标签:
标签(空格分隔): 鸟哥的linux私房菜
Regular Expression,RE
系统每天会产生很多信息,数据量太大,系统管理员用正则表达式需要取出我们需要的信息
正则表达式和通配符是完全不一样的东西
取出满足条件的行
-A (after) 匹配行的后n行也列出
-B (before) 匹配行的前n行也列出
-n 显示行号
-v 反选
-i 忽略大小写
练习的大前提是:
export LANG=C的设置;grep --color=autowget wget http://linux.vbird.org/linux_basic/0330regularex/regular_express.txt该命令获取鸟哥的练习文本
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ grep -n ‘t[ae]st‘ regular_express.txt
8:I can‘t finish the test.
9:Oh! The soup taste good.查找 ‘tast’, ‘test’
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ grep -n ‘[^g]oo‘ regular_express.txt
2:apple is my favorite food.
3:Football game is not use feet only.
18:google is the best tools for search keyword.
19:goooooogle yes!19行满足条件的是 ‘ooo’而不是’goo’
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ grep -n ‘[^a-z]oo‘ regular_express.txt
3:Football game is not use feet only.当我们在一组集合字符串中,如果字符组是连续的,例如大写字母,小写字母,数字等,我们可以使用[A-Z],[a-z],[0-9]等方式来书写。
不同语系,字符的顺序可以略有不同,也可以用以下方式取得前面的连续编码
‘[^[:lower]oo]‘ [[:digit]]
行首与行尾字符^$
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ grep -n ‘^the‘ regular_express.txt
12:the symbol ‘*‘ is represented as start.grep -n ‘^[[:lower:]]‘ regular_express.txt ##or ‘^[a-z]‘grep -n ‘^[^[:lower:]]‘ regular_express.txt ##or ‘^[a-z]‘注意
1.:[[:lower:]]内层中括号是表示一个序列字符的格式,外层中括号是表示使用括号的若干个字符中的任意一个(即字符集合符号),缺一不可。
2.^符号在外层中括号外是表示行首,在外层中括号内表示“反向选择”
找出行尾结束为小数点(.)的行
grep -n ‘\.$‘ regular_express.txt ## 小数点有其他意义所以需要反斜杠转义grep -n ‘^$‘ regular_express.txt任意一个字符.与重复字符*
和通配符不同 *号不代表任意字符,而代表重复前一个RE字符0到无穷多次的意思,为组合形态
.(小数点)代表一定有一个任意字符的意思
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ grep -n ‘g..d‘ regular_express.txt
1:"Open Source" is a good mechanism to develop programs.
9:Oh! The soup taste good.
16:The world <Happy> is the same with "glad".* 的用法
grep -n ‘o*‘ regular_express.txt 会列出所有行,’o*’代表空字符或者一个o以上的字符
grep -n ‘oo*‘ regular_express.txt 会列出至少有一个o的字符
grep -n ‘ooo*‘ regular_express.txt 会列出至少有两个o的字符
总结:找出有一个以上某字符(X)的行
grep -n ‘XX*‘ filename
限定连续RE字符范围{}
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ grep -n ‘o\{2\}‘ regular_express.txt
1:"Open Source" is a good mechanism to develop programs.
2:apple is my favorite food.
3:Football game is not use feet only.
9:Oh! The soup taste good.
18:google is the best tools for search keyword.
19:goooooogle yes!hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ grep -n ‘go\{2,5\}g‘ regular_express.txt #o\{2,\}指2个以上o
18:google is the best tools for search keyword.sed本身也是一个管道命令,可以分析standard input,sed可以将数据进行替换、删除、新增、选取特定行等功能。
sed [-nefr] [动作]
参数
-n :使用安静模式,(没懂)
-e :直接命令行模式上进行sed的动作编辑’
-f :直接将sed的动作写在一个文件内,-f filename则可以执行filename内的sed动作
-r :sed的动作支持的是扩展型正则表达式的语法(默认是基础正则表达式语法)
-i :直接修改读取的文件内容,而不是由屏幕输出
动作说明: [n1[,n1]]function
n1,n2 :不见得会存在,一般代表选择进行动作的行数,“10,20” 表示10到20行
a :新增,在目前的下一行,增加新的一行
c :替换,替换某些行
d :删除
i :插入,在目前的上一行,增加新的一行
p :打印,
s :替换,例如 1,20s/old/new/g删除2-5行
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:/etc$ nl passwd | sed ‘2,5d‘
删除第二行
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:/etc$ nl passwd | sed ‘2d‘
删除第三行至最后一行
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:/etc$ nl passwd | sed ‘3,$d‘ $表示最后一行
在第二行后(即是加在第三行)加上”drink tea?”字样!
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:/etc$ nl passwd | sed ‘2a drink tea?‘ ##2i就是插在第二行前
1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
2 daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin
drink tea?
3 bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin
4 sys:x:3:3:sys:/dev:/usr/sbin/nologin
……##后面省略hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~$ nl /etc/passwd | sed ‘2i drink tea or drink beer ?‘
1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
drink tea or
drink beer ?
2 daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologinhanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~$ nl /etc/passwd | sed ‘2,5c No 2-5 number‘
1 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash
No 2-5 number
6 games:x:5:60:games:/usr/games:/usr/sbin/nologin
7 man:x:6:12:man:/var/cache/man:/usr/sbin/nologinhanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~$ nl /etc/passwd | sed -n ‘2,5p‘
2 daemon:x:1:1:daemon:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin/nologin
3 bin:x:2:2:bin:/bin:/usr/sbin/nologin
4 sys:x:3:3:sys:/dev:/usr/sbin/nologin
5 sync:x:4:65534:sync:/bin:/bin/synchanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~$ echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin:/usr/games:/usr/local/games
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~$ echo $PATH |sed ‘s/usr/user/g‘
/user/local/sbin:/user/local/bin:/user/sbin:/user/bin:/sbin:/bin:/user/games:/user/local/gameshanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ sed -i ‘s/\.$/!/g‘ regular_express.txt 在最后一行加入’#This is a test’
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ sed -i ‘$#aThis is a test‘ regular_express.txt 可以用来简化命令,比如:取出空白行与行首为#的行我们使用:
grep -v ‘^$‘ regular_express.txt | grep -v ‘^#‘
可以用简化为:
egrep -v ‘^$|^#‘ regular_express.txt
egrep 与grep -E 是类似命令别名的关系
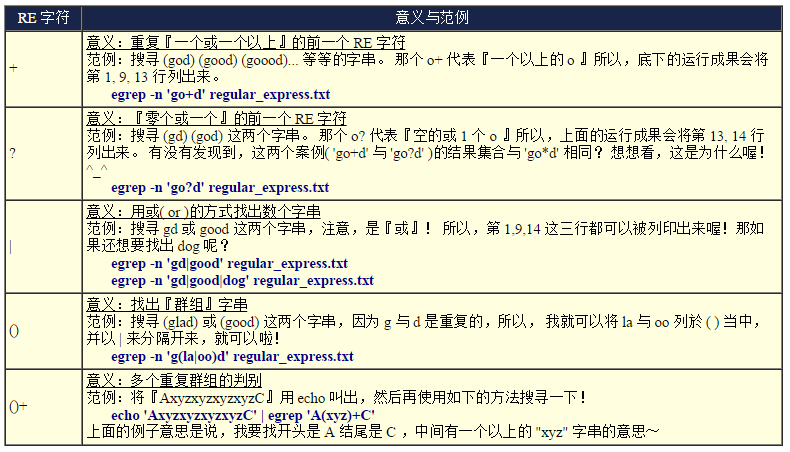
egrep -n ‘g(oo|la)d‘hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ echo ‘AxyzC‘ | egrep ‘A(xyz)?C‘
AxyzC
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ echo ‘AC‘ | egrep ‘A(xyz)?C‘
AC
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ echo ‘AxyzxyzxyzxyzC‘ | egrep ‘A(xyz)+C‘
AxyzxyzxyzxyzC运用一些操作,我们不需要vim去编辑文件,通过数据流重定向配合printf,awk命令,就可以控制文件的输出格式.
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ printf ‘%10s\t %5i\t %5i\t %5i\t %8.2f\t \n‘ $(cat printf_test.txt|grep -v Name)
DmTsai 80 60 92 77.33
VBird 75 55 80 70.00
Ken 60 90 70 73.33
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ cat printf_test.txt
Name Chinese English Math Average
DmTsai 80 60 92 77.33
VBird 75 55 80 70.00
Ken 60 90 70 73.33
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ printf ‘%s\t %s\t %s\t %s\t %s\t \n‘ $(cat printf_test.txt)
Name Chinese English Math Average
DmTsai 80 60 92 77.33
VBird 75 55 80 70.00
Ken 60 90 70 73.33
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ printf ‘%10s\t %5i\t %5i\t %5i\t %8.2f\t \n‘ $(cat printf_test.txt|grep -v Name)
DmTsai 80 60 92 77.33
VBird 75 55 80 70.00
Ken 60 90 70 73.33 列出十六进制数值45 代表的字符
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ printf ‘\x45\n‘
E 相比于sed常常作用于一整行的处理,awk则比较倾向于将一行分成数个”字段”来处理.因此,awk相当适合处理小型的数据处理.
awk的用法
awk ‘条件类型1{动作1} 条件类型2{动作2} …‘ filename 示例
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ last -n 5
hanzhou pts/1 :0 Fri Apr 22 10:29 still logged in
hanzhou :0 :0 Fri Apr 22 10:29 still logged in
reboot system boot 4.2.0-34-generic Fri Apr 22 10:29 - 16:54 (06:24)
hanzhou pts/1 :0 Thu Apr 21 16:30 - crash (17:58)
hanzhou pts/5 :0 Wed Apr 20 17:30 - 17:08 (23:38)
wtmp begins Fri Apr 1 15:13:50 2016
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ last -n 5 | awk ‘{print $1 "\t" $3}‘
hanzhou :0
hanzhou :0
reboot boot
hanzhou :0
hanzhou :0
wtmp Fri
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ awk的内置变量
NF : 每一行($0)拥有的字段总数
NR : 目前awk所处里的是’第几行’数据
FS : 目前的分隔字符默认是空格键
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ last -n 5 | awk ‘{print $1 "\t lines:" NR "\t colume: " NF}‘
hanzhou lines:1 colume: 10
hanzhou lines:2 colume: 10
hanzhou lines:3 colume: 10
reboot lines:4 colume: 11
hanzhou lines:5 colume: 10
lines:6 colume: 0
wtmp lines:7 colume: 7
NF,NR,FS前不需要加$符,单引号里面,不能再用单引号,要用双引号
hanzhou@hanzhou-VirtualBox:~/main$ cat /etc/passwd | awk ‘begin {FS=":"} $3 < 10 {print $1} ‘
说明:1.先改变分隔字符,不加begin的话,第一行还是按默认的分隔字符;
2.$3 < 10,相当于sql里的where条件
$ cat pay.txt | awk ‘NR==1{printf "%10s %10s %10s %10s %10s\n",$1,$2,$3,$4,"Total" }
NR>=2{total = $2 + $3 + $4
printf "%10s %10d %10d %10d %10.2f\n", $1, $2, $3, $4, total}‘
Name 1st 2nd 3th Total
VBird 23000 24000 25000 72000.00
DMTsai 21000 20000 23000 64000.00
Bird2 43000 42000 41000 126000.00
$ cat pay.txt | awk ‘NR==1{printf "%10s %10s %10s %10s %10s\n",$1,$2,$3,$4,"Total" } ;NR>=2{total = $2 + $3 + $4 ;printf "%10s %10d %10d %10d %10.2f\n", $1, $2, $3, $4, total}‘
Name 1st 2nd 3th Total
VBird 23000 24000 25000 72000.00
DMTsai 21000 20000 23000 64000.00
Bird2 43000 42000 41000 126000.00$ cat pay.txt | awk ‘{if (NR==1) printf "%10s %s10s %10s %10s %10s\n",$1,$2,$3,$4,"Total" };NR > 1 {total = $2+$3+$4;printf "%10s %10d %10d %10d %10.2f\n", $1, $2, $3, $4, total}‘diff
通常是用在同一的文件(或软件)的新旧版本区别上。
git diff
cmp ,cmp按字节比较,diff按字节比较
标签:
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/h_hzhou/article/details/51435647