标签:
外观模式(Facade Pattern)隐藏系统的复杂性,并向客户端提供了一个客户端可以访问系统的接口。这种类型的设计模式属于结构型模式,它向现有的系统添加一个接口,来隐藏系统的复杂性。
这种模式涉及到一个单一的类,该类提供了客户端请求的简化方法和对现有系统类方法的委托调用。
意图:为子系统中的一组接口提供一个一致的界面,外观模式定义了一个高层接口,这个接口使得这一子系统更加容易使用。
主要解决:降低访问复杂系统的内部子系统时的复杂度,简化客户端与之的接口。
何时使用: 1、客户端不需要知道系统内部的复杂联系,整个系统只需提供一个"接待员"即可。 2、定义系统的入口。
如何解决:客户端不与系统耦合,外观类与系统耦合。
关键代码:在客户端和复杂系统之间再加一层,这一次将调用顺序、依赖关系等处理好。
应用实例: 1、去医院看病,可能要去挂号、门诊、划价、取药,让患者或患者家属觉得很复杂,如果有提供接待人员,只让接待人员来处理,就很方便。 2、JAVA 的三层开发模式。
优点: 1、减少系统相互依赖。 2、提高灵活性。 3、提高了安全性。
缺点:不符合开闭原则,如果要改东西很麻烦,继承重写都不合适。
使用场景: 1、为复杂的模块或子系统提供外界访问的模块。 2、子系统相对独立。 3、预防低水平人员带来的风险。
注意事项:在层次化结构中,可以使用外观模式定义系统中每一层的入口。
我们将创建一个 Shape 接口和实现了 Shape 接口的实体类。下一步是定义一个外观类 ShapeMaker。
ShapeMaker 类使用实体类来代表用户对这些类的调用。FacadePatternDemo,我们的演示类使用 ShapeMaker 类来显示结果。
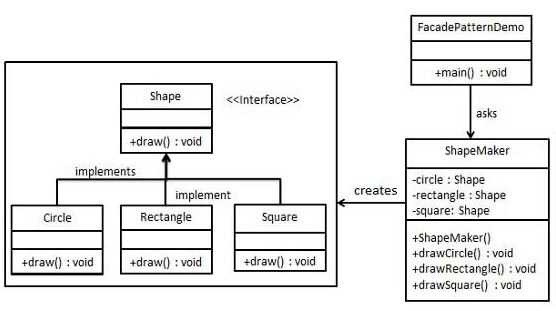
创建一个接口。
public interface Shape { void draw(); }
创建实现接口的实体类。
public class Rectangle implements Shape { @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("Rectangle::draw()"); } }
public class Square implements Shape { @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("Square::draw()"); } }
public class Circle implements Shape { @Override public void draw() { System.out.println("Circle::draw()"); } }
创建一个外观类。
public class ShapeMaker { private Shape circle; private Shape rectangle; private Shape square; public ShapeMaker() { circle = new Circle(); rectangle = new Rectangle(); square = new Square(); } public void drawCircle(){ circle.draw(); } public void drawRectangle(){ rectangle.draw(); } public void drawSquare(){ square.draw(); } }
使用该外观类画出各种类型的形状。
public class FacadePatternDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { ShapeMaker shapeMaker = new ShapeMaker(); shapeMaker.drawCircle(); shapeMaker.drawRectangle(); shapeMaker.drawSquare(); } }
验证输出。
Circle::draw()
Rectangle::draw()
Square::draw()
标签:
原文地址:http://www.cnblogs.com/anni-qianqian/p/5595980.html