标签:
1 直方图均衡化
直方图均衡化,是将给定图像的直方图改造成均匀分布的直方图,从而扩大像素灰度值的动态范围,达到增强图像对比度的效果。

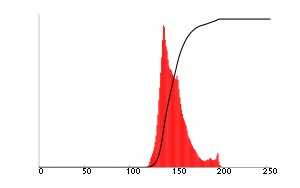

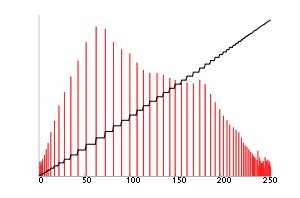
1) 标准化直方图
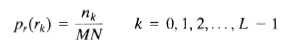
rk - 第k个像素灰度值; nk - 像素灰度值为rk的像素数目;
MN - 图像中总的像素个数; [0, L-1] - 像素灰度值的范围
2) 直方图均衡化
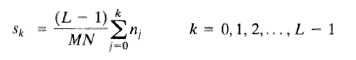
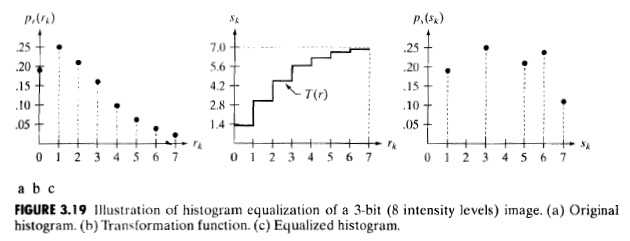
3) 实例
一幅灰度值范围是[0, L-1],64行64列的数字图像,其灰度分布如下表所示,求直方图均衡化之后的灰度分布。
| r(k) | n(k) | P(rk) |
| r(0) = 0 | 790 | 0.19 |
| r(1) = 1 | 1023 | 0.25 |
| r(2) = 2 | 850 | 0.21 |
| r(3) = 3 | 656 | 0.16 |
| r(4) = 4 | 329 | 0.08 |
| r(5) = 5 | 245 | 0.06 |
| r(6) = 6 | 122 | 0.03 |
| r(7) = 7 | 81 | 0.02 |
根据上述公式得, s(0)=1.33≈1,s(1)=3.08≈3,s(2)≈5,s(3)≈6,s(4)≈6,s(5)≈7,s(6)≈7,s(7)≈7
因为 r(k) -> s(k),所以 s(0)=1 有790个像素值。
r(3), r(4) -> s(3), s(4),且 s(3)=s(4)=6,故有像素值为6的像素数为 (656+329),同理可计算像素值为7的像素数。
将不同像素值对应的的像素数除以MN(图像的像素总数),便得到均衡化之后的灰度直方图,如下所示:
2 OpenCV中的函数
1) equalizeHist定义

void cv::equalizeHist( InputArray src, OutputArray dst ) /* 1) src Source 8-bit single channel image. 2) dst Destination image of the same size and type as src */
2) equalizeHist源码

void cv::equalizeHist( InputArray _src, OutputArray _dst ) { CV_Assert( _src.type() == CV_8UC1 ); if (_src.empty()) return; CV_OCL_RUN(_src.dims() <= 2 && _dst.isUMat(), ocl_equalizeHist(_src, _dst)) Mat src = _src.getMat(); _dst.create( src.size(), src.type() ); Mat dst = _dst.getMat(); Mutex histogramLockInstance; const int hist_sz = EqualizeHistCalcHist_Invoker::HIST_SZ; int hist[hist_sz] = {0,}; int lut[hist_sz]; EqualizeHistCalcHist_Invoker calcBody(src, hist, &histogramLockInstance); EqualizeHistLut_Invoker lutBody(src, dst, lut); cv::Range heightRange(0, src.rows); if(EqualizeHistCalcHist_Invoker::isWorthParallel(src)) parallel_for_(heightRange, calcBody); else calcBody(heightRange); int i = 0; while (!hist[i]) ++i; int total = (int)src.total(); if (hist[i] == total) { dst.setTo(i); return; } float scale = (hist_sz - 1.f)/(total - hist[i]); int sum = 0; for (lut[i++] = 0; i < hist_sz; ++i) { sum += hist[i]; lut[i] = saturate_cast<uchar>(sum * scale); } if(EqualizeHistLut_Invoker::isWorthParallel(src)) parallel_for_(heightRange, lutBody); else lutBody(heightRange); }
3 实例

#include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> using namespace cv; using namespace std; int main( int, char** argv ) { Mat src, dst; const char* source_window = "Source image"; const char* equalized_window = "Equalized Image"; // Load image src = imread( argv[1], 1 ); if( src.empty() ) { cout<<"Usage: ./Histogram_Demo <path_to_image>"<<endl; return -1; } // Convert to grayscale cvtColor( src, src, COLOR_BGR2GRAY ); // Apply Histogram Equalization equalizeHist( src, dst ); // Display results namedWindow( source_window, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); namedWindow( equalized_window, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); imshow( source_window, src ); imshow( equalized_window, dst ); // Wait until user exits the program waitKey(0); return 0; }
摘自 <Digital Image Processing_3rd> 和 Opencv 3.1.0_tutorial
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xinxue/p/5290660.html