标签:
There are well-known formulas: 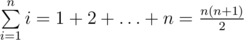 ,
, 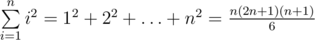 ,
,  . Also mathematicians found similar formulas for higher degrees.
. Also mathematicians found similar formulas for higher degrees.
Find the value of the sum  modulo 109 + 7 (so you should find the remainder after dividing the answer by the value 109 + 7).
modulo 109 + 7 (so you should find the remainder after dividing the answer by the value 109 + 7).
The only line contains two integers n, k (1 ≤ n ≤ 109, 0 ≤ k ≤ 106).
Print the only integer a — the remainder after dividing the value of the sum by the value 109 + 7.
4 1
10
拉格朗日插值:本质就是通过给定函数的n个点,求未知自变量的函数值;万能公式
细节:题目中给了k前几项的n的通项公式,其中n的最高次为k + 1次;由拉格朗日插值的构造多项式知,当代入k个点时,得到的是k - 1次多项式,
所以要得到最终的k + 1次多项式就需要先求出在函数中的k+2,这样就可以按照得到的多项式代入n求出最终的结果;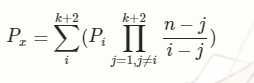
pi就是已知点的函数值,原本得到的k + 1次多项式n是x才对,这里直接将n替换成了x,得到的就是最终的结果;因为我们知道最终的多项式的次数(关键)
实现细节: 对内层阶乘先预处理出来,但是里面并不是连续的阶乘,需要用到乘法逆元,即欧拉函数推导式;至于分母的正负,可以求完逆元之后在判断(这并没有证明)
时间复杂度:对于n小于maxn时,其实是可以直接求的,时间复杂度为O(maxn*log(maxn));但是当n接近1e9时,一定要用拉格朗日插值法,时间复杂度为O(klog(k));
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef __int64 ll; const int mod = 1e9 + 7; const int maxn = 1e6 + 7; ll p[maxn],fac[maxn]; ll pow_mod(ll a,ll n) { ll ans = 1; while(n){ if(n & 1) ans = ans*a%mod; a = a*a%mod; n >>= 1; } return ans; } int main() { int n,k; scanf("%d%d",&n,&k); p[0] = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= k + 2;i++) p[i] = (p[i - 1] + pow_mod(i,k))%mod; if(n <= k + 2) return printf("%I64d",p[n]),0; fac[0] = 1; for(int i = 1;i <= k + 2;i++) fac[i] = fac[i - 1]*i%mod; ll t = 1; for(int i = 1;i <= k+2; i++) t = (n - i)*t%mod; ll ans = 0; for(int i = 1;i <= k + 2;i++){ ll t1 = pow_mod(fac[i-1]*fac[k+2-i]%mod,mod - 2);//求解逆元 ll t2 = pow_mod(n-i,mod - 2)%mod; if((k+2-i)&1) t1 = -t1; ans = (ans + p[i]*t%mod*t2%mod*t1%mod + mod)%mod; } cout<<ans; }
Educational Codeforces Round 7 F - The Sum of the k-th Powers 拉格朗日插值
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/hxer/p/5246905.html