标签:
如图,如果单链表有环,则在遍历时,在通过6之后,会重新回到3,那么我们可以在遍历时使用两个指针,看两个指针是否相等。
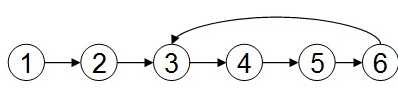
方法一:使用p、q两个指针,p总是向前走,但q每次都从头开始走,对于每个节点,看p走的步数是否和q一样。如图,当p从6走到3时,用了6步,此时若q从head出发,则只需两步就到3,因而步数不等,出现矛盾,存在环
方法二:使用p、q两个指针,p每次向前走一步,q每次向前走两步,若在某个时候p == q,则存在环。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #define LEN 8 typedef struct node* node_t; struct node{ char val; struct node *next; }; //method 1 int has_loop(struct node *head); //method 2 int has_loop2(node_t head); int main() { node_t* arr = (node_t*)malloc(sizeof(struct node)*LEN); arr[0] = (node_t)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); int i; for(i = 1; i < LEN; i++) { arr[i] = (node_t)malloc(sizeof(struct node)); arr[i - 1]->next = arr[i]; } arr[LEN - 1]->next = NULL; //you can add a loop here to test //arr[6]->next = arr[0]; if (has_loop(arr[0])) printf("method1: has loop.\n"); else printf("method1: has no loop.\n"); if (has_loop2(arr[0])) printf("method2: has loop.\n"); else printf("method2: has no loop.\n"); return 0; } //if two pointer are equal, but they don‘t have the same steps, then has a loop int has_loop(node_t head) { node_t cur1 = head; int pos1 = 0; while(cur1){ node_t cur2 = head; int pos2 = 0; pos1 ++; while(cur2){ pos2 ++; if(cur2 == cur1){ if(pos1 == pos2) break; else return 1; } cur2 = cur2->next; } cur1 = cur1->next; } return 0; } //using step1 and step2 here //if exists a loop, then the pointer which use step2 will catch up with the pointer which uses step1 int has_loop2(node_t head) { node_t p = head; node_t q = head; while (p != NULL && q != NULL) { /* p = p->next; if (q->next != NULL) q = q->next->next; if (p == q) return 1; */ //correct it on 17/11/2012 p = p->next; q = q->next; if (q != NULL) q = q->next; if (p != NULL && p == q) return 1; } return 0; }
原文转自 http://www.cnblogs.com/shuaiwhu/archive/2012/05/03/2480509.html
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/happykoukou/p/5427312.html