标签:
在《实现View的移动的方法总结》一文中,介绍了实现View的移动的几种方法:setLayoutParams(),scrollTo()和scrollBy(),layout(),offsetLeftAndRight()和offsetTopAndBottom(),位移动画和属性动画。以上这几种方法中,只有位移动画和属性动画才是平滑滚动的,其他的几种方法都是瞬间让View移动到目标位置,给人的视觉体验并不太好,Android在一些ViewGroup中使用Scroller类来解决这个问题,比如ViewPager和ScrollView就是使用Scroller来让子View实现平滑滚动的。
Scroller虽然能让View产生平滑滚动的效果,但其实Scroller本身并不会直接让View发生滚动,它是被动作用于View之上的。下面通过例子来看看Scroller的使用方法:
MyButton.java
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Scroller;
public class MyButton extends Button {
private Scroller mScroller;
public MyButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
// 实例化Scroller
mScroller = new Scroller(context);
}
@Override
protected void onSizeChanged(int w, int h, int oldw, int oldh) {
super.onSizeChanged(w, h, oldw, oldh);
width = w;
height = h;
}
public void startScroll(int startX, int startY, int dx, int dy, int duration) {
// 对Scroller进行初始设置
mScroller.startScroll(startX, startY, dx, dy, duration);
invalidate();
}
private int currX, currY;
private int width, height;
@Override
public void computeScroll() {
// 如果滑动仍在进行
if (mScroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
currX = mScroller.getCurrX();
currY = mScroller.getCurrY();
layout(currX, currY, currX + width, currY + height);
invalidate();
}
}
}
FirstActivity.java
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
public class FirstActivity extends Activity implements OnClickListener {
private MyButton button;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_first);
button = (MyButton) findViewById(R.id.button1);
button.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
button.startScroll(0, 0, 200, 0, 1500);
}
}
activity_first.xml
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<com.hellomagic.learnscroller.MyButton
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Button" />
</LinearLayout>
运行之后的效果是这样的:
一般来说,Scroller的使用分为以下几个步骤:
为什么调用Scroller的startScroll()方法进行设置之后,调用View的invalidate()方法就能开始滑动?为什么滑动会自己进行?
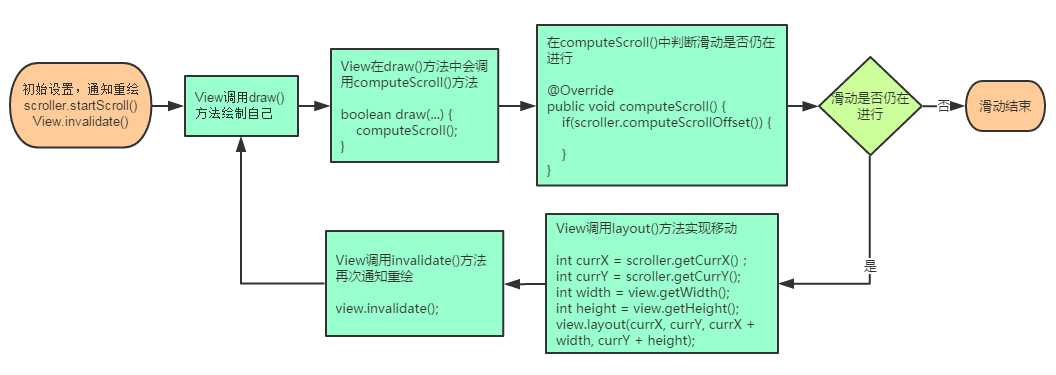
从上图可以看到,View调用invalidate()之后,如果scroller.computeScrollOffset()返回true也就是滑动正在进行的时候,就会形成一个循环,view会不断重绘,不断layout。而每次调用scroller.computeScrollOffset()的时候,scroller内部都会改变currX和currY的值。
/**
* Call this when you want to know the new location. If it returns true,
* the animation is not yet finished.
*/
public boolean computeScrollOffset() {
if (mFinished) { // 如果滑动结束了,就返回false
return false;
}
// 用 现在的时间 - 滑动开始时的时间 = 滑动进行的时间(即滑动进行了多久)
int timePassed = (int)(AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis() - mStartTime);
if (timePassed < mDuration) { // 如果 滑动进行的时间 < 滑动持续的时间
switch (mMode) {
case SCROLL_MODE:
// 根据滑动进行的时间 timePassed 和 插值器 mInteerpolator 计算得到当前的currX和currY
final float x = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(timePassed * mDurationReciprocal);
mCurrX = mStartX + Math.round(x * mDeltaX);
mCurrY = mStartY + Math.round(x * mDeltaY);
break;
case FLING_MODE:
final float t = (float) timePassed / mDuration;
final int index = (int) (NB_SAMPLES * t);
float distanceCoef = 1.f;
float velocityCoef = 0.f;
if (index < NB_SAMPLES) {
final float t_inf = (float) index / NB_SAMPLES;
final float t_sup = (float) (index + 1) / NB_SAMPLES;
final float d_inf = SPLINE_POSITION[index];
final float d_sup = SPLINE_POSITION[index + 1];
velocityCoef = (d_sup - d_inf) / (t_sup - t_inf);
distanceCoef = d_inf + (t - t_inf) * velocityCoef;
}
mCurrVelocity = velocityCoef * mDistance / mDuration * 1000.0f;
mCurrX = mStartX + Math.round(distanceCoef * (mFinalX - mStartX));
// Pin to mMinX <= mCurrX <= mMaxX
mCurrX = Math.min(mCurrX, mMaxX);
mCurrX = Math.max(mCurrX, mMinX);
mCurrY = mStartY + Math.round(distanceCoef * (mFinalY - mStartY));
// Pin to mMinY <= mCurrY <= mMaxY
mCurrY = Math.min(mCurrY, mMaxY);
mCurrY = Math.max(mCurrY, mMinY);
if (mCurrX == mFinalX && mCurrY == mFinalY) {
mFinished = true;
}
break;
}
}
else { // 如果滑动进行的时间 >= 滑动持续的时间
mCurrX = mFinalX;
mCurrY = mFinalY;
mFinished = true;
}
return true;
}
由此可见,scroller.getCurrX()和scroller.getCurrY()的值会随着滑动进行的时间而改变,因此每次调用view.layout(currX, currY, currX + width, currY + height方法时),每次view的位置都会发生一点变化,就因为在duration时间内,view每次layout都会移动一点位置,所以就产生了View滑动的动画效果。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hellomagic/p/5233378.html