标签:并査集
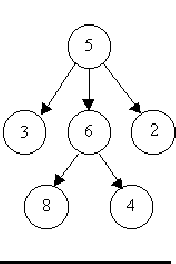
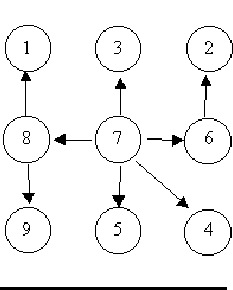
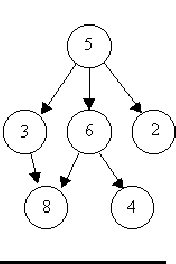
6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4 5 6 0 0 8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5 7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0 3 8 6 8 6 4 5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0 -1 -1
Case 1 is a tree. Case 2 is a tree. Case 3 is not a tree.
树的判断,主要有三点
1:不能有环,
2:不能有两个独立的区间,为此我开了一个vis[N],来标记出现的数字
3:一个点的入度不能大于1,意思就是 a->b c->b,那么b的入度就大于1了
注意的地方应该都说完了,上代码喽(⊙o⊙)…
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define N 1005
int father[N],vis[N],d[N];
int n,m;
int cha(int x)
{
if(x!=father[x])
father[x]=cha(father[x]);
return father[x];
}
int main()
{
int i,a,b,ca=0;
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b))
{
if(a<0&&b<0) break;
if(a==0&&b==0) //空树也是树
{
printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",++ca);
continue;
}
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
father[i]=i;
d[i]=0;
vis[i]=0;
}
int flag=0;
while(a+b)
{
vis[a]=vis[b]=1;
int aa=cha(a);
int bb=cha(b);
if(aa==bb)
flag=1;
father[aa]=bb;
d[b]++;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
}
if(flag)
{
printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",++ca);
continue;
}
else
{
int num=0;
for(i=0;i<N;i++)
{
if(father[i]==i&&vis[i]) //num记录独立区间数(不能大于2)
num++;
if(d[i]>1) flag=1; //单独点的入度不能大于2
if(num>1) flag=1;
if(flag) break;
}
if(flag)
printf("Case %d is not a tree.\n",++ca);
else
printf("Case %d is a tree.\n",++ca);
}
}
return 0;
}
HDU 1325 Is It A Tree?,布布扣,bubuko.com
标签:并査集
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u014737310/article/details/38355269