标签:
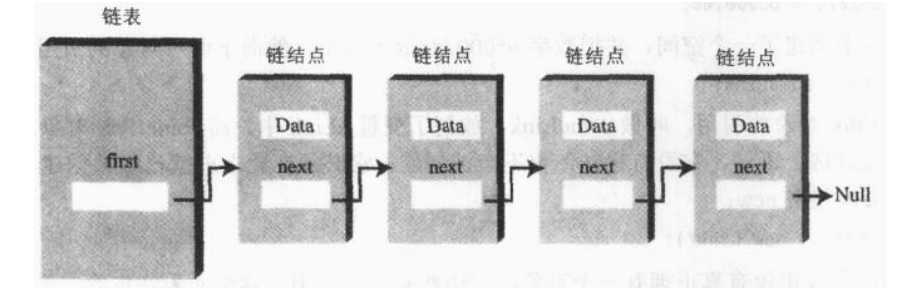
单链表学习
学习第一步:定义存放链表结点的类Node,类中包含两个字段:data字段和next字段,data字段是结点中的数值域,next是指向链表下一个结点的引用
1 //存放单链表节点 2 class Node { 3 private int data; 4 private Node next; 5 6 public Node(int data, Node next) { 7 this.data = data; 8 this.next = next; 9 } 10 11 public int getData() { 12 return data; 13 } 14 15 public void setData(int data) { 16 this.data = data; 17 } 18 19 public Node getNext() { 20 return next; 21 } 22 23 public void setNext(Node next) { 24 this.next = next; 25 } 26 27 public void displayNode() { 28 System.out.println("data:" + data); 29 } 30 31 }
学习第二步:学习单链表的一些操作,插入、删除、查找结点
1 // 单链表的一些操作 2 class LinkList { 3 private Node head; 4 5 public LinkList() { 6 head = null; 7 } 8 9 // 链表的头部插入元素 10 public void insertNode(int data) { 11 Node newNode = new Node(data, null); 12 newNode.setNext(head); 13 head = newNode; 14 } 15 16 // 从链表的头部删除元素 17 public Node deleteNode() { 18 Node tempNode = head; 19 head = head.getNext(); 20 return tempNode; 21 } 22 23 // 打印链表中的结点的数值域的值 24 public void displayList() { 25 Node currentLinkList = head; 26 while (currentLinkList != null) { 27 currentLinkList.displayNode(); 28 currentLinkList = currentLinkList.getNext(); 29 } 30 } 31 32 // 判断单链表是否为空 33 public boolean isEmpty() { 34 return head == null; 35 } 36 37 // 单链表查询是否有关键字为key的结点 38 public Node find(int key) { 39 Node current = head; 40 while (current.getData() != key) { 41 if (current.getNext() == null) { 42 return null; 43 } 44 current = current.getNext(); 45 } 46 return current; 47 48 } 49 50 // 单链表中删除指定关键字的结点 51 public Node delete(int key) { 52 // preNode要删除的结点的前一个结点 53 Node preNode = head; 54 // 标记要删除的结点 55 Node current = head; 56 while (current.getData() != key) { 57 if (current == null) { 58 return null; 59 } else { 60 preNode = current; 61 current = current.getNext(); 62 } 63 } 64 // 要删除的是头head指向的结点 65 if (current == head) { 66 head = head.getNext(); 67 } 68 // 删除结点,preNode指向删除结点的后继结点 69 else { 70 preNode.setNext(current.getNext()); 71 } 72 return current; 73 74 } 75 }
双端链表学习
可以看到我们上面的操作,在链表尾插入、删除结点的操作,虽然也可以做,但是需要从头遍历到尾部,这种方法的效率有点低,双端链表可以解决这个问题。双端链表循序我们跟操作链表头一样去操作链表尾,使得在一些特殊情况下,链表的操作更加便利。其实就是加了一个tail引用,指向链表的最后一个结点。
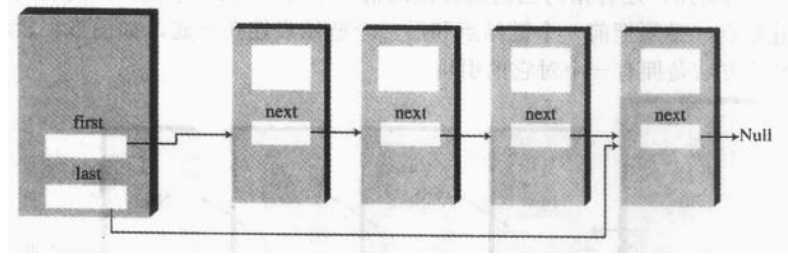
我们在将结点顺序插入到链表中
1 public void insertAtTail(int data) { 2 Node newNode = new Node(data, null); 3 tail.setNext(newNode); 4 tail = newNode; 5 size++; 6 }
但不幸的是双端链表也不能有助于删除最后一个链结点,因为没有一个引用指向倒数第二个链结点。如果最后一个链结点被删除,倒数第二个链结点的next字段应该变为null值,为了方便进行这一操作,我们此刻就需要双向链表,稍后介绍。
链表和数组的区别:
二者都属于一种数据结构
从逻辑结构来看
1. 数组必须事先定义固定的长度(元素个数),不能适应数据动态地增减的情况。当数据增加时,可能超出原先定义的元素个数;当数据减少时,造成内存浪费;数组可以根据下标直接存取。
2. 链表动态地进行存储分配,可以适应数据动态地增减的情况,且可以方便地插入、删除数据项。(数组中插入、删除数据项时,需要移动其它数据项,非常繁琐)链表必须根据next指针找到
下一个元素
从内存存储来看
1. (静态)数组从栈中分配空间, 对于程序员方便快速,但是自由度小
2. 链表从堆中分配空间, 自由度大但是申请管理比较麻烦
从上面的比较可以看出,如果需要快速访问数据,很少或不插入和删除元素,就应该用数组;相反,如果需要经常插入和删除元素就需要用链表数据结构了。
双端链表的一个实际应用:模拟队列
定义存储结点的Node类
1 public class Node { 2 3 public int data; 4 public Node next; 5 public Node(int data,Node next){ 6 this.data=data; 7 this.next=next; 8 } 9 }
定义链表操作
1 public class LinkList { 2 3 private Node head; 4 private Node tail; 5 public LinkList(){ 6 head=null; 7 tail=null; 8 } 9 public void insertLast(int data){ 10 Node newNode=new Node(data, null); 11 if(isEmpty()){ 12 head=newNode; 13 } 14 else { 15 tail.next=newNode; 16 } 17 tail=newNode; 18 } 19 public int deleteHead(){ 20 if(head.next==null){ 21 tail=null; 22 return head.data; 23 } 24 if(head!=null){ 25 26 Node tempNode=head; 27 head=head.next; 28 return tempNode.data; 29 } 30 else { 31 throw new RuntimeException("不能删除元素了"); 32 } 33 } 34 public boolean isEmpty(){ 35 return head==null; 36 } 37 38 }
链表模拟队列
1 //用的是insertLast()和deleteHead()方法,即在尾部插入,在链表头删除 2 public class LinkQueue { 3 4 private LinkList linkList; 5 public LinkQueue(){ 6 linkList=new LinkList(); 7 } 8 public void push(int data){ 9 linkList.insertLast(data); 10 } 11 public int pop(){ 12 return linkList.deleteHead(); 13 } 14 public boolean isEmpty(){ 15 return linkList.isEmpty(); 16 } 17 }
测试类
1 public class QueuqTest { 2 3 /** 4 * @param args 5 */ 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 8 LinkQueue linkQueue=new LinkQueue(); 9 linkQueue.push(10); 10 linkQueue.push(20); 11 linkQueue.push(30); 12 linkQueue.push(40); 13 System.out.println(linkQueue.pop()); 14 } 15 }
有序链表学习
有序链表的结点插入和普通链表不同,其他操作相同,我们这里只给出往有序链表中插入结点的操作,有序列表适合用于需要频繁操作最值(最大或最小),而又不要求快速插入的场合
1 public void insert2SortLink(int data) { 2 Node newNode = new Node(data, null); 3 Node preNode = null; 4 Node currenNode = head; 5 //一直往后查找结点的插入位置直到链表结束或者data不大于currentNode.data 6 //while循环结束,结点的插入位置可能为表头、表尾、表中间的某个位置,或者链表是空表 7 while (currenNode != null && data > currenNode.data) { 8 preNode = currenNode; 9 currenNode = currenNode.next; 10 } 11 //插入点的前一个结点preNode指向结点=null,表明插入点在表头或者表是空表 12 if (preNode == null) { 13 head=newNode; 14 } 15 //插入点在表中间或者在表的尾部 16 else { 17 preNode.next=newNode; 18 } 19 //无论插入点在哪一个位置,新插入的结点的next域都指向currentNode 20 newNode.next=currenNode; 21 }
有序链表的一个应用:表插入排序
有序链表可以用于一种高效的排序机制。假设有一个无序的数组,如果从这个数组中取出数据,然后一个一个地插入到有序链表,他们自动的按顺序排序。把他们从有序链表中取出再放到数组中,那么数组就排好顺序了
表插入排序的效率:插入N个数据,就进行了n^2/2次比较,但移动仅进行了2*N次,效率,相对于简单排序中的插入排序的O(n2),还是要效率高一些的。
具体代码实现:
(1)Node类:
1 public class Node { 2 3 public int data; 4 public Node next; 5 public Node(int data,Node next){ 6 this.data=data; 7 this.next=next; 8 } 9 //显示每个结点的信息 10 public void displayNode(){ 11 System.out.print("data:"+data+" "); 12 } 13 }
(2)SortList类
1 class SortList { 2 private Node head; 3 4 public SortList() { 5 head = null; 6 } 7 8 public SortList(Node[] nodes) { 9 head = null; 10 for (int j = 0; j < nodes.length; j++) { 11 insert2SortLink(nodes[j]); 12 } 13 } 14 15 public void insert2SortLink(Node newNode) { 16 // Node thenewNode = newNode; 17 Node preNode = null; 18 Node currenNode = head; 19 // 一直往后查找结点的插入位置直到链表结束或者data不大于currentNode.data 20 // while循环结束,结点的插入位置可能为表头、表尾、表中间的某个位置,或者链表是空表 21 while (currenNode != null && newNode.data > currenNode.data) { 22 preNode = currenNode; 23 currenNode = currenNode.next; 24 } 25 // 插入点的前一个结点preNode指向结点=null,表明插入点在表头或者表是空表 26 if (preNode == null) { 27 head = newNode; 28 } 29 // 插入点在表中间或者在表的尾部 30 else { 31 preNode.next = newNode; 32 } 33 // 无论插入点在哪一个位置,新插入的结点的next域都指向currentNode 34 newNode.next = currenNode; 35 } 36 37 public Node deleteHead() { 38 if (!isEmpty()) { 39 Node tempNode = head; 40 head = head.next; 41 return tempNode; 42 } else { 43 throw new RuntimeException("不能删除元素了"); 44 } 45 } 46 47 public boolean isEmpty() { 48 return head == null; 49 } 50 }
(3)测试类
1 public class SortedListTest { 2 3 /** 4 * @param args 5 */ 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 8 Node nodeArray[] = new Node[10]; 9 int n; 10 for (int j = 0; j < nodeArray.length; j++) { 11 n = (int) (Math.random() * 99); 12 Node newNode = new Node(n, null); 13 nodeArray[j] = newNode; 14 } 15 System.out.println("--------Unsorted Array--------"); 16 for (int j = 0; j < nodeArray.length; j++) { 17 nodeArray[j].displayNode(); 18 } 19 System.out.println(); 20 SortList sortList = new SortList(nodeArray); 21 System.out.println("--------Sorted Array-------"); 22 for (int j = 0; j < nodeArray.length; j++) { 23 nodeArray[j] = sortList.deleteHead(); 24 System.out.print(nodeArray[j].data + " "); 25 } 26 System.out.println("---------结束线----------"); 27 28 } 29 30 }
学习双向链表
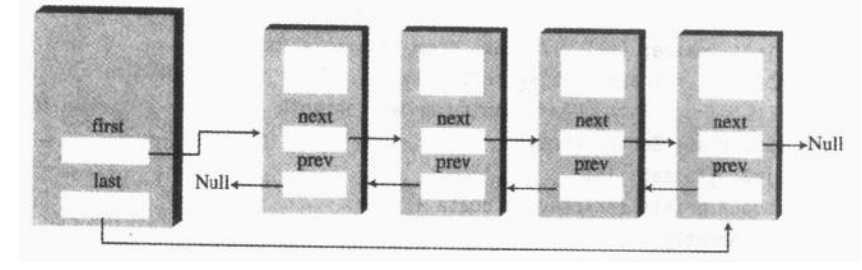
双向链表提供了这样一种能力:允许向前遍历链表,也允许向后遍历链表,秘密在于每个结点存在两个指向其他链结点的引用。
双向链表的缺点:
每次插入或者删除一个结点的时候要处理四个引用,四个引用相对于两个引用,占用空间也变得大了一些,双向链表不必是双端链表,但这种方式(保留对链表最后一个元素的引用)有时候会非常的有用。
具体代码实现:

1 package LinkListQueue; 2 3 class DoubleLinkList { 4 class Node { 5 private int data; 6 private Node next = null; 7 private Node previous = null; 8 9 public Node(int data) { 10 this.data = data; 11 } 12 } 13 14 private Node head = null; 15 private Node tail = null; 16 17 // 在双向链表的头部插入 18 public void insertHead(int data) { 19 Node newNode = new Node(data); 20 // 判断链表是否为空,可以重新组织一下代码,把if-else都要执行的head=newNode这条语句移动到else代码块后面 21 if (head == null) { 22 head = newNode; 23 tail = newNode; 24 } else { 25 newNode.next = head; 26 head.previous = newNode; 27 head = newNode; 28 } 29 // LOOP:就是这个位置 30 } 31 32 // 在双向链表的尾部插入 33 public void insertTail(int data) { 34 Node newNode = new Node(data); 35 if (head == null) { 36 head = newNode; 37 } else { 38 tail.next = newNode; 39 newNode.previous = tail; 40 } 41 tail = newNode; 42 } 43 44 // 在链表的内部的某个位置的后面插入元素,我們假定链表非空 45 public boolean insertAfter(int target, int data) { 46 Node newNode = new Node(data); 47 Node current = head; 48 while (current.data != target) { 49 current=current.next; 50 } 51 if (current == tail) { 52 newNode.next=null; 53 tail=newNode; 54 } else { 55 newNode.next=current.next; 56 current.next.previous = newNode; 57 } 58 current.next = newNode; 59 newNode.previous=current; 60 return true; 61 } 62 63 // 在链表的头部进行删除 64 public Node deleteHead() { 65 if (head == null) { 66 throw new RuntimeException("不能删除节点了"); 67 } 68 Node tmpNode = head; 69 if (head.next == null) { 70 head = null; 71 tail = null; 72 } else { 73 head.next.previous = null; 74 head = head.next; 75 } 76 return tmpNode; 77 } 78 79 // 在链表的尾部进行删除 80 public void deleteTail() { 81 if (head == null) { 82 throw new RuntimeException("不能删除节点了"); 83 } 84 Node tmpNode = tail; 85 //如果只有一个元素 86 if (head.next == null) { 87 head = null; 88 tail = null; 89 } else { 90 tail.previous.next = null; 91 tail = tail.previous; 92 } 93 } 94 95 // 在链表的内部的某个位置删除指定关键字的结点元素 96 public Node deleteKey(int target) { 97 // 链表为空表,不能删除 98 if (head == null) { 99 throw new RuntimeException("不能删除元素"); 100 } 101 Node current = head; 102 while (current.data != target) { 103 current = current.next; 104 if (current == null) { 105 return null; 106 } 107 } 108 // 最关键的理解点,有点绕,引用变化:删除结点的前一个结点的next->删除结点的后一个结点 109 // 删除结点的后一个结点的previous->删除结点的前一个结点 110 if (current == head) { 111 head = current.next; 112 } else { 113 current.previous.next = current.next; 114 } 115 if (current == tail) { 116 tail = current.previous; 117 } else { 118 current.next.previous = current.previous; 119 } 120 return current; 121 } 122 123 public void displayList() { 124 System.out.println("Head-->Tail"); 125 Node current = head; 126 while (current != null) { 127 System.out.print(current.data + " "); 128 current=current.next; 129 } 130 System.out.println(); 131 } 132 } 133 134 public class DouLinkListTest { 135 136 /** 137 * @param args 138 */ 139 public static void main(String[] args) { 140 141 DoubleLinkList dll = new DoubleLinkList(); 142 dll.insertHead(1); 143 dll.insertTail(3); 144 dll.insertAfter(1, 2); 145 dll.insertAfter(3, 4); 146 dll.insertAfter(4, 5); 147 dll.displayList(); 148 dll.deleteHead(); 149 dll.displayList(); 150 dll.deleteTail(); 151 dll.displayList(); 152 dll.deleteKey(3); 153 dll.displayList(); 154 dll.deleteKey(2); 155 dll.displayList(); 156 } 157 158 }
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ysw-go/p/5399138.html