标签:
1. 类之间的组合关系
(1)组合关系:整体与部分的关系
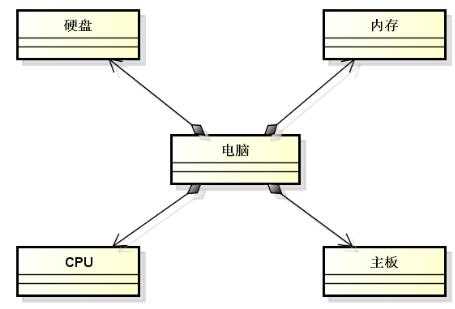
【实例分析】组合关系的描述

#include <iostream> using namespace std; //内存类 class Memory { public: Memory() { cout << "Memory()" << endl; } ~Memory() { cout << "~Memory()" << endl; } }; //硬盘类 class Disk { public: Disk() { cout << "Disk()" << endl; } ~Disk() { cout << "~Disk()" << endl; } }; //CPU类 class CPU { public: CPU() { cout << "CPU()" << endl; } ~CPU() { cout << "~CPU()" << endl; } }; //主板类 class MainBoard { public: MainBoard() { cout << "MainBoard()" << endl; } ~MainBoard() { cout << "~MainBoard()" << endl; } }; //计算机类 class Computer { //组合关系:部分-整体关系(与Computer对象同生命期) Memory mMem; Disk mDisk; CPU mCPU; MainBoard mMainBoard; public: Computer() { cout << "Computer()" << endl; } void power() { cout << "power()" << endl; } void reset() { cout << "reset()" << endl; } ~Computer() { cout << "~Computer()" << endl; } }; int main() { Computer c; //先构造成员对象(按声明顺序),再调用类构造函数 return 0; }
(2)组合关系的特点
①将其它类的对象作为当前类的成员使用
②当前类的对象与成员对象的生命期相同
③成员对象在用法上与普通对象完全一致
2. 继承关系
(1)父子关系
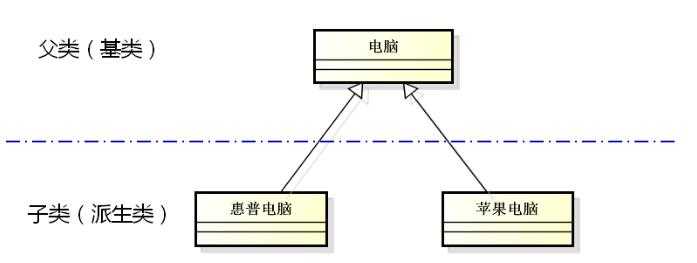
(2)惊艳的继承
①子类拥有父类的所有属性和行为
②子类就是一种特殊的父类
③子类对象可以当作父类对象使用
④子类中可以添加父类没有的方法和属性
【编程实验】继承初体验

#include <iostream> using namespace std; class Parent { int mv; public: Parent() { cout << "Parent()" << endl; mv = 100; } void method() { cout << "mv = " << mv << endl; } }; class Child : public Parent //:public Parent描述继承关系 { public: void hello() { cout << "I‘m Child class!" << endl; } }; int main() { Child c; c.hello(); //子类函数 c.method();//父类 return 0; }
(3)重要规则
①子类就是一个特殊的父类
②子类对象可以直接初始化父类对象
③子类对象可以直接赋值给父类对象
3. 继承的意义
继承是C++是代码复用的重要手段。通过继承,可以获得父类的所有功能,并且可以在子类中重写己有的功能,或者添加新功能。
【编程实验】继承的强化练习
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; //内存类 class Memory { public: Memory() { cout << "Memory()" << endl; } ~Memory() { cout << "~Memory()" << endl; } }; //硬盘类 class Disk { public: Disk() { cout << "Disk()" << endl; } ~Disk() { cout << "~Disk()" << endl; } }; //CPU类 class CPU { public: CPU() { cout << "CPU()" << endl; } ~CPU() { cout << "~CPU()" << endl; } }; //主板类 class MainBoard { public: MainBoard() { cout << "MainBoard()" << endl; } ~MainBoard() { cout << "~MainBoard()" << endl; } }; //计算机类 class Computer { //组合关系:部分-整体关系(与Computer对象同生命期) Memory mMem; Disk mDisk; CPU mCPU; MainBoard mMainBoard; public: Computer() { cout << "Computer()" << endl; } void power() { cout << "power()" << endl; } void reset() { cout << "reset()" << endl; } ~Computer() { cout << "~Computer()" << endl; } }; //惠普笔记本 class HPBook : public Computer { string mOS; public: HPBook() { mOS = "Windows 8"; //预装Windows8操作系统 } void install(string os) { mOS =os; } void OS() { cout << mOS << endl; } }; //苹果电脑 class MacBook : public Computer { public: void OS() { cout << "Mac OS" << endl; } }; int main() { HPBook hp; hp.power(); //开机 hp.install("Ubuntu 16.04 LTS"); hp.OS(); cout << endl; MacBook mac; mac.OS(); return 0; }
4. 小结
(1)继承是面向对象中类之间的一种关系
(2)子类拥有父类的所有属性和行为
(3)子类对象可以当作父类对象使用
(4)子类中可以添加父类没有的方法和属性
(5)继承是面向对象中代码复用的重要手段
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/5iedu/p/5554775.html