标签:
欢迎使用 小书匠(xiaoshujiang)编辑器,您可以通过 设置 里的修改模板来改变新建文章的内容。
A:
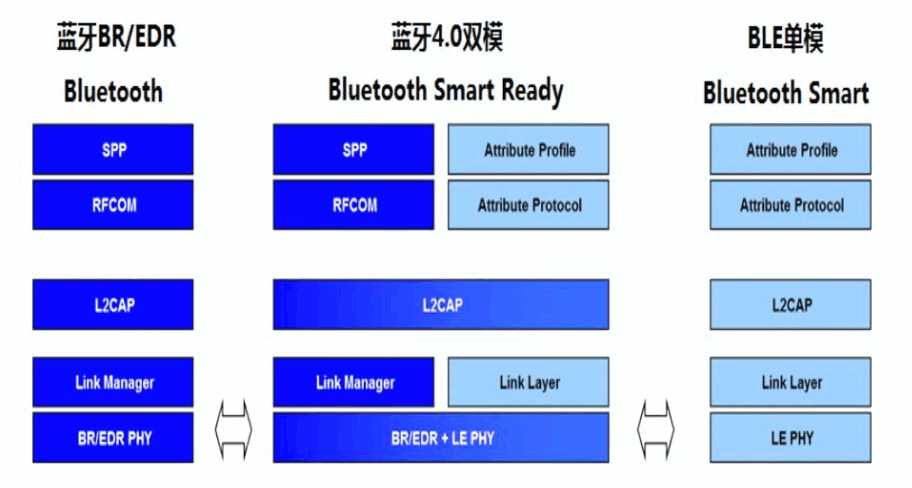
1.Smart Ready 可以和 Smart Ready、传统蓝牙,以及 Smart 之间相互连接和通信。
2.传统蓝牙可以和 Smart Ready、传统蓝牙之间连接和通信
3.Smart 可以和 Smart、 Smart Ready 之间连接和通信

A: 都是蓝牙芯片,双模指的是同时支持1:BasicRate ( BR), 2:Bluetooth Low Energy ( BLE),如手机, PC 等采用的均是双模的蓝牙芯片。很多 android手机都表明支持蓝牙 4.0,其实很大部分只支持 Smart Ready 里的 BR。不是硬件的问题而是软件里还不支持LE。目前 Android4.3 系统才开始全面支持 BLE。iOS 设备对蓝牙 4.0 支持的最好,只要是 iPhone4S 和以后的设备均完美完全支持蓝牙 4.0。单模指的是只支持Bluetooth Low Energy ( 缩写:BLE或者LE),目前我们在使用的如Cypress的PSoC和PRoC系列,TI的CC2640等都是单模芯片,只支持Smart。BLE最主要特点是低功耗和低速率,网上关于蓝牙 4.0 一节纽扣电池能够使用一年均是针对 BLE 而言。
A: These are the different roles defined at different layers of the BLE protocol stack.
Link Layer roles:
Master - Initiates a connection
Slave - Advertises and waits for a connection initiation
GATT roles:
Server - Has data
Client - Wants data
GAP roles:
Central - The primary device in a connection
Peripheral - The secondary device in a connection
The GAP Central is always a Link Layer Master, while the GAP Peripheral is always a Link Layer Slave.
A: For a quick bringup with Bluetooth Low Energy, please refer to the following:
Application note - Getting Started with PSoC 4 BLE
Application note - Getting Started with PRoC BLE
Development kit - CY8CKIT-042 BLE Pioneer Kit - This development kit, provides a number of example projects for a quick start with PSoC / PRoC BLE devices.
If you want to know about the technology, please refer to the videos available at BLE Developer Portal.
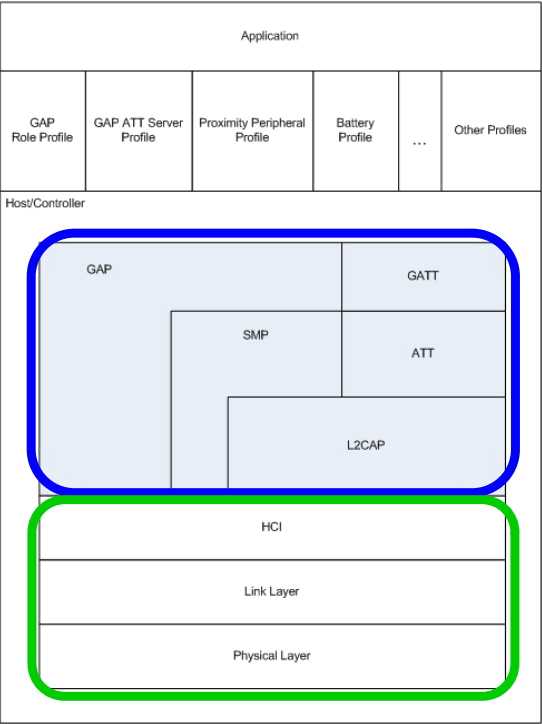
Protocol stack consists of two main sections:
绿色 Controller
蓝色 Host
Profiles and Application sit on top of the GAP and GATT layers of the host
In a “single-device solution” (or “single-chip solution”), the host, controller, profiles, and application are all implemented together on the same chip
In a “dual-device solution”, the BLE controller is implemented on one device, while the host,application, and profiles are implemented separately
In a “network processor”, the host and controller are implemented together, but the application and profiles sit on another device (such as a PC or external microcontroller)
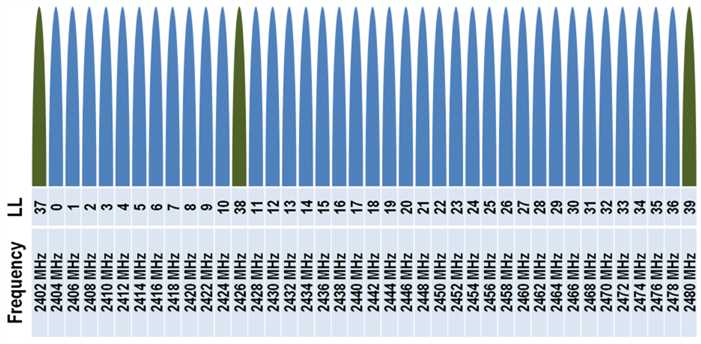
RF Specifications
Operates in 2.4 GHz ISM band
GFSK modulation
40 channels with 2 MHz spacing
3 fixed advertisting channels for broadcasting, which avoid 802.11 interferance
37 adaptively frequency hoppeddynamic data channels
Physical layer can be combined with standard Bluetooth RF in a dual-mode device
2 MHz spacing allows for better adjacent channel rejection
**Channl :**3 Advertising Channels and 37 Data Channels
States and Network Topology
There are six possible Link Layer states of a BLE device:
Standby - device is not transmitting or receiving any data, and is not connected to any other device
Advertiser - periodically broadcasting advertisements
Scanner - actively looking for advertisers
Initiator - actively trying to initiate a connection with another device
Master - connected to another device as a master
Slave - connected to another device as a slave
BLE is a star topology network:
Master device “manages” the connection,and can be connected to multiple slaves
Slave device can only be connected to one master
Advertisement Events
During one “advertising event”, an advertisement packet is transmitted on each of the three advertising channels (37, 38, and 39)
Advertisement Intervals
The advertising device has an “advertising interval”, which is the minimum amount of time between two advertising events
Advertising Interval can be any amount of time between 20ms and 10.24s
Advertisement Types
Four types of advertisements:
Connectable undirected- any scanner device can initiate a connection with this advertiser
Connectable directed- only one specific device can initiate a connection with this advertiser
Non-connectable undirected- no devices can initiate a connection with this advertiser; primarily used for general broadcast of data
Discoverable undirected- any scanner device can request more information from the advertising device, but no devices can initiate a connection with it
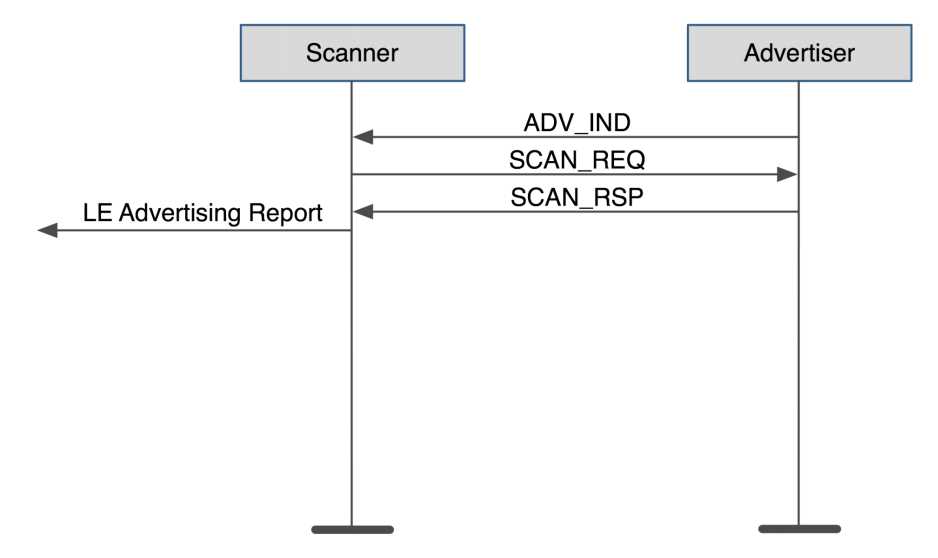
Scanning
Active Scanning Packet Flow
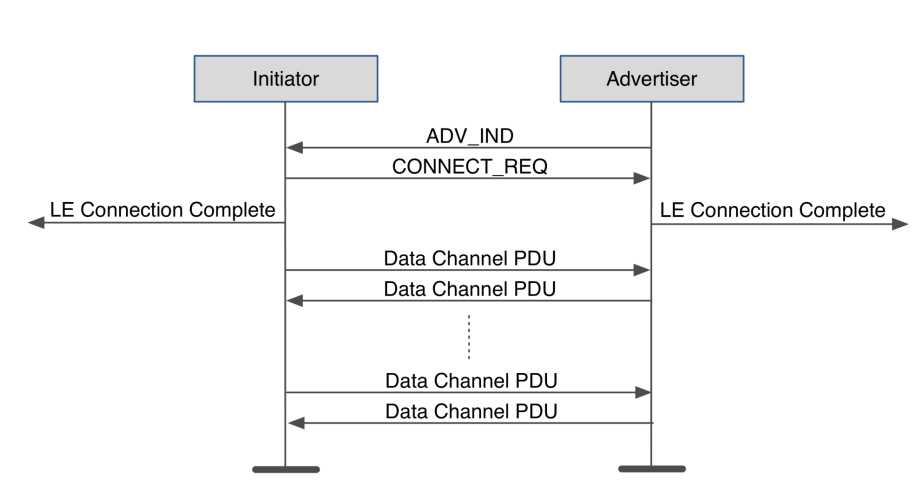
Connection Initiation
Connection Request Packet Flow
Connection Parameters
Channel Map- indicates which data channels are used during the connection
Connection Interval- multiple of 1.25ms in range of 7.5ms and 4.0s
Supervision Timeout- multiple of 10ms in the range of 100ms and 32.0s. Must be larger than: (1 + slaveLatency) * (ConnInterval)
Slave Latency- any value between 0 and 499, though it cannot exceed:((supervisionTimeout / connInterval) – 1)
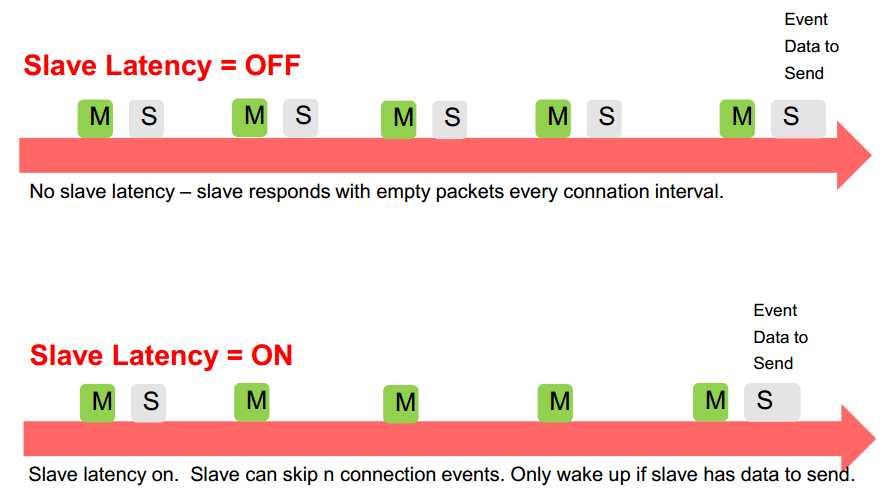
Connection Events
All communications between two connected devices occur in “connection events”
Each event occurs on one data channel (channels 0-36), with the hop increment parameter determining the next channel for the next event
During each connection event, the master transmits first, and the slave responds 150us later
Master and slave can continue transmitting back and forth as many times as they want during a single connection event
Connection events occur even when one (or both) sides have no data to send (the exception to this is when slave latency is enabled; more information on next slide). This allows both devices to acknowledge that the other is still there and keeps the connection active.
Slave Latency
Connection Parameters Tradeoffs
Short connection interval:
Higher power consumption for both devices
Higher throughput in both directions
Shorter wait for data to be sent in either direction
Long connection interval:
Lower power consumption for both devices
Lower throughput in both directions
Longer wait for data to be sent in either direction
Low / Zero slave latency:
Higher power consumption for peripheral
Peripheral receives data sent from central device sooner
High slave latency:
Lower power consumption for peripheral during periods when it has no data to send
to central device
Peripheral may not immediately receive data being sent from central device
Connection Update Request
If the slave does not like the connection parameters (interval, slave latency, or supervision timeout), it can send a connection update request to the master
Connection Termination
A connection can be voluntarily terminated by either the master or the slave for any reason
Connection can also be terminated as a result of a supervision timeout
Direct Test Mode
Allows a tester to directly control the device under test (DUT) in either Rx or Tx mode on any channel with any amount of data
Reused from standard Bluetooth specification,with new additional commands for low energy specific functions
Thin layer; doesn?t perform any processing
In a dual-chip solution (with separate host and controller) allows for host to communicate with controller over a standard interface (UART,USB, SDIO, etc.)
Used internally by the CC2540 BLE protocol stack for communication between higher and lower layers
Also allows for custom “vendor-specific commands”. In the CC2540, vendor-specific commands can be used by an external source to directly interface with the entire stack or application. This is called a “Network Processor”
Permits upper level protocols and applications to transmit and receive upper layer data packets up to 23 bytes in length
Provides channel management, allowing for logical channels between two endpoints,supported by the link layer
Connection Parameter Updates
Performs authentication and key management
Uses AES-128 as the encryption algorithm for security procedures
Defines protocol to setup secure link
Works with GAP to manage relationships between devices:
Pairing – encryption between two devices once a connection has been established between them
Authentication – verification that a peer device can be trusted, providing protection against “Man-in-the-Middle” attacks
Bonding – long-term relationship between devices; security and identity information is saved for re-use next time the devices are connected
Overview
Defines generic procedures for connection-related services:
Device Discovery
Link Establishment
Link Management
Link Termination
Initiation of security features
Many GAP functions correspond directly to the functions of the Link Layer in the controller
Profile Roles
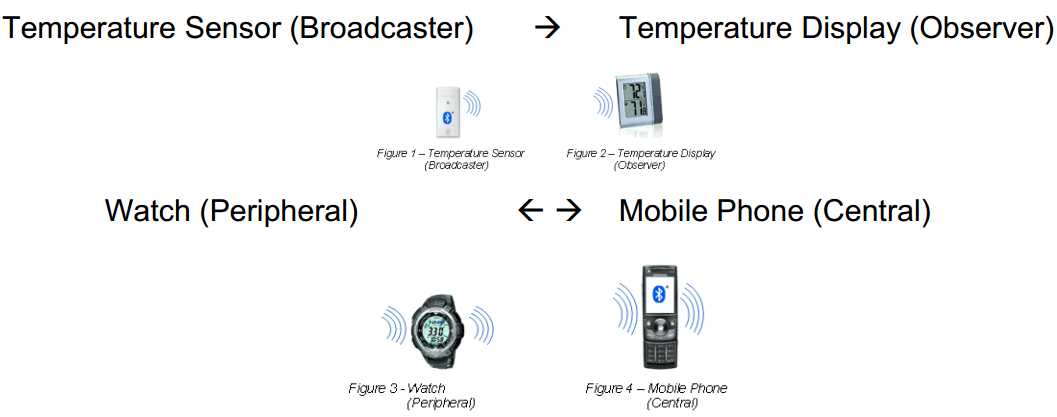
The GAP layer works in one of four profile roles:
Broadcaster – an advertiser that is non-connectable
Observer – scans for advertisements, but cannot initiate connections.
Peripheral – an advertiser that is connectable and can operate as a slave in a single link layer connection.
Central – scans for advertisements and initiates connections; operates as a master in a single or multiple link layer connections.
Profile Multi-Roles
The BLE specification allows for a few different possible multiple-role configurations:
Peripheral and Broadcaster
Peripheral and Observer
Central and Broadcaster
Discoverable Modes
GAP supports three different discoverable modes:
Non-discoverable Mode – No advertisements
Limited Discoverable Mode – Device advertises for a limited amount of time before returning to the standby state
General Discoverable Mode – Devices advertises continuously
Advertisement and Scan Response Data
GAP manages the data that is sent out in advertisement and scan response packets
Pairing
Pairing can be initiated by either the central or peripheral device
Based on the combination of the capabilities of the two devices, one of two methods of pairing will be used:
Passkey entry – one device will display a randomly generator passkey, while the other will require the user to input the passkey. This allows for an authenticated link (MITM protection)
“Just Works” – the pairing process completes without requiring a passkey to be entered. The link will not be authenticated, but is encrypted
During the pairing process, each device states whether it wants authentication to the other device
Each device also states it?s input/output capabilities from among these options:
DisplayOnly – no way user can input anything into device, but it can output data
DisplayYesNo – user can input “yes” or “no” but nothing else; can also display data
KeyboardOnly – user can input a password or PIN, but no display
NoInputNoOutput – device has no means for user input, and has no display
KeyboardDisplay – device has a means for display as well as for input
Overview
ATT defines the over-the-air protocol for reading, writing, and discovering attributes
An attribute is a discrete value that has associated with it the following three properties:
A handle (address)
A type
A set of permissions
Client / Server Architecture
Servers have data, Clients want to use this data
Attribute Table Example
Handle – The address of the attribute in the table
Type – Tells what the data represents; can be a UUID (universal unique identifier) assigned by the Bluetooth SIG, or a custom type
Permissions – Enforces if and how the attribute client can access the attribute?s value
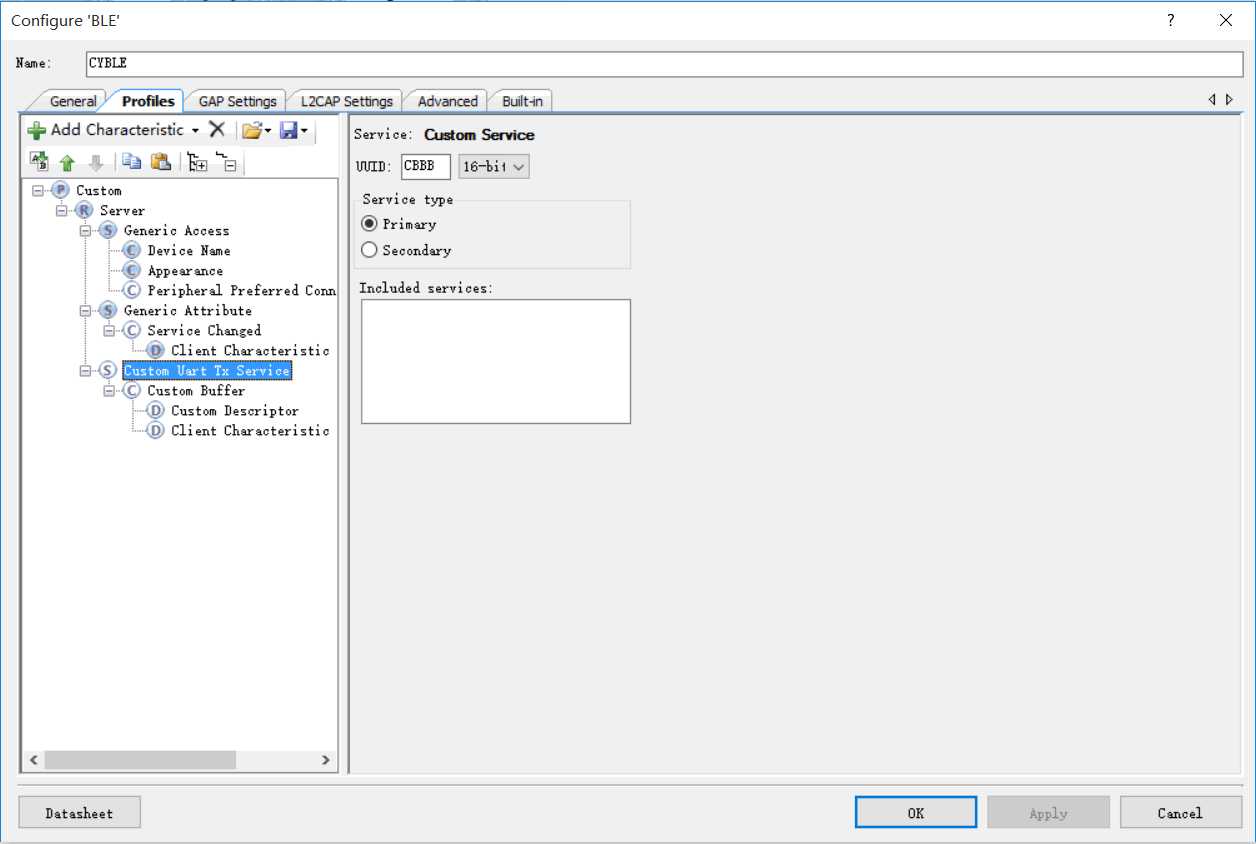
GATT database:
const CYBLE_GATTS_DB_T cyBle_gattDB[0x10u] = {
{ 0x0001u, 0x2800u /* Primary service */, 0x00000001u /* */, 0x0007u, {{0x1800u, NULL}} },
{ 0x0002u, 0x2803u /* Characteristic */, 0x00000201u /* rd */, 0x0003u, {{0x2A00u, NULL}} },
{ 0x0003u, 0x2A00u /* Device Name */, 0x00000201u /* rd */, 0x0003u, {{0x0009u, (void *)&cyBle_attValuesLen[0]}} },
{ 0x0004u, 0x2803u /* Characteristic */, 0x00000201u /* rd */, 0x0005u, {{0x2A01u, NULL}} },
{ 0x0005u, 0x2A01u /* Appearance */, 0x00000201u /* rd */, 0x0005u, {{0x0002u, (void *)&cyBle_attValuesLen[1]}} },
{ 0x0006u, 0x2803u /* Characteristic */, 0x00000201u /* rd */, 0x0007u, {{0x2A04u, NULL}} },
{ 0x0007u, 0x2A04u /* Peripheral Preferred Connection Par */, 0x00000201u /* rd */, 0x0007u, {{0x0008u, (void *)&cyBle_attValuesLen[2]}} },
{ 0x0008u, 0x2800u /* Primary service */, 0x00000001u /* */, 0x000Bu, {{0x1801u, NULL}} },
{ 0x0009u, 0x2803u /* Characteristic */, 0x00002201u /* rd,ind */, 0x000Bu, {{0x2A05u, NULL}} },
{ 0x000Au, 0x2A05u /* Service Changed */, 0x00002201u /* rd,ind */, 0x000Bu, {{0x0004u, (void *)&cyBle_attValuesLen[3]}} },
{ 0x000Bu, 0x2902u /* Client Characteristic Configuration */, 0x00000A04u /* rd,wr */, 0x000Bu, {{0x0002u, (void *)&cyBle_attValuesLen[4]}} },
{ 0x000Cu, 0x2800u /* Primary service */, 0x00000001u /* */, 0x0010u, {{0xCBBBu, NULL}} },
{ 0x000Du, 0x2803u /* Characteristic */, 0x00001A01u /* rd,wr,ntf */, 0x0010u, {{0xCBB1u, NULL}} },
{ 0x000Eu, 0xCBB1u /* Custom Buffer */, 0x00011A04u /* rd,wr,ntf */, 0x0010u, {{0x00C8u, (void *)&cyBle_attValuesLen[5]}} },
{ 0x000Fu, 0x2901u /* Custom Descriptor */, 0x00010001u /* */, 0x000Fu, {{0x001Cu, (void *)&cyBle_attValuesLen[6]}} },
{ 0x0010u, 0x2902u /* Client Characteristic Configuration */, 0x00010A04u /* rd,wr */, 0x0010u, {{0x0002u, (void *)&cyBle_attValuesLen[7]}} },
};
Custom Uart Tx Service
| Handle | att Type | Permission | value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x000Cu | 0x2800(GATT Service UUID) | read | 0xCBBBu(2bytes) |
| 0x000Du | 0x2803u (GATT Characteristic UUID) | read,write,notify | 0xCBB1u(2bytes) |
| 0x000Eu | 0xCBB1u (Custom Buffer UUID) | read,write,notify | (200bytes) |
| 0x000Fu | 0x2901u (Custom Descriptor UUID) | read | (28bytes) |
| 0x0010u | 0x2902u (Client Characteristic Configuration UUID) | read,write | (2bytes) |
Overview
Designed for use by the application or a profile, so that an attribute client can communicate with attribute server
GATT defines:
Procedures for using the attribute protocol (ATT) to discover, read, write, and obtain indications of these attributes
The grouping and relationship of characteristics within a service or profile
Procedures for configuring the broadcast of attributes
Client / Server Architecture
GATT specifies the structure in which profile data is exchanged
Same client server architecture as Attribute Protocol, except that data is encapsulated in “Services” and data is exposed in “Characteristic”
Profile Hierarchy
A profile is composed of one or more “services” necessary to fulfill a use-case
A service may contain certain attributes called “characteristic values”, which are values used by a service (example: in a temperature sensor, the attribute containing the temperature itself is the characteristic value)
A characteristic value must have a mandatory “characteristic declaration” attribute immediately before the value,containing the properties of the characteristic
Characteristics may also contain optional “descriptor” attributes, with fields such as a configuration or a description
Client Commands
When two BLE devices are in the connected state, the GATT client device can perform several different sub-procedures to communicate with the GATT server device:
Discover Characteristic by UUID – search the GATT server for all attributes with type that matches the specified UUID
Read Characteristic Value – read the value of the characteristic at the specified handle
Write Characteristic Value – write a new value to the characteristic at the specified handle
A GATT server device, when configured to do so, can send out messages to the GATT client device without being prompted:
Notification – The value a characteristic is sent from the server to the client without receiving a read request, and does not need to be acknowledged
Indication – The value a characteristic is sent from the server to the client without receiving a read request, but must be acknowledged before any further data can be sent
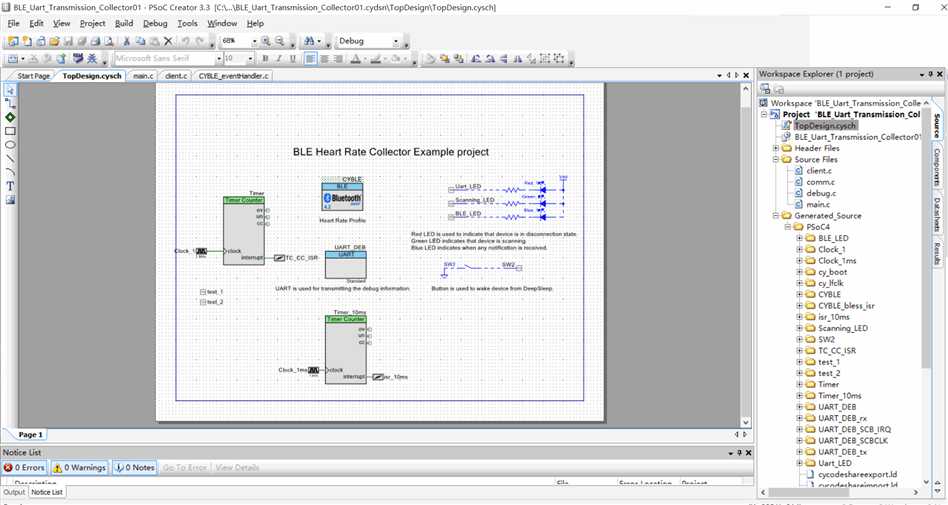
由 BLE_Uart_Transmission_Collector01和BLE_UART_Transmission_Server组成一对主从机程序,实现串口透传功能。
硬件组成:基于 CY8CKIT-042 BLE Pioneer Kit

Psoc Creator 工程图示
| 主机 | 从机 | |
|---|---|---|
| profile | customer profile | customer profile |
| profile role | Client(GATT Client) | server(GATT Server) |
| GAP role | Central | Peripheral |
在主流程上主机和从机是类似的
主机在BLE使能后,执行的 scan
case CYBLE_EVT_STACK_ON:
printf("EVT_STACK_ON \r\n");
goto start_scan;
case CYBLE_EVT_GAP_DEVICE_DISCONNECTED:
BleConnected = 0;
printf("EVT_GAP_DEVICE_DISCONNECTED \r\n");
goto start_scan;
case CYBLE_EVT_TIMEOUT:
printf("EVT_TIMEOUT \r\n");
start_scan:
if(BleConnected == 0)
{
StartScan(CYBLE_UUID_CUSTOMER_SERVICE);//CYBLE_UUID_CUSTOM_UART_TX_SERVICE
//Scanning_LED_Write(LED_ON);
ble_state = BLE_SCAN_STATE;
}
break;
从机在BLE使能后,执行的是Advertisement
case CYBLE_EVT_STACK_ON:
printf("EVT_STACK_ON \r\n");
goto start_advert;
case CYBLE_EVT_GAP_DEVICE_DISCONNECTED:
//ble_state = BLE_DISCONNECTED_STATE;
case CYBLE_EVT_TIMEOUT:
start_advert:
/* Put the device into discoverable mode so that remote can search it. */
StartAdvertisement();
//Advertising_LED_Write(LED_ON);
ble_state = BLE_ADV_STATE;
test_ptr=0;
break;
下面是主机找到从机的关键函数,最终以 flag |= CONNECT; 为出口,并在scan结束后CYBLE_EVT_GAPC_SCAN_START_STOP,发起连接CyBle_GapcConnectDevice(&peerAddr[deviceN]), peerAddr[deviceN]就是找到的从机的mac地址。
void ScanProgressEventHandler(CYBLE_GAPC_ADV_REPORT_T* eventParam)
{
uint8 newDevice = 0u, device = 0u;
uint8 i;
uint8 adStructPtr = 0u;
uint8 adTypePtr = 0u;
uint8 nextPtr = 0u;
printf("SCAN_PROGRESS_RESULT: peerAddrType - %d, ", eventParam->peerAddrType);
printf("peerBdAddr - ");
for(newDevice = 1u, i = 0u; i < advDevices; i++)
{
if((memcmp(peerAddr[i].bdAddr, eventParam->peerBdAddr, CYBLE_GAP_BD_ADDR_SIZE) == 0)) /* same address */
{
device = i;
printf("%x: ", device);
newDevice = 0u;
break;
}
}
if(newDevice != 0u)
{
if(advDevices < CYBLE_MAX_ADV_DEVICES)
{
memcpy(peerAddr[advDevices].bdAddr, eventParam->peerBdAddr, CYBLE_GAP_BD_ADDR_SIZE);
peerAddr[advDevices].type = eventParam->peerAddrType;
device = advDevices;
advDevices++;
printf("%x: ", device);
}
}
for(i = CYBLE_GAP_BD_ADDR_SIZE; i > 0u; i--)
{
printf("%2.2x", eventParam->peerBdAddr[i-1]);
}
printf(", rssi - %d dBm, data - ", eventParam->rssi);
/* Print and parse advertisement data and connect to device which has HRM */
adStructPtr = 0u;
for(i = 0; i < eventParam->dataLen; i++)
{
printf("%2.2x ", eventParam->data[i]);
if(i == adStructPtr)
{
adTypePtr = i + 1;
adStructPtr += eventParam->data[i] + 1;
nextPtr = 1;
}
else if(i == (adTypePtr + nextPtr))
{
switch(eventParam->data[adTypePtr])
{
case CYBLE_GAP_ADV_FLAGS:
break;
case CYBLE_GAP_ADV_INCOMPL_16UUID:
case CYBLE_GAP_ADV_COMPL_16UUID:
if(serviceUuid == CyBle_Get16ByPtr(&(eventParam->data[i])))
{
newDevice = 2; /* temporary use newDevice as a flag */
}
else
{
nextPtr += 2;
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
}
printf("newDevice = %d \r\n",newDevice);
if(2 == newDevice)
{
deviceN = device;
printf(" This device contains ");
switch(serviceUuid)
{
case CYBLE_UUID_HEART_RATE_SERVICE:
printf("Heart Rate Service \r\n");
break;
case CYBLE_UUID_GLUCOSE_SERVICE:
printf("Glucose Service \r\n");
break;
case CYBLE_UUID_BLOOD_PRESSURE_SERVICE:
printf("Blood Pressure Service \r\n");
break;
case CYBLE_UUID_HIDS_SERVICE:
printf("HID Service \r\n");
printf("Stop Scanning, waiting for Scanning event \r\n");
flag |= CONNECT;
CyBle_GapcStopScan();
break;
/* other services */
case 0x290A:
printf("Stop Scanning, waiting for Scanning event \r\n");
flag |= CONNECT;
CyBle_GapcStopScan();
break;
case CYBLE_UUID_CUSTOMER_SERVICE:
printf("Customer Service \r\n");
printf("Stop Scanning, waiting for Scanning event \r\n");
flag |= CONNECT;
CyBle_GapcStopScan();
break;
default:
printf("%x \r\n", serviceUuid);
break;
}
}
else
{
printf("\r\n");
}
}
以主机为例
int main()
{
CYBLE_API_RESULT_T apiResult;
CYBLE_LP_MODE_T lpMode;
CyGlobalIntEnable;
CommInit(); /* Start communication component */
printf("BLE Uart Transmission Collector Example Project \r\n");
Scanning_LED_Write(LED_OFF);
apiResult = CyBle_Start(AppCallBack);
if(apiResult != CYBLE_ERROR_OK)
{
printf("CyBle_Start API Error: %xd \r\n", apiResult);
}
else
{
printf("CyBle_Start API ok \r\n");
}
/* Enable the Interrupt component connected to interrupt */
TC_CC_ISR_StartEx(InterruptHandler);
/* Start the components */
Timer_Start();
以主机为例
while(1)
{
if(CyBle_GetState() != CYBLE_STATE_INITIALIZING)
{
/* Enter DeepSleep mode between connection intervals */
lpMode = CyBle_EnterLPM(CYBLE_BLESS_DEEPSLEEP);
if(lpMode == CYBLE_BLESS_DEEPSLEEP)
{
/* Put the device into the Deep Sleep mode only when all debug information has been sent
if(UART_DEB_SpiUartGetTxBufferSize() == 0u)
{
CySysPmDeepSleep();
}
else
{
CySysPmSleep();
}*/
CySysPmSleep();
/* Handle scanning led blinking */
HandleLEDs(ble_state);
}
HandleLEDs(ble_state);
}
/***********************************************************************
* Wait for connection established with Central device
***********************************************************************/
if(CyBle_GetState() == CYBLE_STATE_CONNECTED)
{
/*******************************************************************
* Periodically measure a battery level and temperature and send
* results to the Client
*******************************************************************/
CommMonitorUart();
CommMonitorBLE();
#if 0
if(mainTimer != 0u)
{
mainTimer = 0u;
if(storeBondingData == ENABLED)
{
cystatus retValue;
retValue = CyBle_StoreBondingData(0u);
printf("Store bonding data, status: %lx \r\n", retValue);
storeBondingData = DISABLED;
}
}
#endif
}
/*******************************************************************
* Processes all pending BLE events in the stack
*******************************************************************/
CyBle_ProcessEvents();
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/// \brief MonitorBLE
/// \param none
/// \return none
/// \deprecated monitor ble send usd uart tx
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void CommMonitorBLE(void)
{
if(uCommState.Bit.BLERxFinshed == ENABLED)
{
uCommState.Bit.BLERxFinshed = DISABLED;
CommUartTxByte();
// Then switch to Uart RX state
CommUartRxReady();
BLE_LED_OFF;
// Then switch to RF RX state
CommBLERxReady();
}
}
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
/// \brief CommMonitorUart
/// \param none
/// \return none
/// \deprecated monitor uart send use ble
///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void CommMonitorUart(void)
{
CYBLE_API_RESULT_T apiResult;
CYBLE_GATT_HANDLE_VALUE_PAIR_T CustomNotificationhandle;
if(uCommState.Bit.UartRxFinished == ENABLED)
{
uCommState.Bit.UartRxFinished = DISABLED;
uCommState.Bit.BLERxRDY = DISABLED;
CustomNotificationhandle.attrHandle = UART_TX_HANDLE;
CustomNotificationhandle.value.val = &Buffer[1];
CustomNotificationhandle.value.len = Buffer[0];
CustomNotificationhandle.value.actualLen = Buffer[0];
#if 0
/* Send notification to client using previously filled structure */
apiResult = CyBle_GattsNotification(cyBle_connHandle, &CustomNotificationhandle);
#else
apiResult = CyBle_GattcWriteWithoutResponse(cyBle_connHandle,&CustomNotificationhandle);
#endif
/* Send uart receive handle as attribute for read by central device */
CyBle_GattsWriteAttributeValue(&CustomNotificationhandle,FALSE,&cyBle_connHandle,FALSE);
#ifdef test
if(apiResult != CYBLE_ERROR_OK)
{
printf("ble send Error: %x \r\n", apiResult);
}
else
{
printf("ble send ok len: %x \r\n", CustomNotificationhandle.value.len);
}
#endif
CommUartRxReady();
Uart_LED_OFF;
// Then switch to RF RX state
CommBLERxReady();
}
}
蓝牙的事件回调函数 接收蓝牙数据,产生uCommState.Bit.BLERxFinshed
void AppCallBack(uint32 event, void* eventParam)
{
...
case CYBLE_EVT_GATTC_HANDLE_VALUE_NTF:
wrReqParam = (CYBLE_GATTS_WRITE_REQ_PARAM_T *) eventParam;
if(wrReqParam->handleValPair.attrHandle == UART_TX_HANDLE)
{
len = wrReqParam->handleValPair.value.len;
Buffer[0] = len;
memcpy(&Buffer[1],wrReqParam->handleValPair.value.val,len);
uCommState.Bit.BLERxFinshed = ENABLED;
//printf("len %d buf[0] %d \r\n", len,Buffer[0]);
}
....
}
串口中断函数及定时器中断函数 接收串口数据,产生uCommState.Bit.UartRxFinished
/*******************************************************************************
* Function Name: Transport_RX_ISR
********************************************************************************
*
* Summary:
* Handles the Interrupt Service Routine for the UART RX.
* Contains cmdRxState m/c to check for valid command reciept and triggers flag
*
* Parameters:
* NONE
*
* Return:
* NONE
*
* Theory:
* NONE
*
* Side Effects:
* Command bufffers and newCmdRxDoneFlag will be modified
*
* Note:
*
*******************************************************************************/
CY_ISR(Transport_RX_ISR)
/*******************************************************************************
* Function Name: Transport_Timer_ISR
********************************************************************************
*
* Summary:
* Handles the Interrupt Service Routine for the UART Timer.
* Resets RX command state m/c for every 10ms delay on RX byte
* If RX packet has started, there should not be more than 10ms delay between each RX byte with-in the packet
*
* Parameters:
* NONE
*
* Return:
* NONE
*
* Theory:
* NONE
*
* Side Effects:
* State m/c and other parameters will be reset
*
* Note:
*
*******************************************************************************/
CY_ISR(Transport_Timer_ISR)
从机的debug信息
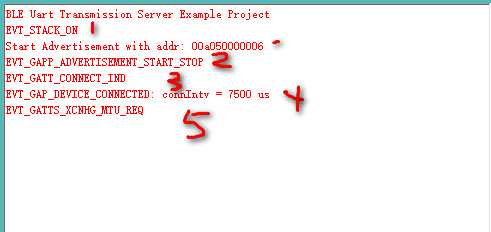
* 1 AppCallBack :CYBLE_EVT_STACK_ON:StartAdvertisement()
* 2 AppCallBack :CYBLE_EVT_GAPC_SCAN_START_STOP (SCAN_START)
* 3&4 AppCallBack :CYBLE_EVT_GAP_DEVICE_CONNECTED 连接间隔 为 7.5ms
* 5 AppCallBack :CYBLE_EVT_GATTC_XCHNG_MTU_RSP 变更成功
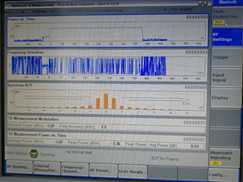
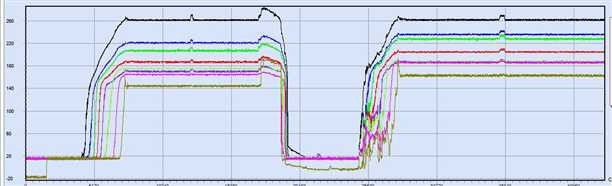
这个透传的程序目前我们用于无线打印数据,配合下图的虚拟示波器使用
PSoC 4 BLE is an easy-to-use, ARM? Cortex?-M0 based, single-chip solution which integrates programmable analog front ends, programmable digital peripherals, CapSense? technology for touch-sensing, and a Bluetooth? LE (Low Energy) or Bluetooth Smart radio. http://www.cypress.com/psoc4ble/ — Edit
利尔达BLE遥控器方案是基于蓝牙4.1的多功能智能遥控器解决方案,可以根据需求加入蓝牙语音,多指触控,体感控制等功能。本方案采样了Cypress的PRco系列,该系列是Cypress公司专门针对低功耗蓝牙设备推出的超低功耗,超高集成度的单芯片解决方案。
| 功能 | 性能 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| BLE stack | Bluetooth 4.2 single-mode device | |
| TX output power | –18 dBm to +3 dBm | |
| RX sensitivity | –89 dBm | |
| TX current | 15.6 mA at 0 dBm | |
| RX current | 16.4 mA | |
| CPU | Cortex-M0 | operating at up to 48 MHz |
| flash memory | 128~256 KB | |
| SRAM memory | 16~32 KB | |
| Other feature | 1.3-μA Deep-Sleep mode | |
| CapSense? Touch Sensing | ||
| Two-finger gestures | ||
| 12-bit, 1-Msps SAR ADC with internal reference | ||
| OTA |
语音部分 实现 256kbps的语音采样
I2S 数字语音接口
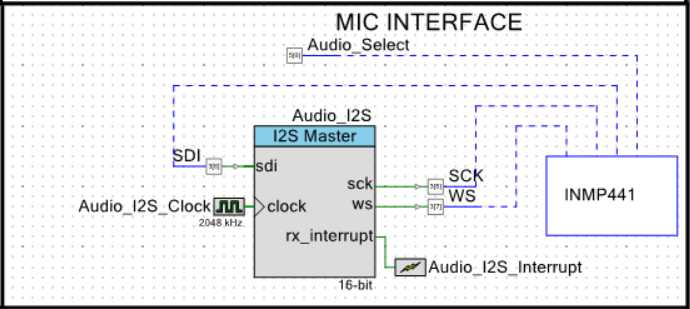
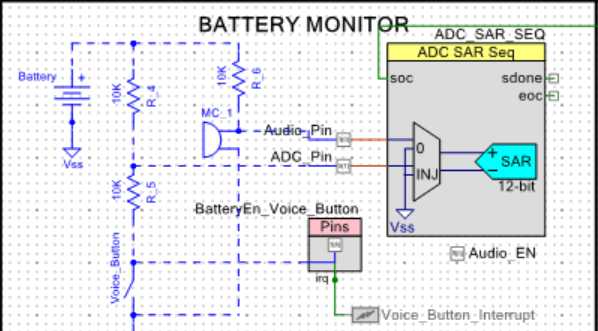
ADC 模拟语音
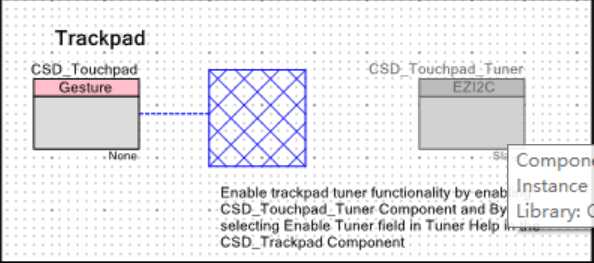
触摸板
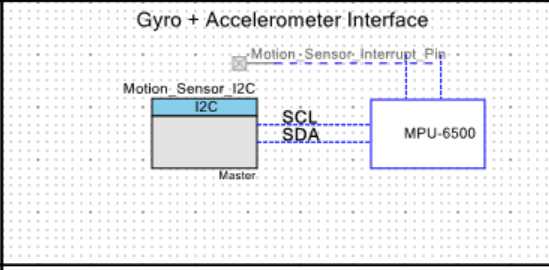
体感空鼠 6轴姿态补偿
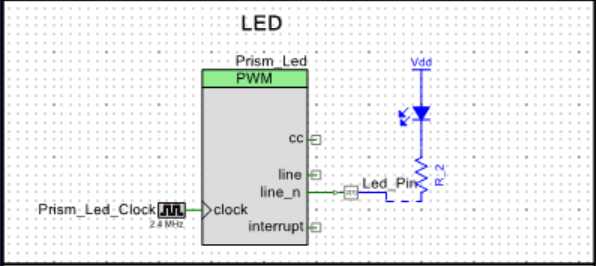
LED & IR 硬件实现呼吸灯 和 红外NEC编码
硬件实现行列键盘
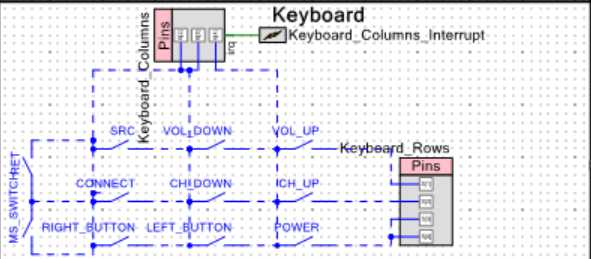
Human Interface Device Service
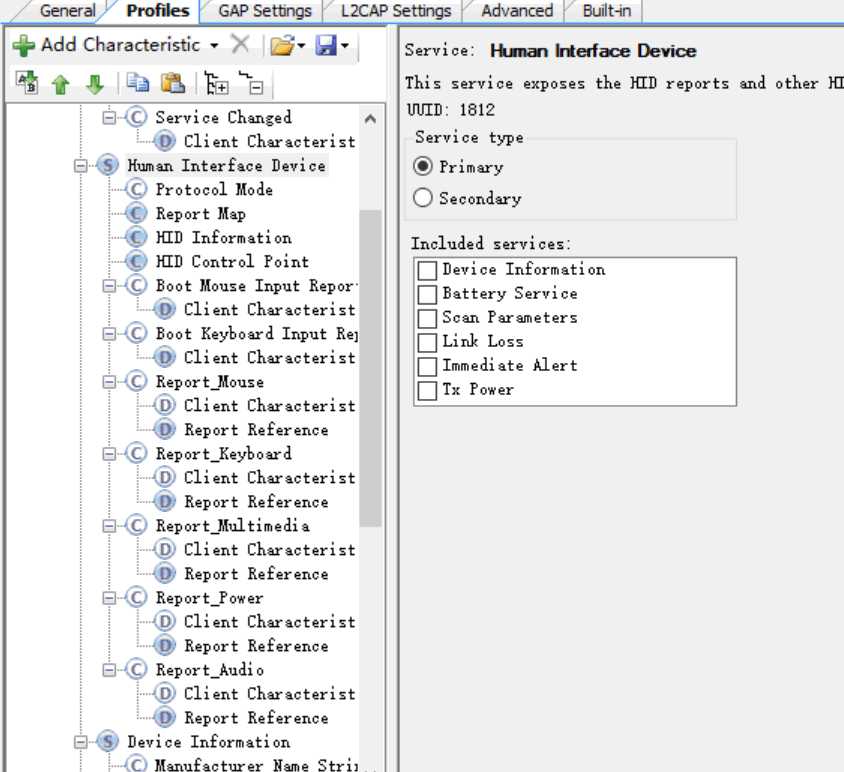
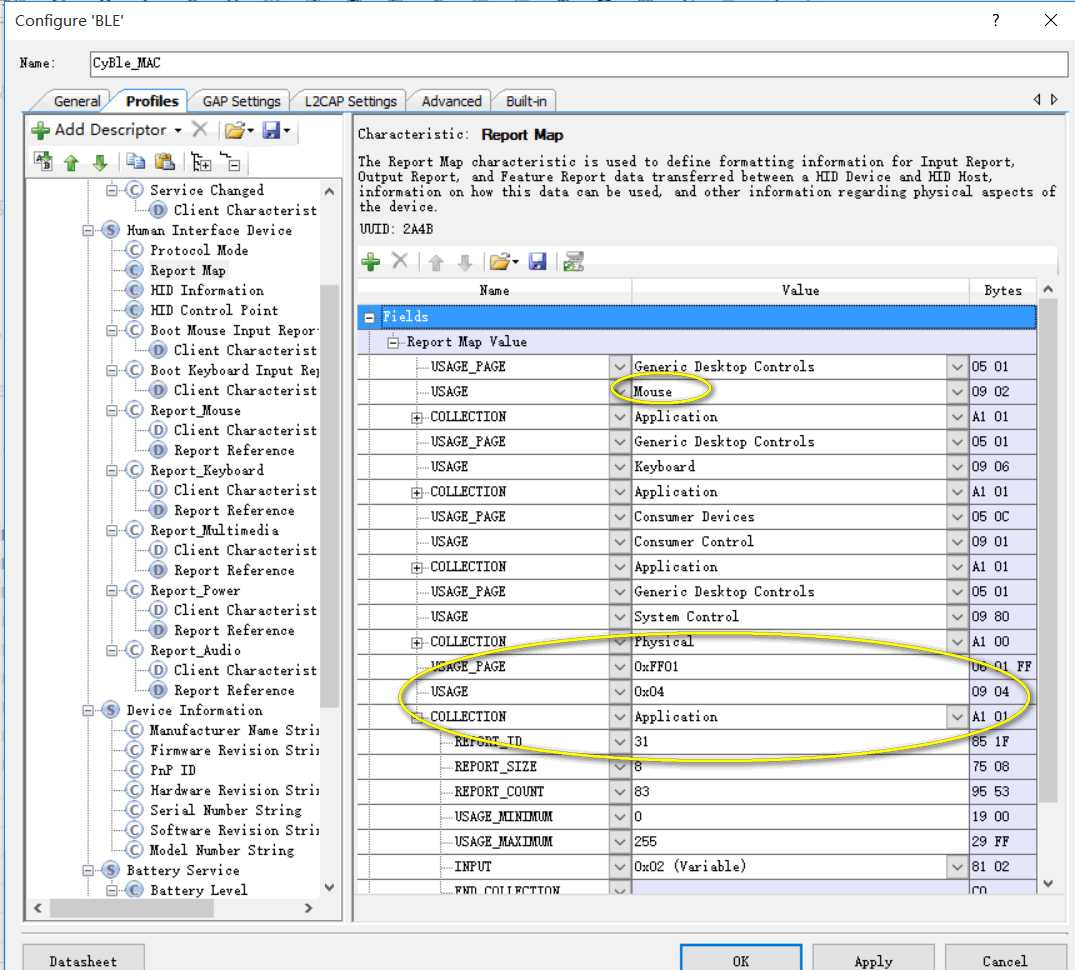
report map
HID设备描述符 其中我们定义了两个私有的描述符,这个是我们用来传输语音的。因为BLE并不支持 A2DP(Advenced Audio Distribution Profile)蓝牙立体声协议,要传语音数据我们只能利用私有的通道。
在 android端提供相应的驱动来解析我们的语音数据,最终提供标准的PCM数据给到android的中间层。
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/zozo825117/p/5588257.html