标签:
在上一篇我简单介绍了MSMQ的相关概念,本篇将以代码说明
Message是MSMQ的数据存储单元,我们的用户数据一般也被填充在Message的body当中,因此很重要,让我们来看一看其在.net中的体现,如图:
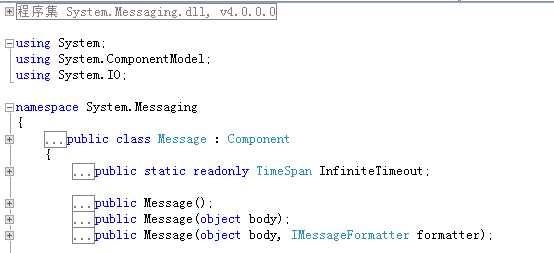
在图上我们可以看见,Message提供了三个构造函数,参数body表示我们的用户数据,当我们在构造函数中传入,数据最终会被赋值给其同名属性body,参数formatter对应同名属性Formatter,它是一个序列化器,当我们的用户数据是一个复杂类型,比如类的时候Message会自动采用该序列化器将我们的复杂类型序列化。message支持3种序列化对象:
-- XMLMessageFormatter对象----MessageQueue组件的默认格式化程序设置。
-- BinaryMessageFormatter对象;
-- ActiveXMessageFormatter对象;
由于后两者格式化后的消息通常不能为人阅读,所以我们经常用到的是XMLMessageFormatter对象。该对象构造方法有三种重载:
public XmlMessageFormatter(); public XmlMessageFormatter(string[] targetTypeNames); public XmlMessageFormatter(Type[] targetTypes);
消息(Message)需要保存在msmq队列中,.net中采用System.Messaging.MessageQueue来管理MSMQ队列,它提供能操作MSMQ的绝大多数API,比如
1.判断指定路径的队列是否存在。其中path代表队列的路径,表示形式为"主机名\队列名称",例如:".\private$\myQueue",其中"."代表本地主机,"\private$\myQueue"则代表队列的名称,"private$"表示我们创建的是专用队列,在网络上我们可以通过路径来唯一确定一个队列。
public static bool Exists(string path);
2.创建队列。path代表队列的路径,transactional表示是否创建事务队列,默认为fasle。关于事务队列我在上一篇做了详细的论述,这里不在重复。
public static MessageQueue Create(string path); public static MessageQueue Create(string path, bool transactional);
3.删除队列
public static void Delete(string path);
4.发送消息到MSMQ。obj代表我们的用户数据,transation表示将我们的发送操作纳入事务当中。在前面我们说过MSMQ接收的是Message,但是在这里我们看到Send操作并未强制要求我们采用Message类型参数。这是因为当我传入一个Object参数数据时,在Send操作的内部自动的给我们创建了一个Message消息对象,并且将我们的传入的Object参数采用默认的序列化器序列化,然后装入Message的body属性当中,如果我们在Send方法中指定label属性,它将被赋值给Message的同名Label属性。当然我们完全可以自定义一个message对象传入Send方法中
public void Send(object obj); public void Send(object obj, MessageQueueTransaction transaction); public void Send(object obj, string label);
5.接收消息。同理接收消息也可以被纳入事务当中,采用Receive方法在取MSMQ的消息时,如果成功,会把MSMQ的对应消息给删除掉,并且只能取到消息队里中的排队头的消息。
public Message Receive(); public Message Receive(MessageQueueTransaction transaction); public Message Receive(TimeSpan timeout);
如果我们想取指定标识的消息,就的采用如下的方法了,id代表消息的唯一标示。
public Message ReceiveById(string id); public Message ReceiveById(string id, MessageQueueTransaction transaction);
如果我们在接收消息的后,不想把MSMQ队列中的消息删除怎么办呢?那么采用下面的方法吧,因为这两个方法接收MSMQ的消息,不会删除MSMQ中对应的消息,所以他们不支持事务,即没有提供事务的参数。
public Message Peek(); public Message PeekById(string id);
我们也可以一次性吧队列里面的所有消息取出来
public Message[] GetAllMessages();
说了这么多,下面让我们来代码实战一下,我们采用控制台程序做测试,我把MSMQ队列做了简单的封装,如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
public class QueueManger
{
/// <summary>
/// 创建MSMQ队列
/// </summary>
/// <param name="queuePath">队列路径</param>
/// <param name="transactional">是否事务队列</param>
public static void Createqueue(string queuePath, bool transactional = false)
{
try
{
//判断队列是否存在
if (!MessageQueue.Exists(queuePath))
{
MessageQueue.Create(queuePath);
Console.WriteLine(queuePath + "已成功创建!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(queuePath + "已经存在!");
}
}
catch (MessageQueueException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除队列
/// </summary>
/// <param name="queuePath"></param>
public static void Deletequeue(string queuePath)
{
try
{
//判断队列是否存在
if (MessageQueue.Exists(queuePath))
{
MessageQueue.Delete(@".\private$\myQueue");
Console.WriteLine(queuePath + "已删除!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(queuePath + "不存在!");
}
}
catch (MessageQueueException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 发送消息
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">用户数据类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="target">用户数据</param>
/// <param name="queuePath">队列名称</param>
/// <param name="tran"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool SendMessage<T>(T target, string queuePath, MessageQueueTransaction tran = null)
{
try
{
//连接到本地的队列
MessageQueue myQueue = new MessageQueue(queuePath);
System.Messaging.Message myMessage = new System.Messaging.Message();
myMessage.Body = target;
myMessage.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(T) });
//发送消息到队列中
if (tran == null)
{
myQueue.Send(myMessage);
}
else
{
myQueue.Send(myMessage, tran);
}
Console.WriteLine("消息已成功发送到"+queuePath + "队列!");
return true;
}
catch (ArgumentException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 接收消息
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">用户的数据类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="queuePath">消息路径</param>
/// <returns>用户填充在消息当中的数据</returns>
public static T ReceiveMessage<T>(string queuePath,MessageQueueTransaction tran=null)
{
//连接到本地队列
MessageQueue myQueue = new MessageQueue(queuePath);
myQueue.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(T) });
try
{
//从队列中接收消息
System.Messaging.Message myMessage = tran == null ? myQueue.Receive() : myQueue.Receive(tran);
return (T)myMessage.Body; //获取消息的内容
}
catch (MessageQueueException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
catch (InvalidCastException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
return default(T);
}
/// <summary>
/// 采用Peek方法接收消息
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">用户数据类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="queuePath">队列路径</param>
/// <returns>用户数据</returns>
public static T ReceiveMessageByPeek<T>(string queuePath)
{
//连接到本地队列
MessageQueue myQueue = new MessageQueue(queuePath);
myQueue.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(T) });
try
{
//从队列中接收消息
System.Messaging.Message myMessage = myQueue.Peek();
return (T)myMessage.Body; //获取消息的内容
}
catch (MessageQueueException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
catch (InvalidCastException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
return default(T);
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取队列中的所有消息
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">用户数据类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="queuePath">队列路径</param>
/// <returns>用户数据集合</returns>
public static List<T> GetAllMessage<T>(string queuePath)
{
MessageQueue myQueue = new MessageQueue(queuePath);
myQueue.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(T) });
try
{
Message[] msgArr= myQueue.GetAllMessages();
List<T> list=new List<T>();
msgArr.ToList().ForEach((o) =>
{
list.Add((T)o.Body);
});
return list;
}
catch(Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
return null;
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
public class QueueManger
{
/// <summary>
/// 创建MSMQ队列
/// </summary>
/// <param name="queuePath">队列路径</param>
/// <param name="transactional">是否事务队列</param>
public static void Createqueue(string queuePath, bool transactional = false)
{
try
{
//判断队列是否存在
if (!MessageQueue.Exists(queuePath))
{
MessageQueue.Create(queuePath);
Console.WriteLine(queuePath + "已成功创建!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(queuePath + "已经存在!");
}
}
catch (MessageQueueException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 删除队列
/// </summary>
/// <param name="queuePath"></param>
public static void Deletequeue(string queuePath)
{
try
{
//判断队列是否存在
if (MessageQueue.Exists(queuePath))
{
MessageQueue.Delete(@".\private$\myQueue");
Console.WriteLine(queuePath + "已删除!");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine(queuePath + "不存在!");
}
}
catch (MessageQueueException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 发送消息
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">用户数据类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="target">用户数据</param>
/// <param name="queuePath">队列名称</param>
/// <param name="tran"></param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static bool SendMessage<T>(T target, string queuePath, MessageQueueTransaction tran = null)
{
try
{
//连接到本地的队列
MessageQueue myQueue = new MessageQueue(queuePath);
System.Messaging.Message myMessage = new System.Messaging.Message();
myMessage.Body = target;
myMessage.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(T) });
//发送消息到队列中
if (tran == null)
{
myQueue.Send(myMessage);
}
else
{
myQueue.Send(myMessage, tran);
}
Console.WriteLine("消息已成功发送到"+queuePath + "队列!");
return true;
}
catch (ArgumentException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
return false;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 接收消息
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">用户的数据类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="queuePath">消息路径</param>
/// <returns>用户填充在消息当中的数据</returns>
public static T ReceiveMessage<T>(string queuePath,MessageQueueTransaction tran=null)
{
//连接到本地队列
MessageQueue myQueue = new MessageQueue(queuePath);
myQueue.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(T) });
try
{
//从队列中接收消息
System.Messaging.Message myMessage = tran == null ? myQueue.Receive() : myQueue.Receive(tran);
return (T)myMessage.Body; //获取消息的内容
}
catch (MessageQueueException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
catch (InvalidCastException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
return default(T);
}
/// <summary>
/// 采用Peek方法接收消息
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">用户数据类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="queuePath">队列路径</param>
/// <returns>用户数据</returns>
public static T ReceiveMessageByPeek<T>(string queuePath)
{
//连接到本地队列
MessageQueue myQueue = new MessageQueue(queuePath);
myQueue.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(T) });
try
{
//从队列中接收消息
System.Messaging.Message myMessage = myQueue.Peek();
return (T)myMessage.Body; //获取消息的内容
}
catch (MessageQueueException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
catch (InvalidCastException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
return default(T);
}
/// <summary>
/// 获取队列中的所有消息
/// </summary>
/// <typeparam name="T">用户数据类型</typeparam>
/// <param name="queuePath">队列路径</param>
/// <returns>用户数据集合</returns>
public static List<T> GetAllMessage<T>(string queuePath)
{
MessageQueue myQueue = new MessageQueue(queuePath);
myQueue.Formatter = new XmlMessageFormatter(new Type[] { typeof(T) });
try
{
Message[] msgArr= myQueue.GetAllMessages();
List<T> list=new List<T>();
msgArr.ToList().ForEach((o) =>
{
list.Add((T)o.Body);
});
return list;
}
catch(Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
return null;
}
}
}
我们的用户实体也很简单,如下
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
public class Student
{
/// <summary>
/// 年龄
/// </summary>
public int Age { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 姓名
/// </summary>
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
public class Student
{
/// <summary>
/// 年龄
/// </summary>
public int Age { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// 姓名
/// </summary>
public string Name { get; set; }
}
}
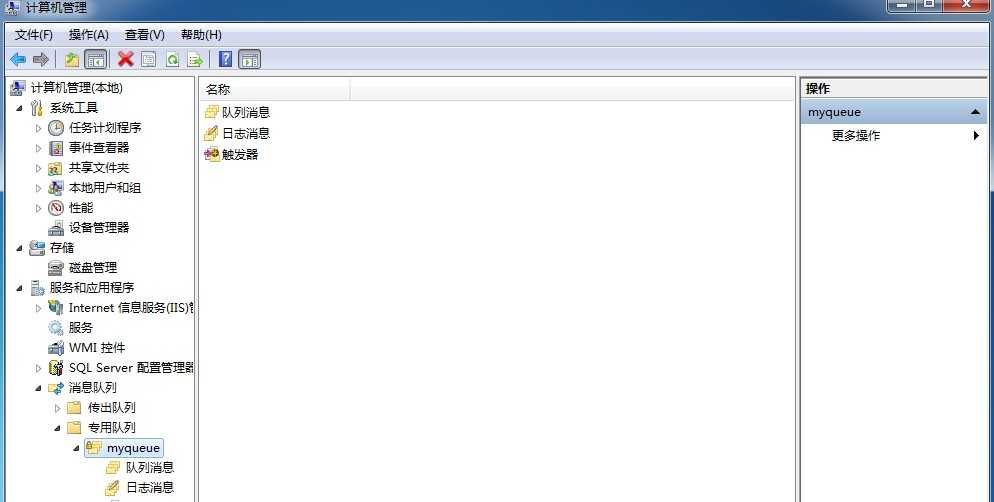
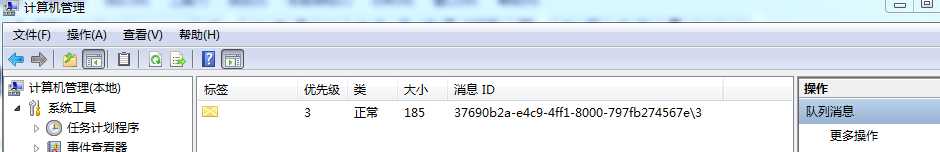
下面我们来创建一个队列,如图我们成功的创建了"myqueue"队列
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string queuepath = @".\private$\myQueue";
QueueManger.Createqueue(queuepath);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string queuepath = @".\private$\myQueue";
QueueManger.Createqueue(queuepath);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
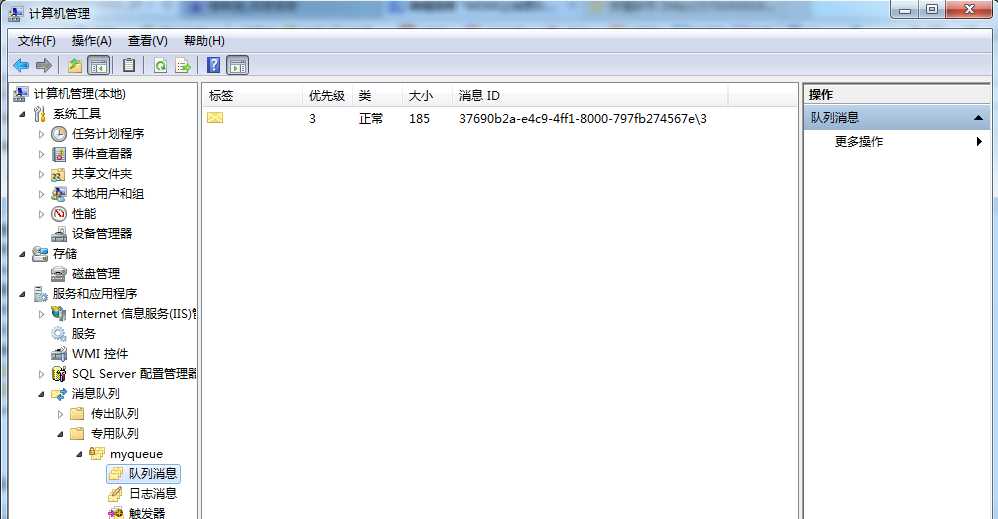
下面我们向队列中发送消息。如图,从图右边可以看到消息成功被加入到队列中
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string queuepath = @".\private$\myQueue";
//QueueManger.Createqueue(queuepath);
Student stu = new Student() { Name="shaoshun",Age=18};
QueueManger.SendMessage<Student>(stu, queuepath);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
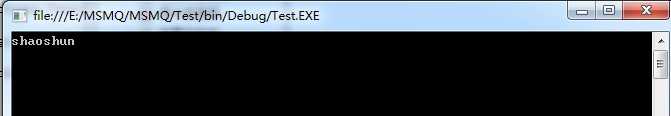
接着我们采用Peek方法接收消息(即不移除MSMQ的对应消息),很显然图中的Message依然存在MSMQ队列中
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string queuepath = @".\private$\myQueue";
//QueueManger.Createqueue(queuepath);
//Student stu = new Student() { Name="shaoshun",Age=18};
//QueueManger.SendMessage<Student>(stu, queuepath);
Student stu= QueueManger.ReceiveMessageByPeek<Student>(queuepath);
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
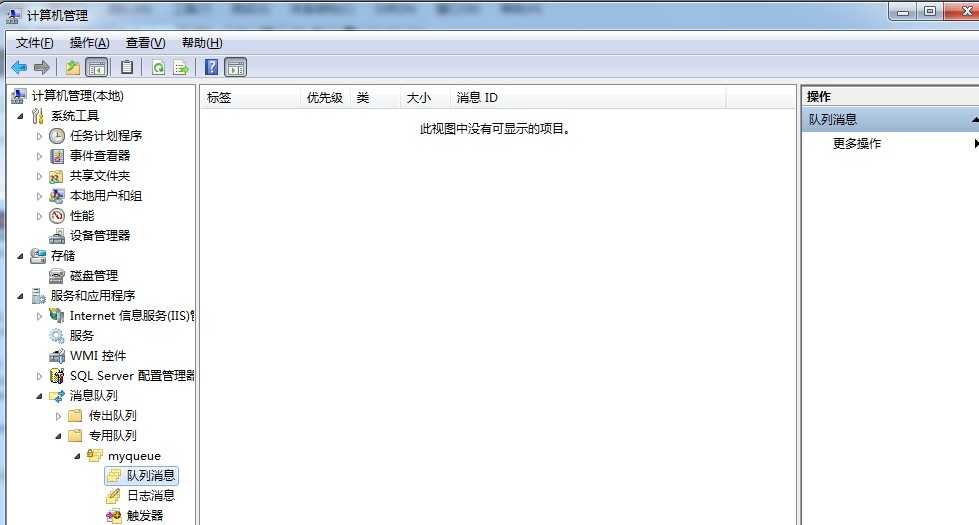
接着我们采用Receive方法来接收消息。这个时候我们可以很明显的看见MSMQ原来对应的消息被删除了
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string queuepath = @".\private$\myQueue";
//QueueManger.Createqueue(queuepath);
//Student stu = new Student() { Name="shaoshun",Age=18};
//QueueManger.SendMessage<Student>(stu, queuepath);
//Student stu= QueueManger.ReceiveMessageByPeek<Student>(queuepath);
Student stu = QueueManger.ReceiveMessage<Student>(queuepath);
Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
最后让我来测试,MSMQ的事务性。我们先删除我们的队列,在重新创建。我们连续向队列中插入5个消息,但是在插入第5个消息的时候我们抛出异常,如果MSMQ支持事务的话那么前面发送的4个Message将被回滚掉,MSMQ队列中应该为0个消息
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Messaging;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace Test
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string queuepath = @".\private$\myQueue";
//QueueManger.Createqueue(queuepath);
//Student stu = new Student() { Name="shaoshun",Age=18};
//QueueManger.SendMessage<Student>(stu, queuepath);
//Student stu= QueueManger.ReceiveMessageByPeek<Student>(queuepath);
//Student stu = QueueManger.ReceiveMessage<Student>(queuepath);
//Console.WriteLine(stu.Name);
QueueManger.Deletequeue(queuepath);
QueueManger.Createqueue(queuepath);
MessageQueueTransaction tran = new MessageQueueTransaction();
tran.Begin();
try
{
Student stu;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
stu=new Student(){Name="shaoshun"+i,Age=i};
QueueManger.SendMessage<Student>(stu, queuepath, tran);
if (i == 3)
{
throw new Exception();
}
}
tran.Commit();
}
catch
{
tran.Abort();
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
另外值得注意的是,MSMQ的消息发送与接收,采用的是同步的方式。这样假如我们的消息队列中一个消息都没有,我们调用Receive()去接收该队列的消息会怎么样呢? 程序会被阻塞在这里,直到消息队列中有消息,程序才会接着往下走。碰到这种情况是很要命的,但是不怕MSMQ支持异步消息,由于篇幅有限我就不在多少,这里我给出一个异步操作的链接有兴趣的朋友可以去研究下,点击 这里
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mfc-itblog/p/5229546.html