标签:
使用数组自上而下,自左至右存储完全二叉树上的结点元素,即将完全二叉树上编号为i的结点元素存储在某个数组下标为i-1的分量中,然后通过一些方法确定结点在逻辑上的父子和兄弟关系。
根据二叉树的性质,完全二叉树和满二叉树树采用顺序存储比较合适,树中结点的序号可以唯一地反映出结点之间的逻辑关系,既能节省存储空间,又能利用数组元素下标值确定结点在二叉树中的位置,以及结点之间的关系。
而对于一般的二叉树也必须按照完全二叉树的形式存储,也就是必须添加一些并不存在的虚拟结点,造成空间的浪费。
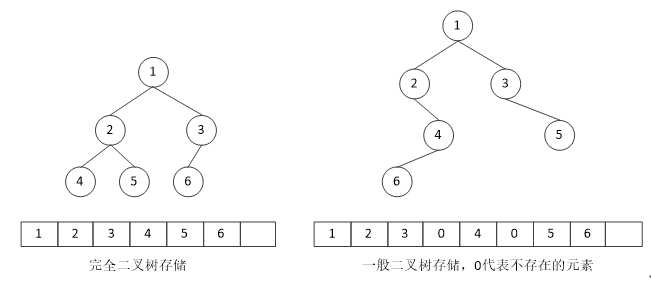
图1 二叉树顺序存储
顺序存储的关键是数组下标确定结点的位置,如结点从1开始编号,那么结点i的左孩子为2*i,右孩子为2*i+1。不存在结点用0表示。
先回忆一下二叉树的一些性质:
(1) 非空二叉树第k层最多有2k-1个结点
(2) 高度为h的二叉树至多有2h-1个结点
首先按照树的高度height初始化一颗树,以及一些有用的方法,代码如下:
public class ArrayBiTree<T> {
private Object[] data;
private int height = 3; // 树的高度 默认为3
private int n; // 结点个数
public ArrayBiTree() {
data = new Object[(int) Math.pow(2, height)];
init();
}
/**
* 指定深度初始化一个树
* @param height 树的深度
*/
public ArrayBiTree(int height) {
this.height = height;
data = new Object[(int) Math.pow(2, height) - 1];
}
private void init(){
System.out.println("默认生成一颗完全二叉树,高度为3:");
for(int i=0; i<(int) Math.pow(2, height) - 1; i++){
data[i] = i+1;
n++;
}
print();
}
/**
* 判断结点是否存在
* @param index 根节点从 1 开始
* @return
*/
public boolean isExist(int index){
if(index > n) return false;
return Integer.valueOf(data[index-1].toString()) != 0;
}
}
/**
* 层次遍历,利用队列是实现
*/
public void levelOrder(){
RingBuffer<Integer> queue = new RingBuffer<Integer>(n+1);
queue.put(1); // 根节点先进队列
while(queue.size()>0){
int tmp = queue.get();
System.out.print(data[tmp-1]+" ");
if (isExist(2 * tmp)) { // 如果左子树存在,把左子树编号入栈
queue.put(2 * tmp);
}
if (isExist(2 * tmp + 1)) { // 如果右子树存在,把右子树编号入栈,
queue.put(2 * tmp + 1);
}
}
}
/**
* 先序遍历,递归实现Recursion
* @param index 根节点从 1 开始
*/
public void preOrderRecur(int index){
if(isExist(index)){ //判断结点是否存在
System.out.print(data[index-1]+" "); // 访问根节点
preOrderRecur(2*index); // 递归遍历左子树
preOrderRecur(2*index + 1); // 递归遍历右子树
}
}
实现方法1:
/**
* 先序遍历,非递归实现,借助栈来实现<p>
* 根节点先入栈,访问栈顶结点,若栈顶元素的右孩子存在则入栈,若栈顶元素的左孩子存在则入栈,如此循环直到栈空
*/
public void preOrder(){
ArrayStack<Integer> stack = new ArrayStack<Integer>(n);
stack.push(1); // 根节点入栈
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
int tmp = stack.pop(); // 取根结点,把每个结点都看作根节点
System.out.print(data[tmp-1]+" "); // 访问根结点
if (isExist(2 * tmp + 1)) { // 如果根节点的右子树存在,把右子树编号入栈
stack.push(2 * tmp + 1);
}
if (isExist(2 * tmp)) { // 如果根节点的左子树存在,把左子树编号入栈
stack.push(2 * tmp);
}
}
}
实现方法2:
/**
* 先序遍历1,非递归实现,借助栈来实现<p>
* @param index 根节点从 1 开始
*/
public void preOrderOne(int index){
ArrayStack<Integer> stack = new ArrayStack<Integer>(n);
while (isExist(index) || !stack.isEmpty()) {
// (1) 首先访问根节点,一直往左下方走,直到一个左孩子不存在的结点。
while (isExist(index)) {
System.out.print(data[index - 1] + " ");
stack.push(index); // 根节点入栈,把每个结点都看作一个根节点,检查其左右孩子是否存在
index = 2 * index;
}
// 此时,栈内是从根节点左孩子开始的左孩子,最后一个结点是不存在左孩子的结点
// (2) 拿栈顶元素,看其右孩子是否存在,把当前结点置为其右孩子,继续循环判断(1)
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int tmp = stack.pop(); // 弹出的左子树结点
index = 2 * tmp + 1; // 看它的右孩子是否存在
}
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历,递归实现Recursion
* @param index 根节点从 1 开始
*/
public void inOrderRecur(int index){
if(isExist(index)){
inOrderRecur(2*index); // 递归遍历左子树
System.out.print(data[index-1]+" "); // 访问根节点
inOrderRecur(2*index + 1); // 递归遍历右子树
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历,非递归实现,更改访问时机即可
* @param index
*/
public void inOrder(int index){
ArrayStack<Integer> stack = new ArrayStack<Integer>(n);
while(isExist(index) || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(isExist(index)){
stack.push(index); // 根节点入栈
index = 2 * index; // 是否存在左孩子
}
if(!stack.isEmpty()){
int tmp = stack.pop(); // 弹出左孩子
System.out.print(data[tmp-1]+" "); // 访问结点
index = 2 * tmp + 1; // 看左孩子的右孩子是否存在
}
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历,递归实现Recursion
* @param index 根节点从 1 开始
*/
public void postOrderRecur(int index){
if(isExist(index)){
postOrderRecur(2*index); // 递归遍历左子树
postOrderRecur(2*index + 1); // 递归遍历右子树
System.out.print(data[index-1]+" "); // 访问根节点
}
}
/**
* 后序遍历,非递归实现<p>
* 与前中序相比实现比较麻烦,先访问左子树再访问右子树
*/
public void postOrder(int index){
ArrayStack<Integer> stack = new ArrayStack<Integer>(n);
int visited = 0; // 标记前一个已被访问的结点
while(isExist(index) || !stack.isEmpty()){
while(isExist(index)){
stack.push(index); // 根节点入栈
index = 2 * index;
}// 先把 index 的左孩子全部找到
int top = stack.peek(); // 查看栈顶元素,没有弹出,访问完右孩子之后在弹出访问根节点
// 如果当前结点不存在右孩子或者右孩子已经访问过,则访问当前结点
if(!isExist(2*top+1) || (2*top+1) == visited){
int tmp = stack.pop();
System.out.print(data[tmp-1]+" ");
visited = tmp;
} else { // 否则访问右孩子
index = 2 * top + 1;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayBiTree<Integer> biTree = new ArrayBiTree<Integer>();
System.out.print("先序遍历(递归):");
biTree.preOrderRecur(1);
System.out.print("\n中序遍历(递归):");
biTree.inOrderRecur(1);
System.out.print("\n后序遍历(递归):");
biTree.postOrderRecur(1);
System.out.print("\n层次遍历:");
biTree.levelOrder();
System.out.print("\n先序遍历(非递归):");
biTree.preOrder();
// biTree.preOrderOne(1);
System.out.print("\n中序遍历(非递归):");
biTree.inOrder(1);
System.out.print("\n后序遍历(非递归):");
biTree.postOrder(1);
System.out.println();
biTree.stdIn();
}

标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/cyhe/p/5521587.html