标签:
一、沙盒机制(SandBox)
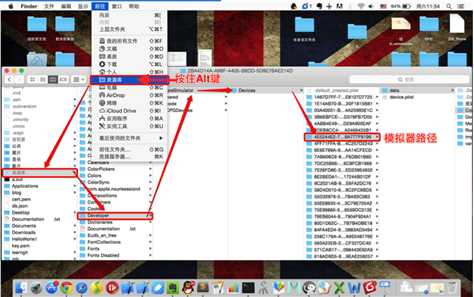
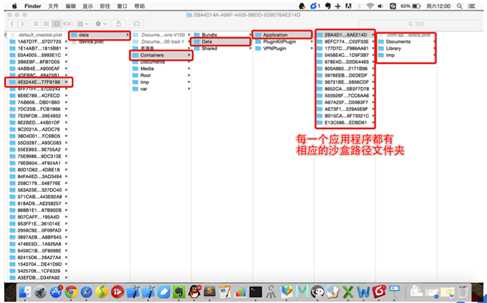
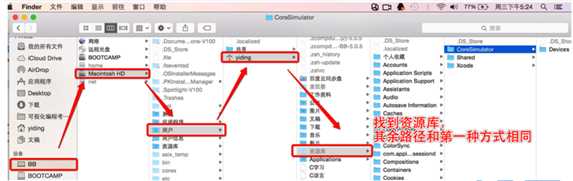
1 #pragma mark - 第一种打开应用程序沙盒路径的方式
2 // 地址是一个字符串
3 // 第一个参数是:枚举值,枚举你具体要查找的文件夹【要进入哪个文件夹直接修改其值即可】NSDocumentDirectory:进入Document文件夹
4 // 第二个参数:NSUserDomainMask表示用户的主目录
5 // 第三个参数:一般设置为Yes表示展示完成的路径
6 // NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains 是用来查找沙盒路径的,返回值是一个数组,这个数组中只有一个元素,这个元素就是路径,直接使用下标取出即可。
7 NSString *documentPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0];
8 NSLog(@"documentPath = %@", documentPath);
9 // 打印Caches路径
10 NSString *cachesPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSCachesDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0];
11 NSLog(@"caches = %@", cachesPath);
12
13 #pragma mark - 第二种打开应用程序沙盒路径的方式
14 // 第一步:先找到主目录文件夹 -- 到Application
15 NSString *homePath = NSHomeDirectory();
16 NSLog(@"homePath = %@", homePath);
17 // 第二步:然后拼接自己想进入的文件夹名称
18 NSString *documentPathTwo = [homePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Documents"];
19 NSLog(@"documentPathTwo = %@", documentPathTwo);
20
21 // Library路径
22 NSString *libraryPath = [homePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Library"];
23 NSLog(@"libraryPath = %@", libraryPath);
24
25 // Caches路径
26 NSString *cachesPathTwo = [homePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"Library/Caches"];
27 NSLog(@"cachesPathTwo = %@", cachesPathTwo);
28
29 #pragma mark - 特殊的文件夹 tmp
30 // 打印tmp路径 -- 有自己的方法
31 NSString *tmpPath = NSTemporaryDirectory();
32 NSLog(@"%@", tmpPath);
33 // 打印tmp路径 -- 拼接的方式,与别的路径查找方式相同
34 NSString *tmpPathTwo = [homePath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"tmp"];
35 NSLog(@"tmpPathTwo = %@", tmpPathTwo);
二、简单对象的读写(I/O)操作
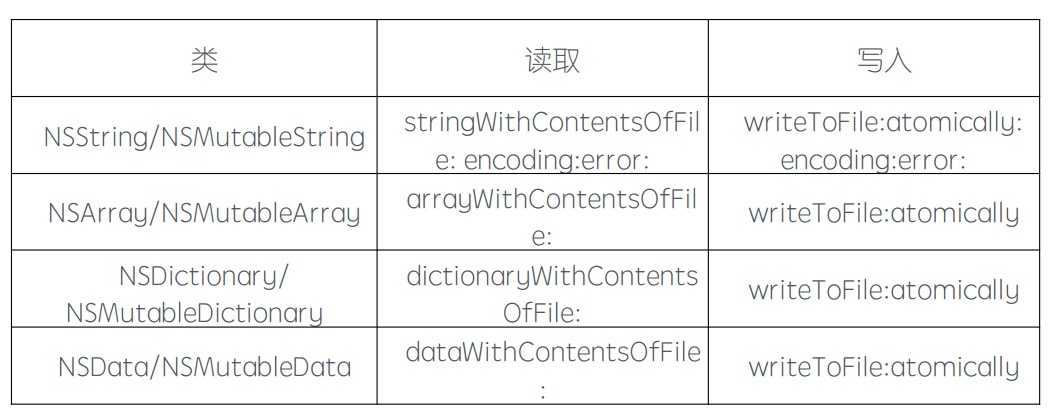
注意:数组和字典中元素对象的类型,也必须是上述的四种,否则不能直接写入文件。

1 #pragma mark - 将NSString类型的数据存储到本地 2 3 // 1、需要知道这个对象存在哪里,所以需要一个文件夹的路径 4 // 找到Document的路径 5 NSString *documentPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0]; 6 // 2、创建要存储的内容:字符串 7 NSString *str = @"AJAR"; 8 // 3、创建一个最终存储字符串的路径存储字符串 9 NSString *strPath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"yyp.txt"]; 10 // 4、将字符串写入文件 11 // 第一个参数:要写入的文件的路径 12 // 第二个参数:在程序突然中断的情况下,是否要自动保存 13 // 第三个参数:编码格式 14 // 第四个参数:错误信息 15 [str writeToFile:strPath atomically:YES encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil]; 16 #pragma mark - 将文件中存储的字符串取出 17 // 取出字符串 18 // 第一个参数:字符串存储路径 19 // 第二个参数:编码格式 20 NSString *newStr = [NSString stringWithContentsOfFile:strPath encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding error:nil];

#pragma mark - 将NSArray类型的数据存储到本地 // 1、找到Documents路径 NSString *documentPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0]; // 2、创建要存储的内容:数组 NSArray *array = @[@"Black", @"MBBoy", @"BPY", @"SPY", @"SeaRoot", @"BoomSky"]; // 3、创建数据存储的最终路径 NSString *arrayPath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"yyp.plist"]; // 4、将数组写入文件 [array writeToFile:arrayPath atomically:YES]; // 将存在本地的数组取出 NSArray *newArray = [NSArray arrayWithContentsOfFile:arrayPath]; NSLog(@"%@", newArray);

#pragma mark - 将NSDictionary类型的数据存储到本地 NSString *documentsPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0]; NSDictionary *dict = @{@"name" : @"yyp", @"gender" : @"girl", @"age" : @23}; NSString *dictPath = [documentsPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person.plist"]; [dict writeToFile:dictPath atomically:YES]; // 从本地文件中取出字典 NSDictionary *newDict = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithContentsOfFile:dictPath]; NSLog(@"newDict = %@", newDict);

#pragma mark - 将NSData类型的数据存储到本地(以UIImage为例) NSString *oldImagePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"v_red_heart_selected@2x" ofType:@"png"]; UIImage *image1 = [UIImage imageWithContentsOfFile:oldImagePath]; // 将image类型的对象转换为NSData类型的数据进行存储,最后保存的图片是JPEG类型 // 第一个参数:要转换的UIImage对象 // 第二个参数:表示图片压缩质量的值 1 -- 保持原样 // iPhone中会将大于2M的图片自动旋转90度,进行压缩处理,最后保存的图片是JPEG类型 NSData *imageData = UIImageJPEGRepresentation(image1, 1.0); NSLog(@"%@", imageData); // 找到存储路径 NSString *documentPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0]; // 图片的最终文件路径 NSString *imagePath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"heart.jpeg"]; // 将图片存为jpeg类型 [imageData writeToFile:imagePath atomically:YES]; // 将image从本地文件读取出来 // 读取NSData对象 NSData *newData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:imagePath]; // 将NSData对象转换成UIImage对象 UIImage *imageWithData = [UIImage imageWithData:newData]; // 将UIImage对象放到UIImageView上 // 创建一个UIImageView对象用来显示取出来的UIImage对象 UIImageView *imageView = [[UIImageView alloc] initWithImage:imageWithData]; [self.view addSubview:imageView];
三、复杂对象的读写(I/O)操作
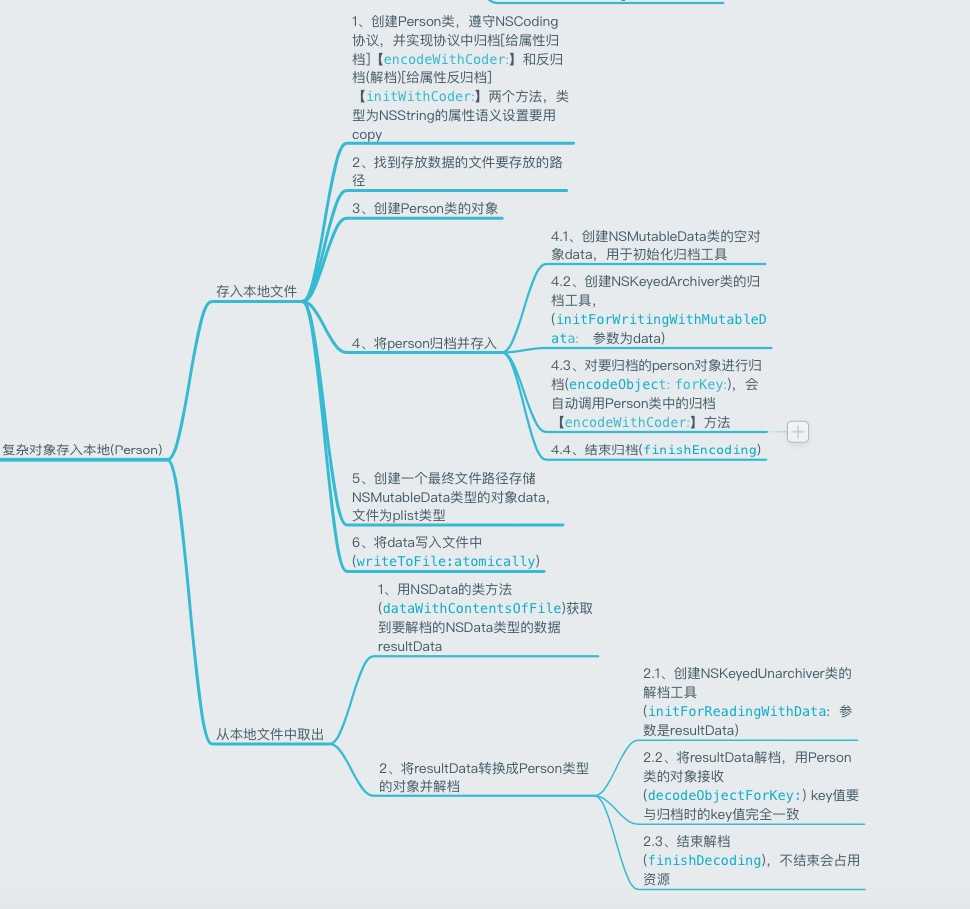
复杂对象因为不能调用writeToFile:方法写入本地文件中,也无法直接从本地文件中读取出来,所以复杂对象的读写操作需要借助归档、反归档(解档)来进行。
Person.m
// 归档 // 将所有的属性进行归档 - (void)encodeWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aCoder { // key一般与属性名一直 [aCoder encodeObject:self.name forKey:@"name"]; [aCoder encodeObject:self.gender forKey:@"gender"]; [aCoder encodeInteger:self.age forKey:@"age"]; } // 解档(返归档) - (instancetype)initWithCoder:(NSCoder *)aDecoder { self = [super init]; if (self) { // key值就是上面方法中定义的key值 self.name = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"name"]; self.gender = [aDecoder decodeObjectForKey:@"gender"]; self.age = [aDecoder decodeIntegerForKey:@"age"]; } return self; }
ViewController.m 的 viewDidLoad方法中
// 复杂对象的本地化 // 如何把一个Person类的对象存入本地? // 前提条件:Person类必须遵守NSCoding协议,并实现协议中的两个方法,属性如果是字符串,语义设置建议用copy #pragma mark - 复杂对象的本地化 // 1、寻找Documents文件夹的目录 NSString *documentPath = [NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(NSDocumentDirectory, NSUserDomainMask, YES) objectAtIndex:0]; // 2、创建Person类的对象 Person *person = [[Person alloc] init]; person.name = @"BaekHyun"; person.gender = @"boy"; person.age = 24; // 3、将person归档并存入 // 3.1、创建NSMutableData,用于初始化归档工具的 NSMutableData *data = [NSMutableData data]; // 3.2、创建归档工具 NSKeyedArchiver *archiver = [[NSKeyedArchiver alloc] initForWritingWithMutableData:data]; // 3.3、对要归档的person对象进行归档 [archiver encodeObject:person forKey:@"person"]; // 3.4、结束归档 [archiver finishEncoding]; // 4、将归档的内容(NSMutableData类型的对象)存储到本地 NSString *personPath = [documentPath stringByAppendingPathComponent:@"person1.plist"]; [data writeToFile:personPath atomically:YES]; #pragma mark - 解档 // 1、将要解档的数据找出 NSData *resultData = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:personPath]; // 2、将resultData转换成Person类型的对象 // 2.1、创建解档工具 NSKeyedUnarchiver *unarchiver = [[NSKeyedUnarchiver alloc] initForReadingWithData:resultData]; // 2.2、将resultData解档,用Person类的对象进行接收 // key值要与归档时的key值完全一致 Person *newPerson = [unarchiver decodeObjectForKey:@"person"]; // 2.3、结束解档 不结束会占用资源 [unarchiver finishDecoding]; NSLog(@"%@", newPerson);
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/fearlessyyp/p/5456886.html