标签:
一般数字图像的边缘,基本上都是像素值变化剧烈的区域,因此,常用求一阶导数或二阶导数的方法来检测图像的边缘。
1 Sobel 索贝尔
1) 公式
Gx = f(x+1, y) - f(x, y)
Gy = f(x, y+1) - f(x, y)
G = |Gx| + |Gy|
2) 3X3 操作算子
$\quad G_x = \begin{bmatrix} -1 & 0 & 1 \\ -2 & 0 & 2 \\ -1 & 0 & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix}\qquad G_y = \begin{bmatrix} -1 & -2 & -1 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 1 & 2 & 1 \\ \end{bmatrix} $
3) Scharr
实际应用中 Sobel 算子并不是很精确,因此常用 Scharr 算子来代替。
$\quad G_x = \begin{bmatrix} -3 & 0 & 3 \\ -10 & 0 & 10 \\ -3 & 0 & 3 \\ \end{bmatrix}\qquad G_y = \begin{bmatrix} -3 & -10 & -3 \\ 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 3 & 10 & 3 \\ \end{bmatrix} $
2 Laplace 拉普拉斯
索贝尔是求解一阶导数,而拉普拉斯是求二阶导数。
1) 公式
$\quad Laplace(f) = \frac{\partial^2f}{\partial x^2} + \frac{\partial^2f}{\partial y^2} = f(x+1, y) + f(x-1, y) + f(x, y+1) + f(x, y-1) - 4f(x, y)$
2) 图示
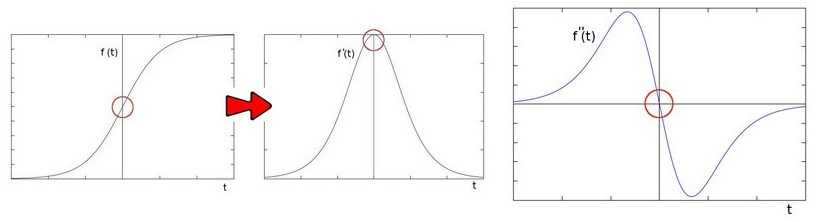
3 Canny
Canny 边缘检测算子,其算法步骤如下所示:
1) smooth the input image with a Gaussian filter 用高斯滤波器对输入图像做平滑处理
2) compute the gradient magnitude and angle images
3) apply nonmaxima suppression to the gradient magnitude image
4) use double thresholding and connectivity analysis to detect and link edges
4 OpenCV 实例
1) 函数定义(sobel/scharr, laplacian, canny)

void cv::Sobel ( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth, int dx, int dy, int ksize = 3, double scale = 1, double delta = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT ) void cv::Scharr ( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth, int dx, int dy, double scale = 1, double delta = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT ) void cv::Laplacian ( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, int ddepth, int ksize = 1, double scale = 1, double delta = 0, int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT ) void cv::Canny ( InputArray image, OutputArray edges, double threshold1, double threshold2, int apertureSize = 3, bool L2gradient = false )
2) 代码实例
Sobel 或 Scharr:

#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> using namespace cv; int main( int, char** argv ) { Mat src, src_gray; Mat grad; const char* window_name = "Sobel Demo - Simple Edge Detector"; int scale = 1; int delta = 0; int ddepth = CV_16S; /// Load an image src = imread( argv[1] ); if( src.empty() ) { return -1; } GaussianBlur( src, src, Size(3,3), 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT ); /// Convert it to gray cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY ); /// Create window namedWindow( window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); /// Generate grad_x and grad_y Mat grad_x, grad_y; Mat abs_grad_x, abs_grad_y; /// Gradient X //Scharr( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); Sobel( src_gray, grad_x, ddepth, 1, 0, 3, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( grad_x, abs_grad_x ); /// Gradient Y //Scharr( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); Sobel( src_gray, grad_y, ddepth, 0, 1, 3, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); convertScaleAbs( grad_y, abs_grad_y ); /// Total Gradient (approximate) addWeighted( abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0, grad ); imshow( window_name, grad ); waitKey(0); return 0; }
Laplace:

1 #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" 2 #include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" 3 #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <stdio.h> 6 7 using namespace cv; 8 9 int main( int, char** argv ) 10 { 11 12 Mat src, src_gray, dst; 13 int kernel_size = 3; 14 int scale = 1; 15 int delta = 0; 16 int ddepth = CV_16S; 17 const char* window_name = "Laplace Demo"; 18 19 /// Load an image 20 src = imread( argv[1] ); 21 22 if( src.empty() ) 23 { return -1; } 24 25 /// Remove noise by blurring with a Gaussian filter 26 GaussianBlur( src, src, Size(3,3), 0, 0, BORDER_DEFAULT ); 27 28 /// Convert the image to grayscale 29 cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_RGB2GRAY ); 30 31 /// Create window 32 namedWindow( window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); 33 34 /// Apply Laplace function 35 Mat abs_dst; 36 37 Laplacian( src_gray, dst, ddepth, kernel_size, scale, delta, BORDER_DEFAULT ); 38 convertScaleAbs( dst, abs_dst ); 39 40 /// Show what you got 41 imshow( window_name, abs_dst ); 42 43 waitKey(0); 44 45 return 0; 46 }
Canny:

#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" #include "opencv2/imgcodecs.hpp" #include "opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp" #include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> using namespace cv; /// Global variables Mat src, src_gray; Mat dst, detected_edges; int edgeThresh = 1; int lowThreshold; int const max_lowThreshold = 100; int ratio = 3; int kernel_size = 3; const char* window_name = "Edge Map"; /** * @function CannyThreshold * @brief Trackbar callback - Canny thresholds input with a ratio 1:3 */ static void CannyThreshold(int, void*) { /// Reduce noise with a kernel 3x3 blur( src_gray, detected_edges, Size(3,3) ); /// Canny detector Canny( detected_edges, detected_edges, lowThreshold, lowThreshold*ratio, kernel_size ); /// Using Canny‘s output as a mask, we display our result dst = Scalar::all(0); src.copyTo( dst, detected_edges); imshow( window_name, dst ); } int main( int, char** argv ) { /// Load an image src = imread( argv[1] ); if( src.empty() ) { return -1; } /// Create a matrix of the same type and size as src (for dst) dst.create( src.size(), src.type() ); /// Convert the image to grayscale cvtColor( src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY ); /// Create a window namedWindow( window_name, WINDOW_AUTOSIZE ); /// Create a Trackbar for user to enter threshold createTrackbar( "Min Threshold:", window_name, &lowThreshold, max_lowThreshold, CannyThreshold ); /// Show the image CannyThreshold(0, 0); /// Wait until user exit program by pressing a key waitKey(0); return 0; }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/xinxue/p/5348743.html