标签:
/******************************************************* * Finds and prints n prime integers * Jeff Offutt, Spring 2003 ******************************************************/ public static void printPrimes (int n) { int curPrime; // Value currently considered for primeness int numPrimes; // Number of primes found so far. boolean isPrime; // Is curPrime prime? int [] primes = new int [MAXPRIMES]; // The list of prime numbers. // Initialize 2 into the list of primes. primes [0] = 2; numPrimes = 1; curPrime = 2; while (numPrimes < n) { curPrime++; // next number to consider ... isPrime = true; for (int i = 0; i <= numPrimes-1; i++) { // for each previous prime. if (curPrime%primes[i]==0) { // Found a divisor, curPrime is not prime. isPrime = false; break; // out of loop through primes. } } if (isPrime) { // save it! primes[numPrimes] = curPrime; numPrimes++; } } // End while // Print all the primes out. for (int i = 0; i <= numPrimes-1; i++) { System.out.println ("Prime: " + primes[i]); } } // end printPrimes
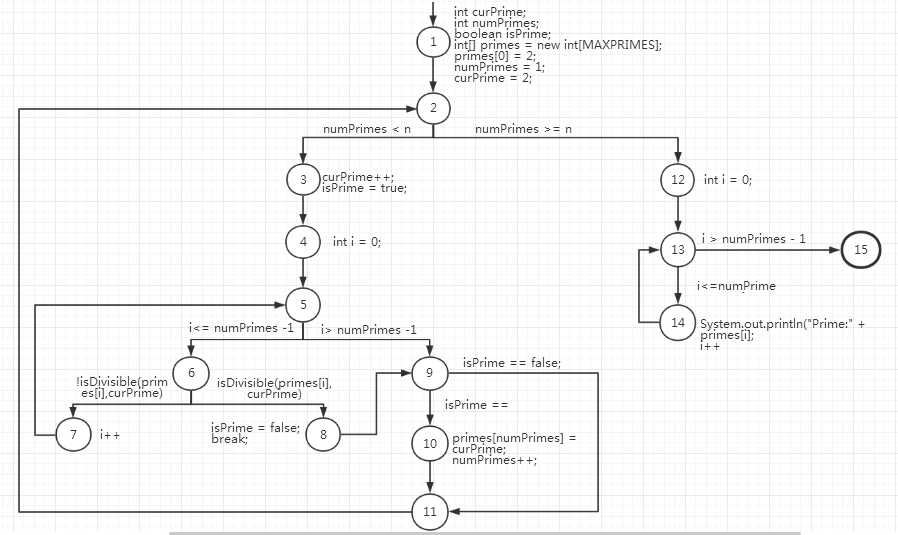
题目代码如上,Method printPrimes()
(a)控制流图
(b)当发生数组越界错误时,此时考虑测试用例 t1=(n=3) 和 t2=(n=5)则t2比t1更容易发现错误。
(c)当n=1时可以不通过while循环。
(d)
节点覆盖: { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 }
边覆盖: { (1,2), (2,3), (2,12), (3,4), (4,5), (5,6), (5,9), (6,7), (6,8), (8,9), (7,5), (9,10),(9,11) (10,11), (11,2), (12,13), (13,14), (14,13), (13,15) }
主路径覆盖:
[1,2,3,4,5,6,7];
[1,2,3,5,6,8,9,11];
[1,2,3,5,6,8,9,10,11];
[1,2,3,5,9,11];
[1,2,3,5,9,10,11];
[1,2,12,13,14];
[1,2,12,13,15];
[3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,2,12,13,14];
[3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,2,12,13,15];
[3,4,5,6,8,9,11,2,12,13,14];
[3,4,5,6,8,9,11,2,12,13,15];
[3,4,5,9,11,2,12,13,15];
[3,4,5,9,11,2,12,13,14];
[3,4,5,9,10,11,2,12,13,15];
[3,4,5,9,10,11,2,12,13,14];
[6,9,5,9,11,2,12,13,15];
[6,9,5,9,11,2,12,13,14];
[6,9,5,9,10,11,2,12,13,15];
[6,9,5,9,10,11,2,12,13,14];
[14,13,15];
[2,3,4,5,6,8,9,11,2];
[2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10,11,2] ;
[2,3,4,5,9,11,2];
[2,3,4,5,9,10,11,2];
[13,14,13];
[5,6,7,5];
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/lightfire/p/5339649.html