个Arc_node节点,将Arc_node接到该节点的最后)
1 void g_create(Graph * graph) 2 { 3 int num; 4 int i, j, k; 5 char c; 6 Arc_node * tmp; 7 8 printf("输入节点个数:"); 9 scanf("%d", &graph->vertex); 10 getchar(); 11 printf("输入顶点信息:"); 12 for ( i = 0; i < graph->vertex; i++ ) 13 { 14 scanf("%c", &graph->vertexs[i].info); 15 graph->vertexs[i].next = NULL; 16 getchar(); 17 } 18 19 for ( i = 0; i < graph->vertex; i++ ) 20 { 21 printf("输入与节点%c相邻的节点和权值,#号键结束\n", graph->vertexs[i].info); 22 for ( j = 0; j < graph->vertex; j++ ) 23 { 24 scanf("%c", &c); 25 if ( c == ‘#‘ ) 26 { 27 getchar(); 28 break; 29 } 30 scanf("%d", &num); 31 getchar(); 32 for ( k = 0; k < graph->vertex; k++ ) 33 { 34 if ( graph->vertexs[k].info != c ) 35 continue; 36 if ( graph->vertexs[k].next == NULL ) 37 graph->vertexs[k].next = make_node(i, num); 38 else 39 { 40 tmp = graph->vertexs[k].next; 41 while ( tmp->next != NULL ) 42 tmp = tmp->next; 43 tmp->next = make_node(i, num); 44 } 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 }
深度优先遍历
邻接表的深度优先遍历根邻接矩阵的差不多.只是由于数据的存储方式有点差别,所以代码实现会有些不同,但思路还是一样的.
1 static void dfs_graph(Graph * graph, bool visited[], const int i); 2 void g_depth_first_search(Graph * graph) 3 { 4 bool visited[graph->vertex]; 5 int i; 6 7 for ( i = 0; i < graph->vertex; i++ ) 8 visited[i] = false; 9 10 visited[0] = true; 11 dfs_graph(graph, visited, 0); 12 } 13 14 static void dfs_graph(Graph * graph, bool visited[], const int i) 15 { 16 Arc_node * tmp; 17 printf("%c\t", graph->vertexs[i].info); 18 19 tmp = graph->vertexs[i].next; 20 while ( tmp != NULL ) 21 { 22 if ( !visited[tmp->pos] ) 23 { 24 visited[tmp->pos] = true; 25 dfs_graph(graph, visited, tmp->pos); 26 } 27 tmp = tmp->next; 28 } 29 }
广度优先遍历
1 void g_breadth_first_search(Graph * graph) 2 { 3 Queue queue; 4 bool visited[graph->vertex]; 5 int pos; 6 int i; 7 Arc_node * tmp; 8 9 q_init(&queue); 10 for ( i = 0; i < graph->vertex; i++ ) 11 visited[i] = false; 12 13 visited[0] = true; 14 q_push(&queue, 0); 15 while ( !q_empty(&queue) ) 16 { 17 pos = q_front(&queue); 18 printf("%c\t", graph->vertexs[pos].info); 19 tmp = graph->vertexs[pos].next; 20 while ( tmp != NULL ) 21 { 22 if ( !visited[tmp->pos] ) 23 { 24 visited[tmp->pos] = true; 25 q_push(&queue, tmp->pos); 26 } 27 tmp = tmp->next; 28 } 29 q_pop(&queue); 30 } 31 printf("\n"); 32 }
对于深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历的算法思路不清楚的同学请先看邻接矩阵.
graph.c
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include "aqueue.h" #define MAX_NUM 100 typedef char node_type; typedef struct arc_node { int pos; int distance; struct arc_node * next; } Arc_node;//保存Node节点的相邻节点信息 typedef struct node { node_type info; Arc_node * next; } Node;//保存节点信息 typedef struct graph { Node vertexs[MAX_NUM]; int vertex, arc; } Graph;//邻接表 static Arc_node * make_node(const int pos, const int distance) { Arc_node * new_node = (Arc_node *)malloc( sizeof(Arc_node) ); if ( new_node == NULL ) exit(1); new_node->next = NULL; new_node->distance = distance; new_node->pos = pos; return new_node; } void g_create(Graph * graph) { int num; int i, j, k; char c; Arc_node * tmp; printf("输入节点个数:"); scanf("%d", &graph->vertex); getchar(); printf("输入顶点信息:"); for ( i = 0; i < graph->vertex; i++ ) { scanf("%c", &graph->vertexs[i].info); graph->vertexs[i].next = NULL; getchar(); } for ( i = 0; i < graph->vertex; i++ ) { printf("输入与节点%c相邻的节点和权值,#号键结束\n", graph->vertexs[i].info); for ( j = 0; j < graph->vertex; j++ ) { scanf("%c", &c); if ( c == ‘#‘ ) { getchar(); break; } scanf("%d", &num); getchar(); for ( k = 0; k < graph->vertex; k++ ) { if ( graph->vertexs[k].info != c ) continue; if ( graph->vertexs[k].next == NULL ) graph->vertexs[k].next = make_node(i, num); else { tmp = graph->vertexs[k].next; while ( tmp->next != NULL ) tmp = tmp->next; tmp->next = make_node(i, num); } } } } } static void dfs_graph(Graph * graph, bool visited[], const int i); void g_depth_first_search(Graph * graph) { bool visited[graph->vertex]; int i; for ( i = 0; i < graph->vertex; i++ ) visited[i] = false; visited[0] = true; dfs_graph(graph, visited, 0); } static void dfs_graph(Graph * graph, bool visited[], const int i) { Arc_node * tmp; printf("%c\t", graph->vertexs[i].info); tmp = graph->vertexs[i].next; while ( tmp != NULL ) { if ( !visited[tmp->pos] ) { visited[tmp->pos] = true; dfs_graph(graph, visited, tmp->pos); } tmp = tmp->next; } } void g_breadth_first_search(Graph * graph) { Queue queue; bool visited[graph->vertex]; int pos; int i; Arc_node * tmp; q_init(&queue); for ( i = 0; i < graph->vertex; i++ ) visited[i] = false; visited[0] = true; q_push(&queue, 0); while ( !q_empty(&queue) ) { pos = q_front(&queue); printf("%c\t", graph->vertexs[pos].info); tmp = graph->vertexs[pos].next; while ( tmp != NULL ) { if ( !visited[tmp->pos] ) { visited[tmp->pos] = true; q_push(&queue, tmp->pos); } tmp = tmp->next; } q_pop(&queue); } printf("\n"); } int main(void) { Graph graph; Arc_node * node; int i; g_create(&graph); for ( i = 0; i < graph.vertex; i++ ) { printf("%c\t", graph.vertexs[i].info); node = graph.vertexs[i].next; while ( node != NULL ) { printf("%d %d\t", node->distance, node->pos); node = node->next; } printf("\n"); } printf("\n"); g_depth_first_search(&graph); printf("\n"); g_breadth_first_search(&graph); return 0; }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ITgaozy/p/5187526.html