标签:
| Solved | Pro.ID | Title | Ratio(Accepted / Submitted) | Language |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1001 | D++游戏 | 13.79% (16/116) | 中文 | |
| 1002 | K个联通块 | 17% (136/800) | 中文 | |
 |
1003 | 拍照 | 22.49% (434/1930) | 中文 |
| 1004 | XOR 游戏 | 22.14% (114/515) | 中文 | |
| 1005 | 带可选字符的多字符串匹配 | 0.52% (1/194) | 中文 | |
| 1006 | 矩阵方程的解 | 6.61% (8/121) | 中文 |
1003 拍照
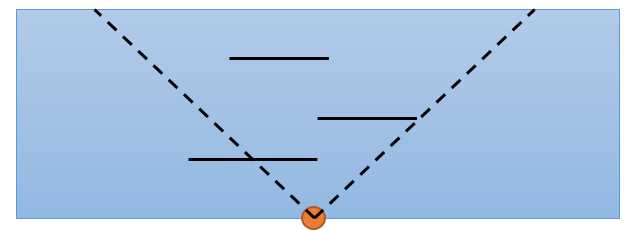
题意:给出n艘船的(x,y,z,d),x和y代表船左端点和右端点的横坐标,z为船的纵坐标,都为整数,d代表每艘船的方向,1为向右、-1为向左。所有船运动速度相同。如下图,主角可以在z=0的直线上任意一点拍照,照相机视角90度,只能垂直向上拍,问一张照片最多能拍到多少艘完整的船。
题解:
因为相同方向的船是相对静止的,我们可以先考虑静止的情况,分别对两种方向的船进行考虑,然后再综合各自的结果来得出总的答案。
考虑静止情况:
要是枚举每艘船的左端点与左射界重合,检查有多少船在视野中,肯定能得到最优解,但复杂度O(n^2),要思考能否低复杂度枚举船并计算视野中船数。
我们可以把船按照x+z排序(x+z即以该船左端点与左射界重合时,拍照点的横坐标),然后从大到小扫,讲扫到的点的y-z加入大端优先队列中。每当优先队列中最大的数大于当前的x+z,就把它弹出,因为它在视野右边了。这样,当前的优先队列大小就是看到的船数。O(n)得出以各个船为左射界时的船数。
对两个方向做以上处理,得到往左的若干个照相点,往右的若干个照相点,然后考虑两个方向的某个照相点能否重合。
也用优先队列,先把两方向照相点各自按横坐标排序,把往左照相点从小到大扫一遍,扫的时候把 往右照相点集中的 横坐标小于当前照相点的照相点 的船数加入优先队列,更新答案 ans = max(ans , 优先队列中最大的 + 当前点船数),扫一遍就无敌了,也是O(n)。
总的复杂度就是排序的nlog(n)
代码:

1 //#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:102400000,102400000") 2 /**Header!**/ //{ 3 #include<cstdio> 4 #include<cmath> 5 #include<iostream> 6 #include<cstring> 7 #include<algorithm> 8 #include<cmath> 9 #include<map> 10 #include<set> 11 #include<stack> 12 #include<queue> 13 using namespace std; 14 15 #define MZ(array) memset(array, 0, sizeof(array)) 16 #define MF1(array) memset(array, -1, sizeof(array)) 17 #define MINF(array) memset(array, 0x3f, sizeof(array)) 18 #define REP(i,n) for(i=0;i<(n);i++) 19 #define FOR(i,x,n) for(i=(x);i<=(n);i++) 20 #define ROF(i,x,y) for(i=(x);i>=(y);i--) 21 #define RD(x) scanf("%d",&x) 22 #define RD2(x,y) scanf("%d%d",&x,&y) 23 #define RD3(x,y,z) scanf("%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z) 24 #define RD4(x,y,z,w) scanf("%d%d%d%d",&x,&y,&z,&w) 25 #define WN(x) printf("%d\n",x); 26 #define RE freopen("D.in","r",stdin) 27 #define WE freopen("huzhi.txt","w",stdout) 28 #define MP make_pair 29 #define PB push_back 30 #define PF push_front 31 #define PPF pop_front 32 #define PPB pop_back 33 #define lowbit(x) ((x)&(-x)) 34 #define cindiao ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0) 35 #define fcout(x,y) cout << fixed << setprecision(x) << (y) << endl 36 typedef long long LL; 37 typedef unsigned long long ULL; 38 typedef pair<int,int> PII; 39 template<class T>inline void OA(const T &a,const int &st,const int &ed) { 40 if(ed>=st)cout<<a[st]; 41 int i; 42 FOR(i,st+1,ed)cout<<‘ ‘<<a[i]; 43 puts(""); 44 } 45 template <class T> inline T quickPow(T p,T e,const T &M){ 46 LL ret = 1; 47 for(; e > 0; e >>= 1){ 48 if(e & 1) ret = (ret * p) % M; 49 p = (p * p) % M; 50 } return (T)ret; 51 } 52 template <class T> inline T gcd(const T &a,const T &b){return (b==0) ? a : gcd(b,a%b);} 53 template <class T> inline T niyuan(const T &a, const T &M){return quickPow(a,M-2,M);} 54 template <class T> inline T exgcd(const T &a,const T &b,T &x,T &y) { 55 if (!b) {x=1,y=0;return a;} 56 T ret=exgcd(b,a%b,x,y), t; 57 t=x,x=y,y=t-a/b*y; 58 return ret; 59 } 60 template <class T> inline T niyuanex(const T &a, const T &M){ 61 T x,y; 62 exgcd(a,M,x,y); 63 return (x+M)%M; 64 } 65 inline LL calC(const int &n,int m,const LL &MOD){ 66 m=(n-m>m)?m:(n-m); 67 LL up=1,down=1; 68 int i; 69 for(i=1;i<=m;i++){ 70 down*=i; 71 down%=MOD; 72 up*=(n-i+1); 73 up%=MOD; 74 } 75 return (up*niyuanex(down, MOD))%MOD; 76 } 77 inline LL Lucas(const int &n,const int &m, const int &MOD) { 78 if(m==0)return 1; 79 return (1LL * Lucas(n/MOD, m/MOD, MOD)*calC(n%MOD, m%MOD, MOD))%MOD; 80 } 81 const int gx[4] = {-1,0,1,0}; 82 const int gy[4] = {0,1,0,-1}; 83 const double PI=acos(-1.0); 84 //} 85 const double EPS=1e-10; 86 inline int sgn(double &x) { 87 if(fabs(x) < EPS)return 0; 88 if(x < 0)return -1; 89 else return 1; 90 } 91 const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; 92 const int NINF=0x80000001; 93 const int MAXN=11111; 94 const int MAXM=33; 95 const int MOD = 1000000007; 96 97 struct Node{ 98 int x,y,z; 99 Node(){} 100 Node(int _x,int _y,int _z){ 101 x=_x; 102 y=_y; 103 z=_z; 104 } 105 inline bool operator<(const Node &q)const{ 106 return x+z < q.x +q.z; 107 } 108 }a[2][MAXN]; 109 int an[2]; 110 111 int n; 112 113 inline int farm(){ 114 int i,j; 115 map<int,int> ans[2]; 116 int ans2[2]; 117 map<int,int>::iterator it,it2; 118 REP(i,2){ 119 sort(a[i],a[i]+an[i]); 120 priority_queue<int> pq; 121 while(!pq.empty())pq.pop(); 122 ans[i].clear(); 123 ans2[i]=0; 124 // printf("%d!%d!\n",i,an[i]); 125 ROF(j,an[i]-1,0){ 126 Node now = a[i][j]; 127 int mid = now.x + now.z; 128 pq.push(now.y-now.z); 129 while(!pq.empty() && pq.top() > mid) 130 pq.pop(); 131 // printf("%d,%d,%d\n",now.x,now.y,now.z); 132 int sz = pq.size(); 133 ans[i][mid] = max(ans[i][mid], sz); 134 ans2[i] = max(ans2[i], sz); 135 } 136 } 137 // printf("%d,%d\n",ans2[0],ans2[1]); 138 int re = max(ans2[0], ans2[1]); 139 it2 = ans[1].begin(); 140 set<int> st; 141 st.clear(); 142 for(it = ans[0].begin(); it!=ans[0].end(); it++){ 143 while(it2!=ans[1].end() && it2->first <= it->first){ 144 st.insert(it2->second); 145 it2++; 146 } 147 if(st.size()!=0){ 148 set<int>::iterator it3 = st.end(); 149 it3--; 150 re = max(re , it->second + *it3); 151 } 152 } 153 return re; 154 } 155 156 int main(){ 157 int T,t=1; 158 int i; 159 int x,y,z,d; 160 RD(T); 161 while(T--){ 162 RD(n); 163 MZ(an); 164 an[0]=an[1]=0; 165 REP(i,n){ 166 RD4(x,y,z,d); 167 if(d==-1){ 168 a[0][an[0]]=Node(x,y,z); 169 an[0]++; 170 }else{ 171 a[1][an[1]]=Node(x,y,z); 172 an[1]++; 173 } 174 } 175 // printf("%d,%d!\n",an[0],an[1]); 176 printf("Case #%d:\n",t++); 177 WN(farm()); 178 } 179 return 0; 180 }
听说1002是状压DP,1004是Trie树乱搞。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/yuiffy/p/5540948.html