标签:
一、题目要求
使用下面方法printPrimes()完成后面的问题(a)-(d):
代码如下:
/******************************************************* * Finds and prints n prime integers * Jeff Offutt, Spring 2003 ******************************************************/ public static void printPrimes (int n) { int curPrime; // Value currently considered for primeness int numPrimes; // Number of primes found so far. boolean isPrime; // Is curPrime prime? int [] primes = new int [MAXPRIMES]; // The list of prime numbers. // Initialize 2 into the list of primes. primes [0] = 2; numPrimes = 1; curPrime = 2; while (numPrimes < n) { curPrime++; // next number to consider ... isPrime = true; for (int i = 0; i <= numPrimes-1; i++) { // for each previous prime. if (isDivisible(primes[i], curPrime)) { // Found a divisor, curPrime is not prime. isPrime = false; break; // out of loop through primes. } } if (isPrime) { // save it! primes[numPrimes] = curPrime; numPrimes++; } } // End while // Print all the primes out. for (int i = 0; i <= numPrimes-1; i++) { System.out.println ("Prime: " + primes[i]); } } // end printPrimes
(a)画出流程控制图
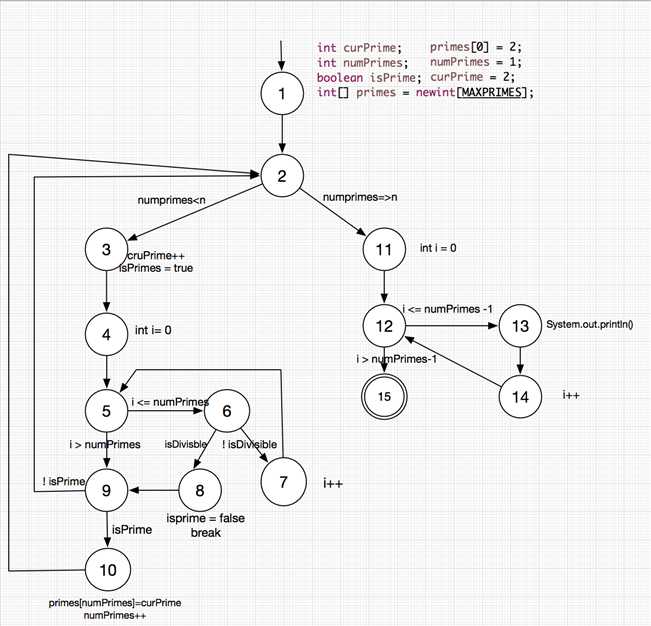
(b)将MAXPRIMES设为4,这样t2=(n=5)就会出现数组越界的错误,但t1=(n=3)无影响。
(c)n=0判断时会不满足numPrimes < n的循环条件,因此不会进入while循环
(d)点覆盖:{1,2,3,4,5,6,7,5,6,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15}
边覆盖:{(1,2),(2,3),(2,11),(3,4),(4,5),(5,6),(6,7),(6,8),(7,5),(8,9), (5,9),(9,10),(9,2),(10,2),(11,12),(12,13),(13,14),(14,12),(12,15)}
主路径覆盖:{(1,2,3,4,5,6,7),(1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10),(1,2,3,4,5,6,8,9),(1,2,3,4,5,9,10),(1,2,3,4,5,9),(1,2,11,12,13,14),(1,2,11,15),(3,4,5,6,8,9,10,2,11,12,13,14),(3,4,5,6,8,9,2,11,12,13,14),(3,4,5,6,8,9,10,2,11,12,15),(3,4,5,6,8,9,2,11,12,15),(3,4,5,9,10,2,11,12,13,14),(3,4,5,9,2,11,12,13,14),(3,4,5,9,10,2,11,12,15),(3,4,5,9,2,11,12,15),(6,7,5,9,10,2,11,12,13,14),(6,7,5,9,2,11,12,13,14),(6,7,5,9,10,2,11,12,15),(6,7,5,9,2,11,12,15),(13,14,12,15),(12,13,14,12),(5,6,7,5),(2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,2),(2,3,4,5,6,8,9,2),(2,3,4,5,9,10,2),(2,3,4,5,9,2)}
附加:实现其中一个主路径覆盖:
import static org.junit.Assert.*; import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream; import java.io.PrintStream; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import org.junit.* public class Test { private PrintPrimes p; PrintStream console = null; ByteArrayOutputStream bytes = null; @Before public void setUp() throws Exception { p = new PrintPrimes(); bytes = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); console = System.out; System.setOut(new PrintStream(bytes)); } @After public void tearDown() throws Exception { System.setOut(console); } @Test public void testResult() throws Exception { String s = new String("Prime:2" + ‘\r‘+‘\n‘); s += "Prime:3" + ‘\r‘+‘\n‘; s += "Prime:5" + ‘\r‘+‘\n‘; Class pp = p.getClass(); Method method = pp.getDeclaredMethod("printPrimes", new Class[]{int.class}); method.setAccessible(true); method.invoke(p, 3); assertEquals(s, bytes.toString()); } }
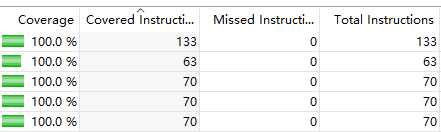
结果图:
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/mycode2016/p/5337573.html