标签:
2016 年宁波工程学院第七届ACM校赛题解报告
本题解代码直接为比赛代码,仅供参考。
A,B,C,D,G,H,J,K,L,M 来自 Ticsmtc 同学.
F 来自 Gealo 同学.
E,I 来自Alex 学长.
Promblem A : Two Sum
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
给出n个数,另外给出?个整数S,判断是否可以从中取出2个数,使得这两个数的和是S。
输入:
第?行有个整数T(1 <= T <= 10),代表数据组数。 对于每组数据,第?行包含两个整数n,S(2 <= n <= 103, 1 <= S <= 1000) 接下来?行包含n个整数,整数的?小在1到1000。
输出:
对于每组数据,如果存在2个整数,和为S,则输出Yes,否则输出No。
样例输入:
2
5 6
1 2 3 4 5
5 10
1 2 3 4 5
样例输出:
Yes
No
题解:
题目意思不难理解,我们控制两重循环枚举一下是哪两个数,然后用加法判断下是不是S,如果是就可以,如果枚举完了所有的都没有发现能等于S的,那么就是不行。
这里注意下,n个数,我们从下标零读入所有的数的话,那么外层循环i从0 ~ n- 1,考虑内层的时候,由于两个数不能够选重,所以内层循环 j 应当从 i + 1 ~ n - 1 ,然后看存储数字的save数组,save[i] + save[j] 是否等于 S 。
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <string> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 int save[10000]; 10 int main(){ 11 int t; 12 cin >> t; 13 while(t--){ 14 int n; 15 int S; 16 cin >> n; 17 cin >> S; 18 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){ 19 cin >> save[i]; 20 } 21 /// 22 bool ok = 0; 23 for(int i = 0 ; i < n - 1 ; i++){ 24 for(int j = i + 1 ; j < n ; j++){ 25 if(save[i] + save[j] == S){ 26 ok = 1; break; 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 //// 31 if(ok) cout << "Yes" << endl; 32 else cout << "No" << endl; 33 34 } 35 return 0; 36 }
Problem B : Poker
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB
题目描述:
很多牌中都有顺子,今天?小编给您5张牌,需要客官您判断下这5张牌能不能连成?把同花顺。
同花顺即花?一致的顺子,注意最?的顺子是A 2 3 4 5,最?的是10 J Q K A。
输入:
第?行有?个整数T(1 <= T <= 30),代表数据组数。 每组数据包含5行,每?行包含牌的?值和花色
?值是{2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 J Q K A}当中的一个, 花?是S(spade)、H(heart)、C(club)、D(diamond)其中之?。
输出:
如果给定的牌可以组成同花顺,输出Yes;否则输出No。
样例输入:
2
5 H
6 H
7 H
8 H
9 H
5 H
6 H
7 S
8 C
9 D
样例输出:
Yes
No
题解:
先解决读入问题,很多同学尝试用两个char 读入前后一个牌号一个花色,那么当牌号是10的时候,char 只读入一个字符,就会出现错误,其次,如果用scanf 方式读取字符,需要很小心的考虑空格和回车符,这些都会被当作字符读入。所以十分麻烦。
我采取的做法是读取字符串,然后转化回数字。
好的,接下来我们用到一个手牌数组,save[] , 假如花色没有不同的,save数组中存储所有牌面的数字。
这题的数字中的 A 比较特别, 既可以当作 1 看待 , 也可以当作 14 看待, 那么很有意思的事是当我们碰到A的时候转化成几。我选择了特判 A , 相当于把 1 和 14 都放进了手牌。
我们对手牌save数组排序,从小到大,然后判断一下连续的五张牌是不是都是递增且相差一,如果有A的话,要判断两遍,因为有A,相当于手牌数组中有六个数,可能由1 ~ 5 个数(A为1)是一个顺子,也可能由2 ~ 6 个数(A为14)是一个顺子。
然后就A掉了呐~。
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <string> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 int save[100010]; 10 11 int trans(string &in){ 12 if(in.size() == 2){ 13 return 10; 14 } 15 char k = in[0]; 16 if(k >= ‘1‘ && k <= ‘9‘) return k - ‘0‘; 17 if(k == ‘J‘) return 11; 18 if(k == ‘Q‘) return 12; 19 if(k == ‘K‘) return 13; 20 } 21 22 23 int main(){ 24 int t; 25 cin >> t; 26 while(t--){ 27 char color = ‘ ‘; 28 bool ok = 1; 29 bool is_A = 0; 30 int p = 0; 31 for(int i = 0 ; i < 5 ; i++){ 32 //cout << i << endl; 33 string temp; char c; 34 cin >> temp >> c; 35 //cout << temp << " " << c << endl; 36 if(color == ‘ ‘) color = c; 37 else if(color != c){ 38 ok = 0; 39 } 40 /// 41 if(temp == "A"){ 42 save[p++] = 1; 43 save[p++] = 14; 44 is_A = 1; 45 } 46 else save[p++] = trans(temp); 47 } 48 if(!ok) {printf("No\n"); continue;} 49 // 50 sort(save,save + p); 51 // 52 int pre = save[0]; 53 for(int i = 1 ; i <= 4 ; i++){ 54 if(save[i] != pre + 1){ 55 ok = 0; break; 56 } 57 pre = save[i]; 58 } 59 //cout << "is A " << is_A << endl; 60 if(is_A && !ok){ 61 ok = 1; 62 pre = save[1]; 63 for(int i = 2 ; i <= 5 ; i++){ 64 if(save[i] != pre + 1){ 65 ok = 0; break; 66 } 67 pre = save[i]; 68 } 69 //cout << "ok " << ok << endl; 70 } 71 //// 72 if(!ok) printf("No\n"); 73 else printf("Yes\n"); 74 } 75 return 0; 76 }
Problem C: I Need Minmum Number
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
你有?个序列,一开始是空的,接下来执行n次操作,每次操作都是以下3种之?
2 value 表示在序列末尾加?一个新的数
1 表?删除序列末尾的那个数(此次操作在序列为空时不会出现)
0 表?示询问当前序列?的最小值(此次操作在序列为空时不会出现)
输入:
第?行有个整数T(1 <= T <= 10),代表数据组数。 对于每组数据,第?行包含?个整数n(1 <= n <= 105) 接下来包含n?,代表n次操作。 如果是一个整数0,代表询问当前序列?的最小值。 如果是一个整数1,代表删除序列末尾的那个数。
否则就是2 value,代表在序列末尾加入value(-10000 <= value <= 10000)。
输出:
对于每个0操作,输出当前序列里的最小值。
样例输入:
1
5
2 3
2 1
0
2 -1
0
样例输出:
1
-1
题解:
想用一个栈,和一个变量存储最小值,插入一个数就比较一下,询问的时候直接输出这个存储最小值变量,这样的同学太天真了。
问题是,还有弹出的操作,万一栈顶是最小值,你弹出了栈顶,然后你记录最小值的这个东西又要更新(你从哪里更新呢)。。。。
很多种做法,我的做法是设置两个数组,save数组模拟栈操作,minlist数组也是一个栈,纪录save栈中连续不增的子序列。那么得到以下规则:
1.插入一个数val时,val插入save栈末尾。如果val比minlist栈顶元素小或等于栈顶元素,那么将val插入minlist栈,如果val比minlist栈顶元素大,则不操作。说明save栈在插入val前还有比val小的数。
2.删除save栈顶的数时,首先删除这个栈顶数,其次比较下,这个栈顶数val,是不是等于minlist栈顶数,如果相等,同样将minlist栈顶删除。如果不等于,那么不做操作。
3.请求save栈中最小元素时,即为minlist的栈顶元素。
然后就A掉了呐~。
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 using namespace std; 6 7 int save[100010]; 8 int minlist[100010]; 9 10 int main(){ 11 int t; 12 scanf("%d",&t); 13 while(t--){ 14 int k; 15 scanf("%d",&k); 16 // 17 int pos = 0; 18 int minpos = 0; 19 // 20 for(int i = 0 ; i < k ; i++){ 21 int op; 22 scanf("%d",&op); 23 if(op == 2){ 24 int val; 25 scanf("%d",&val); 26 save[pos++] = val; 27 /// 28 if(minpos == 0){ 29 minlist[minpos++] = val; 30 } 31 else if(val <= minlist[minpos - 1]){ 32 minlist[minpos++] = val; 33 } 34 } 35 else if(op == 1){ 36 int temp = save[pos - 1]; 37 pos--; 38 //////// 39 if(temp == minlist[minpos - 1]){ 40 minpos--; 41 } 42 } 43 else{ 44 printf("%d\n",minlist[minpos - 1]); 45 } 46 } 47 } 48 return 0; 49 }
Problem D : Two’s Complement
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
现代大部分计算机都采用补码的形式存储有符号数,一个长度为w的补码b,
对应的十进制数字为:
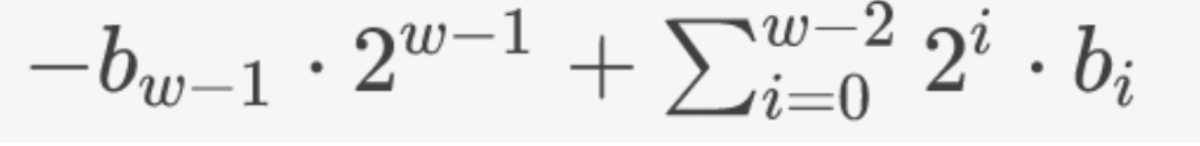
其中bi要么为1,要么为0。
例如,采用5位来表示时,-1的补码就是11111,现在告诉你一串补码,求出对应
的十进制下的数字。
输入:
第一行有一个整数T,代表数据组数(T <= 1000)。
每组数据输入只有一行,代表补码(长度小于等于30,大于等于1)。
输出:
对于每组数据,输出该补码对应的十进制数。
样例输入:
3
1001
10
001
样例输出:
-7
-2
1
题解:
嗯,其实这题需要知道二进制表示的一些知识,一个二进制数,我们从右到左叫做从低位到高位,那么我们从低位到高位的权值依次从2^0 , 2^1 , 2^2 …..
比如,二进制数 101
如何得到十进制数呢 , 从低位到高位,三位的权值分别为 2^0 , 2^1 , 2^2.
那么他的十进制就是1 * 2^0 + 0 * 2^1 + 1 * 2^2.
好了,明白了低位高位和权值的概念,这题就已经可以做了。
这个数学公式的意思是:
-1 * 最高位上的数字 * 最高位上的权值 +(除去最高位后,次高位到最低位表示的这个二进制数。)
比如11111(5个1)是-1,是如何得到的呢?
首先我们发现最高位(也就是最左位)是1,权值是2^4,那么根据公式前一部分 , 计算出为-16.
除去了最高位剩下了1111(四个1)按照二进制计算为15。
那么两部分加起来就是-1啦。
读进来的时候用字符串,然后自己操作下权值就好?
A掉了哇~
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 using namespace std; 6 char save[100010]; 7 int main(){ 8 int t; 9 scanf("%d",&t); 10 while(t--){ 11 scanf("%s",save); 12 int len = strlen(save); 13 int ans = 0; 14 long long quan = 1; 15 for(int i = len - 1; i >= 1 ; i--){ 16 ans += (quan * (save[i] - ‘0‘)); 17 quan*=2; 18 } 19 ans = ans + (-1) * (save[0] - ‘0‘) * quan; 20 cout << ans << endl; 21 } 22 return 0; 23 }
Problem E : Just Go
时间限制: 3 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
There is a river, which contains n stones from left to right. These stones are magic, each
one has a magic number Ai which means if you stand on the ith stone, you can jump to (i +1)th stone, (i+2)th stone, ..., (i+Ai)th stone(when i+Ai > n, you can only reach as far as n), you want to calculate the number of ways to reach the nth stone.
Notice: you can not jump from right to left!
输入:
Input starts with an integer T(1 <= T <= 10), denoting the number of test cases. Each test case contains an integer n(1 <= n <= 105), denoting the number stones. Next line contains n integers Ai(1 <= Ai <= 108).
输出:
For each test case, print the number of way to reach the nth stone module 109+7.
样例输入:
3
5
1 2 3 4 5
1
10
2
2 1
样例输出:
3
1
1
题解:
按照题目意思,模拟操作,套数据结构线段树。
代码:

1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #include <math.h> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 const int N = 110010; 7 const int mod = 1e9 + 7; 8 9 struct SegTree { 10 int l, r; 11 int way; 12 int add; 13 }tree[N << 2]; 14 15 void modify(int &target, int val) { 16 target += val; 17 target = (target % mod + mod) % mod; 18 } 19 20 void pushup(int p) { 21 modify(tree[p].way, (tree[p << 1].way + tree[p << 1 | 1].way) % mod); 22 } 23 24 void build(int p, int l, int r) { 25 tree[p].l = l; 26 tree[p].r = r; 27 tree[p].add = tree[p].way = 0; 28 if (l == r) { 29 if (l == 1) { 30 tree[p].way = 1; 31 } 32 return; 33 } 34 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 35 build(p << 1, l, mid); 36 build(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r); 37 pushup(p); 38 } 39 40 void pushdown(int p) { 41 if (tree[p].add) { 42 modify(tree[p << 1].add, tree[p].add); 43 modify(tree[p << 1 | 1].add, tree[p].add); 44 modify(tree[p << 1].way, tree[p].add); 45 modify(tree[p << 1 | 1].way, tree[p].add); 46 tree[p].add = 0; 47 } 48 } 49 50 void update(int p, int l, int r, int val) { 51 if (l <= tree[p].l && tree[p].r <= r) { 52 modify(tree[p].add, val); 53 modify(tree[p].way, val); 54 return; 55 } 56 pushdown(p); 57 int mid = (tree[p].l + tree[p].r) >> 1; 58 if (r <= mid) { 59 update(p << 1, l, r, val); 60 } 61 else if (l > mid) { 62 update(p << 1 | 1, l, r, val); 63 } 64 else { 65 update(p << 1, l, mid, val); 66 update(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, val); 67 } 68 pushup(p); 69 } 70 71 int query(int p, int pos) { 72 if (tree[p].l == tree[p].r) { 73 return tree[p].way; 74 } 75 pushdown(p); 76 int mid = (tree[p].l + tree[p].r) >> 1; 77 if (pos <= mid) { 78 return query(p << 1, pos); 79 } 80 else { 81 return query(p << 1 | 1, pos); 82 } 83 } 84 85 int main() { 86 int t; 87 scanf("%d", &t); 88 while (t--) { 89 int n; 90 scanf("%d", &n); 91 int val; 92 build(1, 1, n); 93 for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) { 94 scanf("%d", &val); 95 int way = query(1, i); 96 int s = i + 1; 97 int e = min(n, i + val); 98 if (i == n) { 99 continue; 100 } 101 update(1, s, e, way); 102 } 103 printf("%d\n", query(1, n)); 104 } 105 return 0; 106 }
Problem F : Fat Brother’s new way
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
I bet, except Fat Brothers, all of you don’t like strange way to show integers , he is really like this way to showing integers:
1 -> ‘A’
2 -> ‘B’
…….
26 -> ‘Z’
27 -> ‘AA’
28 -> ‘AB’
…….
Unfortunately, Fat Brother’s mathematics is poor, so he needs your help, he will give you some integers, and you must transform it with Fat Brother’s way.
输入:
Input starts with an integer T(T <= 10000), denoting the number of test case.
For each test case, an integers n(1 <= n <= 2147483647) is given.
输出:
For each case, output the corresponding string with upper-case letters.
样例输入:
3
17311
2068
37
样例输出:
YOU
CAN
AK
题解:
先将26个字母存入0~25的数组中,第一步将n - 1对26取余,余数便是对应的字母所在的位置,接下来便是将n除以26直到0为止反复进行这一系列的操作。还有一些细节值得注意。
当n为52时,答案是AZ但只是按这种方法输出会是BZ由于52/26=2。所以在每次n%26=0时n/26
时要减一
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstring> 3 #include <cstdio> 4 using namespace std; 5 char a[27] = "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"; 6 char b[100000]; 7 int main() 8 { 9 int t; 10 scanf("%d" , &t); 11 int n; 12 for(int i = 0 ; i < t ; i++) 13 { 14 scanf("%d" , &n); 15 int g = 0; 16 while(n > 0) 17 { 18 if(n % 26 != 0) 19 b[g++] = a[n % 26 - 1]; 20 else 21 { 22 b[g++] = a[25]; 23 n--; 24 } 25 if(n == 26) 26 break; 27 n /= 26; 28 } 29 for(int i = g - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) 30 printf("%c" , b[i]); 31 printf("\n"); 32 } 33 return 0; 34 }
Problem G : Is The Same?
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
给出2个字符串S和T,如果可以通过循环移位使得S和T相等,则我们称S和T是同构字符串, 例如S=“abcd”, T=“bcda”,则S和T是同构字符串;而S=“abcd”和T=“bcad”则不是同构字符串。
循环移位是指:在?个长度为n的字符串S中,取?个任意下标i,把字符串分为两段,分别为 S1S2...Si 和Si+1Si+2...Sn,然后把字符串变为Si+1Si+2...SnS1S2...Si,例如S=“qwerty”,取i=3, 则变 为”rtyqwe”(注意,一个字符串本?身也算是它的同构字符串)。
输入:
第?行包含一个整数T(1 <= T <= 20),代表测试组数。
对于每组数据,包含2个字符串,字符串长度都小于等于105且非空,输入保证字符串只包含小写字?。
输出:
对于每组数据,如果这两个字符串是同构字符串,则输出Yes,否则输出No。
样例输入:
2
abcd
bcda
abcd
bcad
样例输出:
Yes
No
题解:
姑且算有点算法的水题吧,我们把第一个串叫做A串,第二个叫做B串,如果A串长度和B串都不一样,那么肯定不同构。
那么A串和B串长度相等时,我们继续。
好像有很多的思路,我的想法是将A串倍增两倍,比如A串是abcde,我倍增后A串为abcdeabcde,然后在倍增后的A串中找一下有没有B串就行了。找的到就是同构,找不到就不同构。
字符串匹配,套个KMP就稳稳的过掉了~
A掉了呐~
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 using namespace std; 6 char A[300010]; 7 char B[300010]; 8 int Next[300010]; 9 10 void check(){ 11 int len = strlen(B); 12 for(int i = 0; i < len ; i++){ 13 cout << Next[i] << " "; 14 } 15 cout << endl; 16 return ; 17 } 18 19 void make_next(){ 20 Next[0] = -1; 21 int len = strlen(B); 22 int i = 0, k = -1; 23 while(i < len){ 24 if(k == -1 || B[i] == B[k]){ 25 Next[++i] = ++k; 26 } 27 else k = Next[k]; 28 } 29 return ; 30 } 31 32 bool kmp(){ 33 make_next(); 34 int len1 = strlen(A); 35 int len2 = strlen(B); 36 //// 37 int i = 0 , k = 0; 38 while(i < len1 && k < len2){ 39 if(k == -1 || A[i] == B[k]){i++; k++;} 40 else k = Next[k]; 41 } 42 if(k == len2) return 1; 43 else return 0; 44 } 45 46 int main(){ 47 int t; 48 scanf("%d",&t); 49 while(t--){ 50 scanf("%s",A); 51 scanf("%s",B); 52 int len = strlen(A); 53 // 54 if(len != strlen(B)) {printf("No\n"); continue;} 55 // 56 for(int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++){ 57 A[len + i] = A[i]; 58 } 59 A[2 * len - 1] = ‘\0‘; 60 61 bool ans = kmp(); 62 63 if(ans) printf("Yes\n"); 64 else printf("No\n"); 65 } 66 return 0; 67 }
Problem H : Party
时间限制: 2 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
N students were invited to attend a party, every student has some friends, only if someone’s all friends attend this party, this one can attend the party(ofcourse if he/she has no friends, he/she also can attend it.), now i give the friendship between these students, you need to tell me whether all of them can attend the party.
Note that the friendship is not mature, for instance, if a is b’s friend, but b is not necessary a’s friend.
输入:
Input starts with an integer T(1 <= T <= 10), denoting the number of test case.
For each test case, first line contains an integer N(1 <= N <= 100000), denoting the number of students.
Next n lines, each lines first contains an integer K, denoting the number of friends belong to student i(indexed from 1). Then following K integers, denoting the K friends.
You can assume that the number of friendship is no more than 100000, and the relation like student A is himself’s friend will not be existed.
输出:
For each test case, if all of the students can attend the party, print Yes, otherwise print No.
样例输入:
2
3
1 2
1 3
1 1
3
1 2
0
1 1
样例输出:
No
Yes
题解:
题目大意就是要邀请一堆人去玩,然后呢,有些人要某些人去才肯去,有些人呢,自己就会去。
题目给你N个人,告诉你依赖的关系,或者说这个人不依赖他人。问你能否所有的人都要到。
作为一个有向图,所有人都能到的条件应该就是不存在环,那么首先想到的是简单的用dfs判一下环,可是这里人数太多,用dfs能跑到明年,而且万一不是全部联通的,跑都跑不清楚了。所以改变思路。
先进行规定,如果A依赖B,我们说A到B有一条边(有向边A—>B)。
接下来:
1.建立这个有向图。
2.寻找出度为0的点,放进队列Q中。
3. while(Q不为空)
{
取出队列中的第一个点,删去这个点的相邻边。并将这个点删除。
如果发现删除这个点相邻边后,有点的出度为0,则将这个点压入队列尾。
}
4.若没有点剩余,则全部能去,反之不行。
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <vector> 5 #include <queue> 6 7 using namespace std; 8 9 const int MAX = 100010; 10 11 vector<int> edge[MAX]; 12 queue<int> Q; 13 int out[MAX]; 14 15 void init(int n){ 16 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++){ 17 edge[i].clear(); 18 } 19 return; 20 } 21 22 int main(){ 23 24 int t; 25 scanf("%d",&t); 26 27 while(t--){ 28 int N; 29 scanf("%d",&N); 30 int all = N; 31 while(!Q.empty()) Q.pop(); 32 init(N); 33 ////////////////////// 34 for(int i = 1 ; i <= N ; i++){ 35 int k; 36 scanf("%d",&k); 37 out[i] = k; 38 if(!k) Q.push(i); 39 for(int j = 0 ; j < k ; j++){ 40 int temp; 41 scanf("%d",&temp); 42 edge[temp].push_back(i); 43 } 44 } 45 ////////////////////// 46 47 while(!Q.empty()){ 48 int now = Q.front(); 49 Q.pop(); 50 all--; 51 /////// 52 int size = edge[now].size(); 53 for(int i = 0; i < size ; i++){ 54 int op = edge[now][i]; 55 out[op]--; 56 if(out[op] == 0) Q.push(op); 57 } 58 } 59 60 /////////// 61 if(all) printf("No\n"); 62 else printf("Yes\n"); 63 64 } 65 66 return 0; 67 }
Problem I : Alex’s Foolish Function
时间限制: 8 Sec 内存限制: 128 MB
题目描述:
Alex has an array F which size is n, initially each element’s value is zero. Now he wants to operate the array, he has 4 different functions:
1) Function A(l, r):
Add the elements between l to r (inclusive) where the ith add i - l + 1, for instance, if l is 4,
r is 6 and the elements between 4 to 6 is 3 4 10, after this operation, these elements will become 4 6 13.
2) Function B(l, r):
Add the elements between l to r (inclusive) where the ith add r - i + 1, for instance, if l is 4,
r is 6 and the elements between 4 to 6 is 3 4 10, after this operation, these elements will become 6 6 11.
3) Function C(l, r, x):
Set all the elements(between l to r) to x, for instance, if l is 4, r is 6 and the elements
between 4 to 6 is 3 4 10, and x = 2, after this operation, these elements will become 2 2 2.
4) Function S(l, r):
Output Fl + Fl+1 + Fl+2 + ...+ Fr.
输入:
Input start with an integer T(1 <= T <= 5), denoting the number of test case.
For each test case, first line contains n, m (1 <= n <= 200000, 1 <= m <= 100000), denoting the array’size and the number of operations.
Next m lines, each line contains an operation, formatting as
A l r
B l r
C l r x
S l r
输出:
For each S Function operations, output the sum.
样例输入:
1
5 4
A 1 3
B 2 5
C 1 1 2
S 1 5
样例输出:
17
题解:
按照提议模拟操作,但是要套数据结构,线段树。
代码:

1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 const double pi = acos(-1.0); 5 const int inf = 0x3f3f3f3f; 6 const double eps = 1e-15; 7 typedef long long LL; 8 typedef unsigned long long ULL; 9 typedef pair <int, int> PLL; 10 const LL INF = (1LL << 60); 11 12 const int N = 250010; 13 struct SegTree { 14 int l, r; 15 LL add1, add2, add3; //add1 -> 覆盖, add2->加某个值, add3->加减下标 16 LL sum; 17 }tree[N << 2]; 18 19 void pushup(int p) { 20 tree[p].sum = tree[p << 1].sum + tree[p << 1 | 1].sum; 21 } 22 23 void pushdown(int p) { 24 if (tree[p].add1 != -inf) { 25 tree[p << 1].add2 = tree[p << 1].add3 = tree[p << 1 | 1].add2 = tree[p << 1 | 1].add3 = 0; 26 tree[p << 1].add1 = tree[p << 1 | 1].add1 = tree[p].add1; 27 tree[p << 1].sum = tree[p].add1 * (tree[p << 1].r - tree[p << 1].l + 1); 28 tree[p << 1 | 1].sum = tree[p].add1 * (tree[p << 1 | 1].r - tree[p << 1 | 1].l + 1); 29 tree[p].add1 = -inf; 30 } 31 if (tree[p].add2) { 32 tree[p << 1].add2 += tree[p].add2; 33 tree[p << 1 | 1].add2 += tree[p].add2; 34 tree[p << 1].sum += tree[p].add2 * (tree[p << 1].r - tree[p << 1].l + 1); 35 tree[p << 1 | 1].sum += tree[p].add2 * (tree[p << 1 | 1].r - tree[p << 1 | 1].l + 1); 36 tree[p].add2 = 0; 37 } 38 if (tree[p].add3) { 39 tree[p << 1].add3 += tree[p].add3; 40 tree[p << 1 | 1].add3 += tree[p].add3; 41 tree[p << 1].sum += tree[p].add3 * (LL)(tree[p << 1].r - tree[p << 1].l + 1) * (tree[p << 1].l + tree[p << 1].r) / 2; 42 tree[p << 1 | 1].sum += tree[p].add3 * (LL)(tree[p << 1 | 1].r - tree[p << 1 | 1].l + 1) * (tree[p << 1 | 1].l + tree[p << 1 | 1].r) / 2; 43 tree[p].add3 = 0; 44 } 45 } 46 47 void build(int p, int l, int r) { 48 tree[p].l = l; 49 tree[p].r = r; 50 tree[p].sum = tree[p].add2 = tree[p].add3 = 0; 51 tree[p].add1 = -inf; 52 if (l == r) { 53 return; 54 } 55 int mid = (l + r) >> 1; 56 build(p << 1, l, mid); 57 build(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r); 58 } 59 60 void update(int p, int l, int r, int id, int val) { 61 if (l <= tree[p].l && tree[p].r <= r) { 62 if (id == 1) { 63 tree[p].add1 = (LL)val; 64 tree[p].add2 = tree[p].add3 = 0; 65 tree[p].sum = (LL)val * (tree[p].r - tree[p].l + 1); 66 } 67 else if (id == 2) { 68 tree[p].add2 += (LL)val; 69 tree[p].sum += (LL)val * (tree[p].r - tree[p].l + 1); 70 } 71 else { 72 tree[p].add3 += (LL)val; 73 tree[p].sum += (LL)val * (LL)(tree[p].r - tree[p].l + 1) * (LL)(tree[p].l + tree[p].r) / 2; 74 } 75 return; 76 } 77 pushdown(p); 78 int mid = (tree[p].l + tree[p].r) >> 1; 79 if (r <= mid) { 80 update(p << 1, l, r, id, val); 81 } 82 else if (l > mid) { 83 update(p << 1 | 1, l, r, id, val); 84 } 85 else { 86 update(p << 1, l, mid, id, val); 87 update(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r, id, val); 88 } 89 pushup(p); 90 //printf("区间[%d, %d], sum = %lld\n", tree[p].l, tree[p].r, tree[p].sum); 91 } 92 93 LL query(int p, int l, int r) { 94 if (l <= tree[p].l && tree[p].r <= r) { 95 return tree[p].sum; 96 } 97 pushdown(p); 98 int mid = (tree[p].l + tree[p].r) >> 1; 99 if (r <= mid) { 100 return query(p << 1, l, r); 101 } 102 else if (l > mid) { 103 return query(p << 1 | 1, l, r); 104 } 105 else { 106 return query(p << 1, l, mid) + query(p << 1 | 1, mid + 1, r); 107 } 108 } 109 110 int main() { 111 int t; 112 scanf("%d", &t); 113 while (t--) { 114 int n, m, l, r, val; 115 char str[3]; 116 scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); 117 build(1, 1, n); 118 while (m--) { 119 scanf("%s", str); 120 if (str[0] == ‘S‘) { 121 scanf("%d%d", &l, &r); 122 printf("%lld\n", query(1, l, r)); 123 } 124 else if (str[0] == ‘A‘) { 125 scanf("%d%d", &l, &r); 126 update(1, l, r, 2, 1 - l); 127 update(1, l, r, 3, 1); 128 } 129 else if (str[0] == ‘B‘) { 130 scanf("%d%d", &l, &r); 131 update(1, l, r, 2, r + 1); 132 update(1, l, r, 3, -1); 133 } 134 else { 135 scanf("%d%d%d", &l, &r, &val); 136 update(1, l, r, 1, val); 137 } 138 } 139 } 140 return 0; 141 }
Problem J : 对数问题
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
Alex有一个问题,给你一个数组,然后给你一个数k,问你数组中和为k的数对有多少对(各个对中下标不同就算一对)。
输入:
有t(t <= 10)组数,每组给你数n(n <= 100)和k(k <= 10000),表示数组的大小,然后下面给你n个数ai(1 <= ai <= 100)表示数组的元素大小。
输出:
输出和为k的对数有多少对,没有的话为0。
样例输入:
1
4 3
1 2 1 2
样例输出:
4
题解:
和对数一点关系都没有,是“数对问题”比较贴切吧。
还是很水的,全部试一遍就好了,两个for,有点像A题,只是这题要你数出几个,不要数重复就好。
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <string> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 long long save[10010]; 10 int main(){ 11 int t; 12 cin >> t; 13 while(t--){ 14 int n; 15 int K; 16 cin >> n; 17 cin >> K; 18 for(int i = 1; i <= n ; i++){ 19 cin >> save[i]; 20 } 21 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ 22 sum[i] = save[i] + sum[i - 1]; 23 } 24 int ans = 0; 25 for(int i = 1 ; i <= n; i++){ 26 for(int j = i + 1 ; j <= n ; j++){ 27 if(save[i] + save[j] == K) ans++; 28 } 29 } 30 /// 31 cout << ans << endl; 32 } 33 return 0; 34 }
Problem K : Page Fault
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
要说起操作系统存储器管理,少不了要谈下分页存储管理,它把进程的虚拟地址空间和实际
的主存地址空间划分为同样?小的页(1KB,2KB或者4KB),然后提供一种从虚拟地址到实际物理地址的翻译机制。另外,虚拟地址空间还把一些表?完整信息的?划分为一个段,且每个段都有?个权限要求。
如果一个虚拟地址?法找到对应的实际物理地址,CPU就会引发一个缺?中断,但是在这之 前,CPU必须知道这个地址是否合法,简单来说,CPU会把这个地址和虚拟地址空间的各个段?较,如果地址没有落在这些段?,或者虽然在一个段中,但是权限不够,就会产?一个Segment Fault 异常;否则说明这是一个合法地址,可以进?页面调度。
输入:
第?行有?个整数T,代表数据组数(T <= 1000)。 每组数据包含一个整数n(1 <= n <= 100),代表段的数目。 接下来n行,包含三个整数 start, end, prot,start是开始地址, end是结束地址,prot是对应权限,保证段与段之间不相交 (即不会出现诸如[3,5], [5,7]之类的情况)。 最后?行包含一个整数address,表?示需要验证的地址。
(0 <= start, end, address <= 231 - 1, 0 <= prot <= 1) 假设我们的程序对prot为1的段没有权限,所以无法访问这些段。
输出:
对于每组数据,如果产?生了段错误,输出Segment Fault,否则输出Missing Page Interrupt。
样例输入:
3
3
0 3 1
4 5 0
6 8 1
7
1
0 3 1
2
2
0 0 0
1 3 0
2
样例输出:
Segment Fault
Segment Fault
Missing Page Interrupt
题解:
用结构体纪录每一个给你的区间的上下段,和记录这个区间的权限,设置成数组,读入所有的段,然后for一遍就可以了,水题。
特别注意一下,假如给你的段最大到达 比如是 8 , 他给你地址是 10 的时候,输出也是 fualt.
我用了long long,貌似是不需要的,用int存就可以了。
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <string> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 pair<long long , long long> save[100010]; 10 bool pro[10100]; 11 12 int main(){ 13 int t; 14 cin >> t; 15 while(t--){ 16 int n; 17 scanf("%d",&n); 18 for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){ 19 long long temp1 , temp2 , p; 20 cin >> temp1 >> temp2 >> p; 21 save[i] = make_pair(temp1,temp2); 22 if(p == 1) pro[i] = 1; 23 else pro[i] = 0; 24 } 25 long long add; 26 cin >> add; 27 bool ok = 0; 28 for(int i = 0; i < n ; i++){ 29 long long begin = save[i].first; 30 long long end = save[i].second; 31 //// 32 if(add >= begin && add <= save[i].second){ 33 if(pro[i] == 1) ok = 0; 34 else ok = 1; 35 break; 36 } 37 } 38 /// 39 if(!ok) cout << "Segment Fault" << endl; 40 else cout << "Missing Page Interrupt" << endl; 41 } 42 return 0; 43 }
Problem L : VectorMultiply
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
There are two vector A(x1, x2, x3, ..., xn) and B(y1, y2, ..., yn), and the dot product(点积) is x1*y1 + x2*y2 + ... + xn*yn.
You can swap the order of any dimension, for example, A = {1, 2, 3}, then you can make A to {1, 3, 2} or {2, 1, 3} and so on.
Now you need to calculate the maximum value of dot product.
输入:
Input starts with an integer T (T <= 20)denoting the test case.
For each test case, first line contains n(n <= 10000)
then two lines follow, each line contains n integers(1 <= xi, yi <= 100000).
输出:
For each test case, print the maximum value of dot product.
样例输入:
1
4
1 3 2 10
2 3 4 1
样例输出:
54
题解:
这两个向量里面的数字都是正数,那么就很简单了,大的乘大的,小的乘小的就好。用sort排序啊,自己写个冒泡的话,实在效率太低了.......
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <stack> 4 #include <cstring> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 #include <string> 7 using namespace std; 8 9 long long save1[10010]; 10 long long save2[10010]; 11 int main(){ 12 int t; 13 cin >> t; 14 while(t--){ 15 long long ans = 0; 16 int n; 17 cin >> n; 18 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){ 19 cin >> save1[i]; 20 } 21 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){ 22 cin >> save2[i]; 23 } 24 sort(save1,save1+n); 25 sort(save2,save2+n); 26 for(int i = 0 ; i < n ; i++){ 27 ans += (save1[i] * save2[i]); 28 } 29 cout << ans << endl; 30 } 31 return 0; 32 }
Problem M : Hot Hot Up
时间限制: 1 Sec 内存限制: 64 MB
题目描述:
欢迎参加本次比赛,请输出谚语: “A young idler, an old beggar”。
输入:
本题没有输?。
输出:
输出”A young idler, an old beggar”(不含引号)。
样例输出:
A young idler, an old beggar
题解:
作为本场比赛最难的一道题,我真不知道这题题解怎么写。
代码:

1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main(){ 5 printf("A young idler, an old beggar\n"); 6 return 0; 7 } 8
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/ticsmtc/p/5478434.html